Abstract
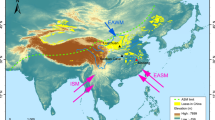
The evolution of Holocene climate was investigated using grain size and magnetic susceptibility of the Holocene paleosols from Baicaoyuan (BCY), Xifeng (XF) and Linyou (LY) sections in the northwest, central and southern Chinese Loess Plateau (CLP). The results show that the Holocene in the BCY, XF and LY paleosol sections could be divided into three phases: during the early Holocene (11.8–10.5 kyr B. P.), increased magnetic susceptibility (χ) and frequency-dependent magnetic susceptibility (χfd) and decreased median grain size (Md) indicate that the East Asian Summer Monsoon (EASM) has become more intense and the climate has changed from cold to warm. During the middle Holocene (10.5–5.0 kyr B. P.), the values of χ, χfd and 2–5 µm grain-size fraction (GT2/5) are higher and Md and 30–63 µm grain-size fraction (GT30/63) are the lowest, which reflect a warm and humid regional climate. At ∼ 8.0 kyr B. P., there was a transient dry-cold climatic spike corresponding to a Heinrich Event, the cold event was likely due to the collapse of the Laurentide ice sheet. During the late Holocene (5.0–0 kyr B. P.), χ and χfd values are the lowest, while Md and GT30/63 are high, as proxies of a weakened EASM, when the dry-cold climate prevailed in the region. Decreased irradiance since 5.0 kyr B.P. may have caused climatic cooling and drying. Spatially, the increased main peak values and skewness from BCY, XF to LY sections show that the grain size became fine, the East Asian Winter Monsoon (EAWM) reduced, and climate was warmer and wetter from northwest to southeast. In addition, Md can be used as alternative proxy for EAWM, while χfd is positive with the intensity of EASM under semiarid climate conditions in CLP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
An Z S, Kutzbach J E, Prell W L et al., 2001. Evolution of Asian monsoons and phased uplift of the Himalaya-Tibetan plateau since Late Miocene times. Nature, 411(6833): 62–66. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/35075035
An Z S, Wu G X, Li J P et al., 2015. Global monsoon dynamics and climate change. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 43: 29–77. doi: https://doi.org/10.1166/annurev-earth-603313-054623
Balsam W, Ji J F, Chen J, 2004. Climatic interpretation of the Luochuan and Lingtai loess sections, China, based on changing iron oxide mineralogy and magnetic susceptibility. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 223(3–4): 335–348. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2004.04.023
Berger A, Loutre M F, 1991. Insolation values for the climate of the last 10 million years. Quaternary Science Reviews, 10(4): 297–317. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/0277-3791(91)90033-Q
Bond G, Showers W, Cheseby M et al., 1997. A pervasive millennial-scale cycle in North Atlantic Holocene and glacial climates. Science, 278(5341): 1257–1266. doi: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.278.5341.1257
Chen Xiaoyun, Wu Naiqin, 2008. Relatively warm-humid climate recorded by Mollusk species in the Chinese Loess Plateau during MIS3 and its possible forcing mechanism. Quaternary Sciences, 28(1): 154–161. (in Chinese)
Dean W E, Forester R M, Bardbury J P, 2002. Early Holocene change in atmospheric circulation in the Northern Great Plains: an upstream view of the 8.2 ka cold event. Quaternary Science Reviews, 21(16–17): 1763–1775. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0277-3791(02)00002-1
Dearing J, 1999. Magnetic susceptibility. In: Walden J et al. (eds.). Environmental Magnetism: A Practical Guide, Technical Guide. London: Quaternary Research Association, 35–62.
