Abstract
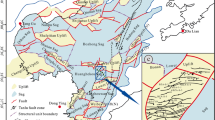
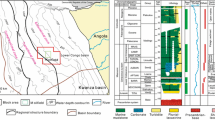
The hydrodynamic conditions present in a river delta’s formation are a highly important factor in the variation between its sedimentary regulation and characteristics. In the case of the lacustrine basin river-dominated delta, water level fluctuations and fluviation, are both important controlling factors of the sedimentary characteristics and reservoir architecture. To discuss the effects of water level fluctuation on sediment characteristics and reservoir architecture of this delta, the Fangniugou section in the east of the Songliao Basin was selected for study. Based on an outcrop investigation of the lacustrine basin river-dominated delta, combining with an analysis of the major and trace chemical elements in the sediments to determine the relative water depth, through architecture bounding surfaces and lithofacies division, sedimentary microfacies recognition and architectural element research, this work illustrated the effects of water level fluctuation on the reservoir architecture and established sedimentary models for the lacustrine basin river-dominated delta under various water level conditions. The results show that there are 8 lithofacies in the Fangniugou section. The fan delta front, which is the main object of this study, develops four sedimentary microfacies that include the underwater distributary channel, river mouth bar, sheet sand and interdistributary bay. The effects of water level fluctuation on different orders geographic architecture elements are respectively reflected in the vertical combination of the composite sand bodies, the plane combination of the single sand bodies, the particle size changes in the vertical of hyperplasia in the single sand body, the coset and lamina. In the case of the sand body development of the petroliferous basin, varying water level conditions and research locations resulted in significant variation in the distribution and combination of the sand bodies in the lacustrine basin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
JIANG Zai-xing. Sedimentology [M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2003: 393–394. (in Chinese)
CARI L J, STEPHAN A G. Sedimentology and reservoir architecture of a synrift lacustrine delta, Southeastern Mongolia [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2004, 74(6): 770–785.
BOYAN K V R, BRUCE A. A hierarchical approach to architectural classification in marginal-marine systems: Bridging the gap between sedimentology and sequence stratigraphy [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2013, 97(7): 1121–1161.
STANLEY D, WARNE A. Worldwide initiation of Holocene marine deltas by deceleration of sea-level rise [J]. Science, 1994, 265: 228–231.
ZHAO Xiao-qing, BAO Zhi-dong, LIU Zong-fei, ZHAO Hua, CHAI Qiu-hui. An in-depth analysis of reservoir architecture of underwater distributary channel sand bodies in a river dominated delta: A case study of T51 Block, Fuyu Oilfield [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2013, 40(2): 181–187. (in Chinese)
SHI Zhan-zhong, JI You-liang. Fan-delta sedimentation formed under the environment of lake level frequently varying—Taking the first member of Kongdian Formation, Huanghua Depression as an example [J]. Journal of Xi’an Petroleum Institute: Natural Science Edition, 2002, 17(1): 24–29. (in Chinese)
LOU Zhang-hua, YUAN Di, JIN Ai-min. Types, characteristics of sandbodies in shallow-water delta front and sedimentary models in Northern Songliao Basin, China [J]. Journal of Zhejiang University: Science Edition, 2004, 31(2): 211–215. (in Chinese)
ZHU Xiao-min. LIU Yuan, FANG Qing, LI Yang, LIU Yun-yan, WANG Rui, SONG Jing, LIU Shi-qi, CAO Hai-tao, LIU Xiang-nan. Formation and sedimentary model of shallow delta in large-scale lake. Example from Cretaceous Quantou Formation in Sanzhao Sag, Songliao Basin [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2012, 19(1): 89–99. (in Chinese)
BUREAU of geology and mineral resources of Jilin province. Journal of the regional geology of Jilin province [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1922: 228.
JIANG Zheng-long, QIU Hai-jun, PENG Yu-jing, ZHANG Wei-min, LIANG Shuang. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating for island arc volcanic rock of Fangniugou area in Yitong region of Jilin Province [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2014, 21: 2877–2884.
