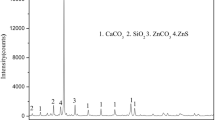
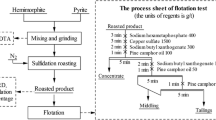
Abstract
To recover Zn, Pb, Fe and Si from a low-grade mining ore in the Lanping basin, Yunnan Province, China, a novel technology using the roasting with pyrite and carbon followed by beneficiation and hydrochloric acid leaching was proposed. Firstly, several factors such as pyrite dosage, roasting temperature, carbon powder dosage, holding time and particle size affecting on the flotation performance of Zn (Pb) and magnetic separation performance of Fe were simultaneously examined and the optimum process parameters were determined. A flotation concentrate, containing 17.46% Zn and 3.93% Pb, was obtained, and the Zn and Pb recoveries were 86.04% and 69.08%, respectively. The obtained flotation tailing was concentrated by a low-intensity magnetic separator. The grade of iron increased from 5.45% to 43.45% and the recovery of iron reached 64.87%. Hydrochloric acid leaching was then carried out for the magnetic separation tailing and a raw quartz concentrate containing 81.05% SiO2 was obtained. To further interpret the sulfidation mechanism of smithsonite, surface morphology and component of the sample before and after reactions were characterized by XRD and EPMA-EDS. The aim was to achieve the comprehensive utilization of the low-grade mining ore.
摘要
为了从兰坪矿区低品位采矿矿石中回收锌、铅、铁和硅等有价元素, 提出一种新的焙烧-选矿-浸出工艺, 焙烧过程中添加了黄铁矿和碳粉. 研究了黄铁矿用量、焙烧温度、碳粉用量、保温时间和颗粒粒度等因素对铅锌浮选效果和铁磁选回收行为的影响, 确定了最佳工艺参数, 得到了含锌 17.46% 和含铅 3.93% 的浮选精矿, 其中锌和铅的回收率分别为 86.04% 和 69.08%. 浮选尾矿进入弱磁选作业, 获得含铁 43.45%, 回收率为 64.87% 的铁精矿. 对弱磁选尾矿进行盐酸浸出, 获得二氧化硅含量为 81.05% 的石英砂. 采用 XRD、SEM-EDS 和 EPMA 等测试手段, 对菱锌矿反应前、后表面形貌和组成进行分析, 进一步揭示了菱锌矿的硫化机理. 本研究是为了实现低品位采矿矿石的综合利用.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ZAW K, PETERS S G, CROMIE P, BURRETT C, HOU Zeng-qian. Nature, diversity of deposit types and metallogenic relations of South China [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2007, 31(1): 3–47. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2005.10.006.
TANG Yong-yong, BI Xian-wu, FAYEK M, HU Rui-zhong, WU Li-yan, ZOU Zhi-chao, FENG Cai-xia, WANG Xin-song. Microscale sulfur isotopic compositions of sulfide minerals from the Jinding Zn-Pb deposit, Yunnan Province, Southwest China [J]. Gondwana Research, 2014, 26(2): 594–607. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2013.07.021. http://news.hexun.com/2015-06-10/176628271.html.
China United Business Daily. Lead zinc mine in Asia: The world-class technical problem of development has been solved [EB/OL] [2015-06-10]. http://news.hexun.com/2015-06-10/176628271.html.
ZHANG Jin-rang, WEN Han-jie, QIU Yu-zhuo, ZHANG Yu-xu, LI Chao. Ages of sediment-hosted Himalayan Pb—Zn—Cu—Ag polymetallic deposits in the Lanping basin, China: Re—Os geochronology of molybdenite and Sm—Nd dating of calcite [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 73: 284–295. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.04.041.
EJTEMAEI M, IRANNAJAD M, GHARABAGHI M. Influence of important factors on flotation of zinc oxide mineral using cationic, anionic and mixed (cationic/anionic) collectors [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2011, 24(13): 1402–1408. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2011.05.018.
KIERSZNICKI T, MAJEWSKI J, MZYK J. 5-alkylsalicylal-doximes as collectors in flotation of sphalerite, smithsonite and dolomite in a Hallimond tube [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 1981, 7(4): 311–318. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0301-7516(81)90026-0.
