Abstract
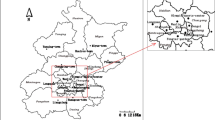
The hallmark of development in the Yangtze River Delta (YRD) of East China has been sprawling urbanization. However, air pollution is a significant problem in these urban areas. In this paper, we investigated and analyzed the air pollution index (API) in four cities (Shanghai, Nanjing, Hangzhou and Ningbo) in the YRD from 2001 to 2012. We attempted to empirically examine the relationship between meteorological factors and air quality in the urban areas of the YRD. According to the monitoring data, the API in Shanghai, Nanjing, Hangzhou slightly declined and that in Ningbo increased over the study period. We analyzed the inter-annual, seasonal, and monthly variations of API, from which we found that the air quality had different temporal changes in the four cities. It was indicated that air quality was poor in winter and spring and best in summer. Furthermore, different weather conditions affected air quality level. The wind direction was considered as an important and influential factor to air pollution, which has an impact on the accumulating or cleaning processes of pollutants. The air quality was influenced by the different wind directions that varied with seasons and cities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akyüz M, Çabuk H, 2009. Meteorological variations of PM2.5/PM10 concentrations and particle-associated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the atmospheric environment of Zonguldak, Turkey. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 170(1): 13–21. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.05.029
Chan C K, Yao X H, 2008. Air pollution in mega cities in China. Atmospheric Environment, 42(1): 1–42. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.09.003
Che H, Zhang X., Li Y et al., 2009. Haze trends over the capital cities of 31 provinces in China, 1981–2005. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 97(3): 235–242. doi: 10.1007/s00704-008-0059-8
Clark L P, Millet D B, Marshall J D, 2011. Air quality and urban form in U.S. urban areas: evidence from regulatory monitors. Environmental Science & Technology, 45(45): 7028–7035. doi: 10.1021/es2006786
Cleveland R B, Cleveland W S, 1990. STL: a seasonal-trend decomposition procedure based on Loess. Journal of Official Statistics, 6(1): 3–33
Daubechies I, 1990. The wavelet transform, time-frequency localization and signal analysis. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 36(5): 961–1005. doi: 0018-9448/90/0900-0961
Deng J J, Wang T J, Jiang Z Q et al., 2011. Characterization of visibility and its affecting factors over Nanjing, China. Atmospheric Research, 101(3): 681–691. doi: 10.1016/j. atmosres.2011.04.016
Dominick D, Juahir H, Latif M T et al., 2012. Spatial assessment of air quality patterns in Malaysia using multivariate analysis. Atmospheric Environment, 60(11): 172–181. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.06.021
Fu X, Wang S, Zhao B et al., 2013. Emission inventory of primary pollutants and chemical speciation in 2010 for the Yangtze River Delta region, China. Atmospheric Environment, 70(70): 39–50. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.12.034
García-Mozo H, Yaezel L, Oteros J et al., 2014. Statistical approach to the analysis of olive long-term pollen season trends in southern Spain. Science of the Total Environment, s473–474(3): 103–109. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.11.142
Gong J, Hu Y, Liu M et al., 2015. Characterization of atmospheric pollution index and its affecting factors in industrial urban areas in Northeast China. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 24(4): 1579–1592. doi: 10.15244/pjoes/37757
Gurjar B R, Butler T M, Lawrence M G et al., 2008. Evaluation of emissions and air quality in megacities. Atmospheric Environment, 42(7): 1593–1606. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.10.048
Harlan S L, Ruddell D M, 2011. Climate change and health in cities: Impacts of heat and air pollution and potential co-benefits from mitigation and adaptation. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, 3(3): 126–134. doi: 10.1016/j.cosust.2011.01.001
Huang K, Zhuang G, Lin Y et al., 2011. Typical types and formation mechanisms of haze in an Eastern Asia megacity, Shanghai. Atmospheric Chemistry & Physics Discussions, 12(1): 105–124. doi: 10.5194/acp-12-105-2012
Ji D, Pan Y, Wang Y, 2012. Analysis of the heavy pollution episodes in selected cities of northern China. Atmospheric Environment, 50(3): 338–348. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.11.053
Gao L, Jia G, Zhang R et al., 2011. Visual range trends in the Yangtze River Delta region of China, 1981–2005. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 61(8): 843–849. doi: 10.3155/1047-3289.61.8.843
Jiang J, Zhang J, Zhang Y et al., 2016. Estimating nitrogen oxides emissions at city scale in China with a nightlight remote sensing model. Science of the Total Environment, 544: 1119–1127. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.11.113
López R E, Thomas V, Wang Y, 2008. The quality of growth: Fiscal policies for better results. IEG World Bank Working Paper2008-6. Washington D.C.: The World Bank Press, 34–38
Li J, Lu K, Wei L et al., 2014. Fast increasing of surface ozone concentrations in Pearl River Delta characterized by a regional air quality monitoring network during 2006–2011. Journal of Environmental Sciences-China, 26(1): 23–36. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0 742(13)60377-0