Deng Shaolin, 2017. Different Responses of Stalagmite Oxygen and Carbon Isotope Records to Holocene Climate. Nanjing: Nanjing Normal University. (in Chinese)
Ding Z L, Xiong S F, Sun J M et al., 1999. Pedostratigraphy and paleomagnetism of a ∼7.0 Ma eolian loess-red clay sequence at Lingtai, Loess Plateau, north-central China and the implications for paleomonsoon evolution. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 152(1–2): 49–66. doi: 101016/S0031-0182(99)00034-6
Ding Z L, Derbyshire E, Yang S L et al., 2002. Stacked 2.6-Ma grain size record from the Chinese loess based on five sections and correlation with the deep-sea δ18O record. Paleoceanography, 17(3): 5–1–5–21. doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/2001PA000725
Dixit Y, Hodell D A, Sinha R et al., 2014. Abrupt weakening of the Indian summer monsoon at 8.2 kyr B. P. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 391: 16–23. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2014.01.026
Emmanouilidis A, Katrantsiotis C, Dotsika E et al., 2022. Holocene paleoclimate variability in the eastern Mediterranean, inferred from the multi-proxy record of Lake Vouliagmeni, Greece. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 595: 110964. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2022.110964
Fleitmann D, Mudelsee M, Burns S J et al., 2008. Evidence for a widespread climatic anomaly at around 9.2 ka before present. Paleoceanography, 23(1): PA1102. doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/2007pa001519
Guo B H, Peng T J, Feng Z T et al., 2019. Pedogenic components of Xijin loess from the western Chinese loess plateau with implications for the quaternary climate change. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 170: 128–137. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.11.012
Guo L C, Xiong S F, Yang P et al., 2018a. Holocene environmental changes in the Horqin desert revealed by OSL dating and δ13C analyses of paleosols. Quaternary International, 469: 11–19. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2017.06.048
Guo Xuelian, Liu Xiuming, Lü Bin et al., 2011. Comparison of topsoil magnetic properties between the Loess Region in Tianshan Mountains and Loess Plateau, China, and its environmental significance. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(4): 485–495. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/c/g2.1631
Guo X L, Banerjee S K, Wang R H et al., 2018b. Why magnetite is not the only indicator of past rainfall in the Chinese Loess Plateau? Geophysical Journal International, 213(3): 2128–2137. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggy097
Hamdan M A, Flower R J, Hassan F A et al., 2020. Geochemical and palynological analysis of Faiyum Lake sediments, Egypt: implications for Holocene paleoclimate. Journal of African earth sciences, 167: 103864. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2020.103864
Han J M, Lü H Y, Wu N Q et al., 1996. The magnetic susceptibility of modern soils in China and its use for paleoclimate reconstruction. Studia Geophysica et Geodaetica, 40(3): 262–275. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02300742
Hao Q Z, Guo Z T, 2005. Spatial variations of magnetic susceptibility of Chinese loess for the last 600 kyr: implications for monsoon evolution. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 110(B12): B12101. doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JB003765
International Commission on Stratigraphy, 2018. International Chronostratigraphic Chart. Journal of Stratigraphy, 4: 365–370.
Jiang Mingli, 2009. Grain size analysis and its geological application. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 31(1): 161–163. (in Chinese)
Jordanova D, Jordanova N, 2021. Updating the significance and paleoclimate implications of magnetic susceptibility of Holocene loessic soils. Geoderma, 391: 114982. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2021.114982
Kang S G, Du J H, Wang N et al., 2020. Early Holocene weakening and mid- to late Holocene strengthening of the East Asian winter monsoon. Geology, 48(11): 1043–1047. doi: https://doi.org/10.1130/G47621.1
Kato H, Amekawa S, Hori M et al., 2021. Influences of temperature and the meteoric water δ18O value on a stalagmite record in the last deglacial to middle Holocene period from southwestern Japan. Quaternary Science Reviews, 253: 106746. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2020.106746
Lan J H, Xu H, Lang Y C et al., 2020. Dramatic weakening of the East Asian summer monsoon in northern China during the transition from the Medieval Warm Period to the Little Ice Age. Geology, 48(4): 307–312. doi: https://doi.org/10.1130/G46811.1
Li P, Zhang C X, Wu H B et al., 2022. Geochemical characteristics of Holocene loess-paleosol sequences in central Chinese Loess Plateau and their implications for East Asian monsoon evolution. Quaternary International, 616: 99–108. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2021.10.017
Li Y R, Zhang W W, Aydin A et al., 2018. Formation of calcareous nodules in loess-paleosol sequences: reviews of existing models with a proposed new “per evapotranspiration model”. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 154: 8–16. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j./seaes.2017.12.002
Liu J, Wang B, Ding Q H et al., 2009. Centennial variations of the global monsoon precipitation in the last millennium: results from ECHO-G model. Journal of Climate, 22(9): 2356–2371. doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/2008JCLI2353.1
Liu Xiuming, An Zhisheng, Rolph T et al., 2001. Magnetic properties of the Tertiary red clay from Gansu. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 44(7): 635–651. doi: https://doi.org/10.1077/BF02875337
Maher B A, 2016. Palaeoclimatic records of the loess/palaeosol sequences of the Chinese Loess Plateau. Quaternary Science Reviews, 154: 23–84. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2016.08.004
Orgeira M J, Egli R, Compagnucci R H, 2011. A quantitative model of magnetic enhancement in Loessic soils. In: Petrovsky E, Ivers D, Harinarayana T et al. (eds.). The Earth’s Magnetic Interior. Dordrecht: Springer, 361–397. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-0323-0_25
Senra E O, Schaefer C E, Corrêa G R et al., 2019. Holocene pedogenesis along a chronotoposequence of soils from the Altiplano to the Cordillera Real, Bolivian Andes. Catena, 178: 141–153. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.03.012
Shen J, Liu X Q, Wang S M et al., 2005. Palaeoclimatic changes in the Qinghai Lake area during the last 18, 000 years. Quaternary International, 136(1): 131–140. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2004.11.014
Shi Yafeng, Kong Zhaozheng, Wang Sumin et al., 1994. The climatic fluctuation and important events of Holocene megathermal in China. Science in China (Series B), 37(3): 353–365. (in Chinese)
Song Y, Hao Q Z, Ge J Y et al., 2014. Quantitative relationships between magnetic enhancement of modern soils and climatic variables over the Chinese Loess Plateau. Quaternary International, 334–335: 119–131. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2013.12.010
Stuut J, 2007. Grain-size records at ODP Site 1146 from the northern South China Sea: implications on the East Asian monsoon evolution since 20 Ma. Science China Earth Sciences, 10: 1536–1547.