WILLS B A, FINCH FRSC J A, PENG F. Chapter 12- Froth Flotation [M]//Wills Mineral Processing Technology, 2016: 265–380. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-097053-0.00012-1.
LAN Zhuo-yue, LI De-fei, LIU Quan-jun, TONG Xiong. Study on flotation of lead-zinc oxide ore from Yunnan [J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2013, 807–809: 2317–2322. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.807-809.2317.
HOSSEINI S H, FORSSBERG E. Studies on selective flotation of smithsonite from silicate minerals using mercaptans and one stage desliming [J]. Mineral Processing & Extractive Metallurgy, 2011, 120(2): 79–84. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1179/1743285510Y.0000000001.
HOSSEINI S H, FORSSBERG E. Adsorption studies of smithsonite flotation using dodecylamine and oleic acid [J]. Mining, Metallurgy & Exploration, 2006, 23(2): 87–96. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03403341.
ÖNAL G, BULUT G, GÜL A, KANGAL O, PEREK K T, ARSLAN F. Flotation of Aladag oxide lead—zinc ores [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2005, 18(2): 279–282. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2004.10.018.
WU Dan-dan, MA Wen-hui, WEN Shu-ming, BAI Shao-jun, DENG Jiu-shuai, YIN Qiong. Contribution of ammonium ions to sulfidation-flotation of smithsonite [J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2017, 78: 20–26. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.05.015.
WANG Jun, LU Jin-feng, ZHANG Qi-wu, SATIO F. Mechanochemical sulfidization of nonferrous metal oxides by grinding with sulfur and iron [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2003, 42(23): 5813–5818. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ie030046b.
LIANG Yan-jie, CHAI Li-yuan, MIN Xiao-bo, TANG Chong-jian, ZHANG Hai-jing, KE Yong, XIE Xian-de. Hydrothermal sulfidation and floatation treatment of heavy-metal-containing sludge for recovery and stabilization [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2012, 217–218: 307–314. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.03.025.
LI Yong, WANG Ji-kun, WEI Chang, LIU Chun-xia, JIANG Ji-bo, WANG Fan. Sulfidation roasting of low grade lead—zinc oxide ore with elemental sulfur [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2010, 23(7): 563–566. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2010.01.004.
ZHENG Yong-xing, LIU Wei, QIN Wen-qing, JIAO Fen, HAN Jun-wei, YANG Kang, LUO Hong-lin. Sulfidation roasting of lead and zinc carbonate with sulphur by temperature gradient method [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2015, 22(5): 1635–1642. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-015-2681-9.
HAN Jun-wei, LIU Wei, ZHANG Tian-fu, XUE Kai, LI Wen-hua, JIAO Fen, QIN Wen-qing. Mechanism study on the sulfidation of ZnO with sulfur and iron oxide at high temperature [J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 42536. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep42536.
XUE Chun-ji, ZENG Rong, LIU Shu-wen, CHI Guo-xiang, QING Hai-ruo, CHEN Yu-chuan, YANG Jian-min, WANG Deng-hong. Geologic, fluid inclusion and isotopic characteristics of the Jinding Zn—Pb deposit, western Yunnan, South China: A review [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2007, 31(1): 337–359. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2005.04.007.
ZHENG Yong-xing, LV Jin-fang, LIU Wei, QIN Wen-qing, WEN Shu-ming. An innovative technology for recovery of zinc, lead and silver from zinc leaching residue [J]. Physicochemical Problems of Mineral Processing, 2016, 52(2): 943–954. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5277/ppmp160233.
ZHENG Yong-xing, LIU Wei, QIN Wen-qing, LUO Hong-lin, HAN Jun-wei. Mineralogical reconstruction of lead smelter slag for zinc recovery [J]. Separation Science and Technology, 2014, 49(5): 783–791. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2013.863342.