CHENG Ri-hui, WANG Teng-fei, SHEN Yan-jie, REN Yan-guang. Architecture of volcanic sequence and its structure control of Yingcheng Formation in Songliao Basin [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2014, 21: 2026–2040.
MIALL A D. Reconstructing the architecture and sequence stratigraphy of the preserved fluvial record as a tool for reservoir development: a reality check [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2006, 90: 989–1002.
MIALL A D. Hierarchies of architectural units in clastic rocks, and their relationship to sedimentation rate [C]// MIALL A D, TYLER N. The Three-Dimensional Facies Architecture of Terrigenous Clastic Sediments, and Its Implications for Hydrocarbon Discovery and Recovery. Soc Eco Paleontol Mineral Conc Sedimentol Paleontol, 1991, 3: 6–12.
WEN Li-feng, WU Sheng-he, WANG Yan-zhong, YUE Da-li, LI Yan-ping. An accurate method for anatomizing architecture of subsurface reservoir in mouth bar of fluvial dominated delta [J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2011, 42(4): 1072–1078. (in Chinese)
CHEN Bin-tao, YU Xing-he, PAN Shu-xin, TANG Cheng-peng, LI Shun-li, ZHANG Yu-pan. Sedimentary characteristics and sedimentogenic-based sandbodies correlation methods of meandering river in Toutunhe Formation, southern margin of Junggar Basin [J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2013, 24(6): 1132–1139. (in Chinese)
EDMONDS D A, SLINGERLAND R L. Mechanics of river mouth bar formation: Implications for the morphodynamics of delta distributary nerworks [J]. Journal of Geophysical research, 2007, 112(F3): 237–254.
LI Zhan-dong, LI Yang, LIU Yun-li, HU Hui-ting, MA Feng-rong, ZHANG Xiao-gang. Sedimentary characteristics of the Cretaceous Denglouku Formation in the southeast uplift of the southern Songliao Basin [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2014, 35(3): 401–409. (in Chinese)
CARROLL A R, BOHACS K M. Stratigraphic classification of ancient lakes: Balancing tectonic and climatic controls [J]. Geology, 1999, 27: 99–102.
WU Wei, LIN Chang-song, ZHOU Xin-huai, LI Quan, XING Zuo-chang, YAN Yu. Paleoclimate evolution and its influence on lake level changes of Paleogene Dongying epoch in Liaodong Bay, East China [J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum, 2012, 36(1): 33–39. (in Chinese)
CHEN Zhong-hong, ZHA Ming. Application of uranium curve to paleoenvironment inversion in sedimentary basin [J]. Journal of the University of Petroleum, China, 2004, 28(6): 11–15. (in Chinese)
ZHANG Yong-sheng, YANG Yu-qing, QI Zhi-xian, QIAO Yue-dong, YUAN He-ran. Sedimentary characteristics and environments of the salt-bearing series of Qianjiang Formation of the Paleogene in Qianjiang sag of Jianghan basin [J]. Journal of Paleogeography, 2003, 5(1): 29–35. (in Chinese)
CHEN Zhong-hong, ZHA Ming, JIN Qiang. Mineral elemental response to the evolution of terrestrial brine faulted-basin: A case study in the Paleogene of Well Haoke-1, Dongying Sag [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2008, 26(6): 925–932. (in Chinese)
BOHACS K M, CARROLL A R, NEAL J E, MANKIEWICZ P J. Lake-basin type, source potential, and hydrocarbon character: An integrated sequence-stratigraphic–geochemical framework [C]// GIERLOWSKI-KORDESCH E H, KELTS K R. Lake Basins through Space and Time, Studies in Geology. New York: American Association of Petroleum Geologists, 2000, 46: 3–34
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(2011ZX05009-002) supported by the National Key Oil & Gas Project, China; Project(15CX06010A) supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Qiu, Lw., Yang, Bl. et al. Effects of water level fluctuation on sedimentary characteristics and reservoir architecture of a lake, river dominated delta. J. Cent. South Univ. 23, 2958–2971 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-016-3360-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-016-3360-1