Sun D H, Bloemendal J, Rea D K et al., 2004. Bimodal grain-size distribution of Chinese loess, and its palaeoclimatic implications. Catena, 55(3): 325–340. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0341-8162(03)00109-7
Sun Xiaohong, Zhao Yan, Li Quan, 2017. Holocene peatland development and vegetation changes in the Zoige Basin, eastern Tibetan Plateau. Science China Earth Sciences, 60(10): 1826–1837. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-017-9086-5
Thomas E R, Wolff E W, Mulvaney R et al., 2007. The 8.2 ka event from Greenland ice cores. Quaternary Science Reviews, 26(1–2): 70–81. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2006.07.017
Verheyden S, Nader F H, Cheng H J et al., 2008. Paleoclimate reconstruction in the Levant region from the geochemistry of a Holocene stalagmite from the Jeita Cave, Lebanon. Quaternary Research, 70: 368–381. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yqres.2008.05.004
Vinther B M, Clausen H B, Johnsen S J et al., 2006. A synchronized dating of three Greenland ice cores throughout the Holocene. Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 111(D13): D13102. doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/2005jd006921
Wang Haibin, Chen Fahu, Zhang Jiawu, 2002. Environmental significance of grain size of loess-paleosol sequence in western part of Chinese Loess Plateau. Journal of Desert Research, 22(1): 21–26. (in Chinese)
Wang H P, Chen J H, Zhang X J et al., 2014. Palaeosol development in the Chinese Loess Plateau as an indicator of the strength of the East Asian summer monsoon: evidence for a mid-Holocene maximum. Quaternary International, 334–335: 155–164. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2014.03.013
Wang Y J, Cheng H, Edwards R L et al., 2005. The Holocene Asian monsoon: links to solar changes and North Atlantic climate. Science, 308(5723): 854–857. doi: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1106296
Wang Y J, Cheng H, Edwards R L et al., 2008. Millennial- and orbital-scale changes in the East Asian monsoon over the past 224, 000 years. Nature, 451(7182): 1090–1093. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06692
Xue J T, Dang X Y, Tang C Y et al., 2016. Fidelity of plant-wax molecular and carbon isotope ratios in a Holocene paleosol sequence from the Chinese Loess Plateau. Organic Geochemistry, 101: 176–183. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2016.09.004
Yan H, Wei W, Soon W et al., 2015. Dynamics of the intertropical convergence zone over the western Pacific during the Little Ice Age. Nature Geoscience, 8(4): 315–320. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/NGEO2375
Zan J B, Fang X M, Zhang W L et al., 2018. A new record of late Pliocene-early Pleistocene aeolian loess-red clay deposits from the western Chinese Loess Plateau and its palaeoenvironmental implications. Quaternary Science Reviews, 186: 17–26. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2018.02.010
Zhang W C, Yan H, Cheng P et al., 2016. Peatland development and climate changes in the Dajiuhu basin, central China, over the last 14, 100 years. Quaternary International, 425: 273–281. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2016.06.039
Zhao G Y, Liu X M, Chen Q et al., 2013. Paleoclimatic evolution of Holocene loess and discussion of the sensitivity of magnetic susceptibility and median diameter. Quaternary International, 296: 160–167. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2012.06.015
Zhao J B, Ma Y D, Cao J J et al., 2020. Holocene pedostratigraphic records from the southern Chinese Loess Plateau and their implications for the effects of climate on human civilization. Catena, 187: 104410. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.104410
Zhu Xiaomin, 2020. Sedimentary Petrology. 5th ed. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item
Under the auspices of the Second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research (STEP) program (No. 2019QZKK0704), Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41772168, 42103046), Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province (No. 20JR5RA272, 20JR5RA226)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, X., He, L., Zhao, G. et al. Spatial-temporal Characteristics of Holocene Paleosols in the Chinese Loess Plateau and Paleoclimatic Significance. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 32, 1110–1118 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-022-1285-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-022-1285-1