LV Jin-fang, ZHANG Han-ping, TONG Xiong, FAN Chun-lin, YANG Wen-tao, ZHENG Yong-xing. Innovative methodology for recovering titanium and chromium from a raw ilmenite concentrate by magnetic separation after modifying magnetic properties [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 325: 251–260. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/jjhazmat.2016.11.075.
LI Chao, SUN Heng-hui, BAI Jing, LI Long-tu. Innovative methodology for comprehensive utilization of iron ore tailings: Part 1. The recovery of iron from iron ore tailings using magnetic separation after magnetizing roasting [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 174(1–3): 71–77. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.09.018.
BIYOUNE M G, ATBIR A, BARI H, HASSNAOUI L, MONGACH E, KHADIR A, BOUKBIR L, BELLAJROU R, ELHADEK M. Remineralization of permeate water by calcite bed in the Daoura’s plant (south of Morocco) [J]. The European Physical Journal Special Topics, 2017, 226(5): 931–941. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2016-60181-6.
GIREESH V S, VINOD V P, KRISHNAN NAIR S, NINAN G. Catalytic leaching of ilmenite using hydrochloric acid: A kinetic approach [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2015, 134: 36–40. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2014.11.004.
ZHENG Y X, LIU W, QIN W Q, HAN J W, YANG K, WANG D W. Improvement for sulphidation roasting and its application to treat lead smelter slag and zinc recovery [J]. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 2015, 54(1): 92–100. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1179/1879139514Y.0000000155.
HAN Jun-wei, LIU Wei, QIN Wen-qing, PENG Bing, YANG Kang, ZHENG Yong-xing. Recovery of zinc and iron from high iron-bearing zinc calcine by selective reduction roasting [J]. Journal of Industrial & Engineering Chemistry, 2015, 22(2): 272–279. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2014.07.020.
LIU Han-qiao, WEI Guo-xia, ZHANG Rui. Removal of carbon constituents from hospital solid waste incinerator fly ash by column flotation [J]. Waste Management, 2013, 33(1): 168–174. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2012.08.019.
WANG Li, SUN Wei, ZHANG Qing-peng. Recovery of vanadium and carbon from low-grade stone coal by flotation [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(11): 3767–3773. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s1003-6326(15)64020-1.
KIENKO L A, VORONOVA O V. Selective flotation of fine-ingrained carbonate-fluorite ore in pulp of increased dispersion uniformity [J]. Journal of Mining Science, 2014, 50(1): 176–181. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/s1062739114010244.
MEHDILO A, IRANNAJAD M, ZAREI H. Smithsonite flotation from zinc oxide ore using alkyl amine acetate collectors [J]. Separation Science and Technology, 2014, 49(3): 445–457. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2013.838966.
HUANG Jin-xiu, CHEN Meng-jun, CHEN Hai-yan, CHEN Shu, SUN Quan. Leaching behavior of copper from waste printed circuit boards with Brønsted acidic ionic liquid [J]. Waste Management, 2014, 34(2): 483–488. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2013.10.027.
ZHOU Fang, WANG Lou-xiang, XU Zheng-he, RUAN Yao-yang, ZHANG Zhen-yue, CHI Ruan. Role of reactive oily bubble in apatite flotation [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2017, 513: 11–19. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2016.11.024.
GUI Xia-hui, XING Yao-wen, RONG Guo-qiang, CAO Yi-jun, LIU Jiong-tian. Interaction forces between coal and kaolinite particles measured by atomic force microscopy [J]. Powder Technology, 2016, 301: 349–355. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2016.06.026.
LV Jin-fang, TONG Xiong, ZHENG Yong-xing, XIE Xian, WANG Cong-bing. Study on the surface sulfidization behavior of smithsonite at high temperature [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 437: 13–18. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.12.163.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(51604131) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2017FB084) supported by the Yunnan Province Applied Basic Research Project, China; Project(2018T20150055) supported by the Testing and Analyzing Funds of Kunming University of Science and Technology, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lan, Zy., Lai, Zn., Zheng, Yx. et al. Recovery of Zn, Pb, Fe and Si from a low-grade mining ore by sulfidation roasting-beneficiation-leaching processes. J. Cent. South Univ. 27, 37–51 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4276-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4276-3