Li L, Qian J, Ou C Q et al., 2014. Spatial and temporal analysis of Air Pollution Index and its timescale-dependent relationship with meteorological factors in Guangzhou, China, 2001–2011. Environmental Pollution, 190(7): 75–81. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2014. 03.020
Liao J, Wang T, Wang X et al., 2014. Impacts of different urban canopy schemes in WRF/Chem on regional climate and air quality in Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmospheric Research, s145–146: 226–243. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2014.04.005
Masiol M, Agostinelli C, Formenton G et al., 2014. Thirteen years of air pollution hourly monitoring in a large city: potential sources, trends, cycles and effects of car-free days. Science of the Total Environment, s494–495: 84–96. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.0 6.122
Mishra S R, Pradhan R P, Prusty B A et al., 2016. Meteorology drives ambient air quality in a valley: A case of Sukinda chromite mine, one among the ten most polluted areas in the world. Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, 188(7): 1–17. doi: 10.1007/s10661-0 16-5393-1
Nalley D, Adamowski J, Khalil B et al., 2013. Trend detection in surface air temperature in Ontario and Quebec, Canada during 1967–2006 using the discrete wavelet transform. Atmospheric Research, 132: 375–398. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2013. 06.011
Özden Ö, Döğeroğlu T, Kara S, 2008. Assessment of ambient air quality in Eskişehir, Turkey. Environment International, 34(5): 678–687. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2007.12.016
Song Y, Qin S, Qu J et al., 2015. The forecasting research of early warning systems for atmospheric pollutants: a case in Yangtze River Delta region. Atmospheric Environment, 118: 58–69. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.06.032
Stein A F, Draxler R R, Rolph G D et al., 2016. NOAA’s HYSPLIT atmospheric transport and dispersion modeling system. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 96(12): 2059–2078. doi: 10.1175/BAMS-D-14-00110.1
Tang Y, An J, Li Y et al., 2014. Uncertainty in the uptake coefficient for HONO formation on soot and its impacts on concentrations of major chemical components in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Atmospheric Environment, 84(1): 163–171. doi: 10.1016/j.at mosenv.2013.11.034
Theodosiou M, 2011. Forecasting monthly and quarterly time series using STL decomposition. International Journal of Forecasting, 27(4): 1178–1195. doi: 10.1016/j.ijforecast. 2010.11.002
Tian G, Zhi Q, Xu X, 2014. Characteristics of particulate matter (PM10) and its relationship withmeteorological factors during 2001–2012 in Beijing. Environmental Pollution, 192: 266–274. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2014.04.036
Unal Y S, Toros H, Deniz A et al., 2011. Influence of meteorological factors and emission sources on spatial and temporal variations of PM10 concentrations in Istanbul metropolitan area. Atmospheric Environment, 45(31): 5504–5513. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosen v.2011.06.039
Wang S, Nan J, Shi C et al., 2015. Atmospheric ammonia and its impacts on regional air quality over the megacity of Shanghai, China. Scientific Reports, 5: 15842–15855. doi: 10.1038/srep15842
Wang T, Wong C H, Cheung T F et al., 2004. Relationships of trace gases and aerosols and the emission characteristics at Lin’an, a rural site in eastern China, during spring 2001. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 109(D19S05): 1–16. doi: 10.1029/2 003JD004119
Wang T, Jiang F, Deng J et al., 2012. Urban air quality and regional haze weather forecast for Yangtze River Delta region. Atmospheric Environment, 58(15): 70–83. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.01.014
Xiao Z M, Zhang Y F, Hong S M et al., 2011. Estimation of the main factors influencing haze, based on a long-term monitoring campaign in Hangzhou, China. Aerosol & Air Quality Research, 11(7): 873–882. doi: 10.4209/aaqr.2011.04.0052
Yu B, Huang C, Liu Z et al., 2011. A chaotic analysis on air pollution index change over past 10 years in Lanzhou, Northwest China. Stochastic Environmental Research & Risk Assessment, 25(5): 643–653. doi: 10.1007/s00477-011-0471-y
Zhang X Y, Wang J Z, Wang Y Q et al., 2015. Changes in chemical components of aerosol particles in different haze regions in China from 2006 to 2013 and contribution of meteorological factors. Atmospheric Chemistry & Physics, 15(2): 12935–12952. doi: 10.5194/acp-15-12935-2015
Zhao P, Fan D, Yang Y et al., 2013. Characteristics of carbonaceous aerosol in the region of Beijing, Tianjin, and Hebei, China. Atmospheric Environment, 71(3): 389–398. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.02.010
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of Special Research Fund of the Ministry of Land and Resources for the Non-Profit Sector (No. 201411014-03), National Key Technology Research and Development Program of China (No. 2012BAH28B04)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, T., Deng, S., Gao, Y. et al. Characterization of air pollution in urban areas of Yangtze River Delta, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 27, 836–846 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-017-0900-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-017-0900-z