Abstract
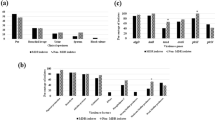
This study aims to investigate the relationship between the antibiotic resistance, biofilm production, virulence factors, and quorum sensing systems of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. First, disc diffusion and microdilution tests were applied to determine the antibiotic susceptibility of isolates. Second, virulence factors of isolates were determined phenotypically. Then, intact and internal lasI, lasR, rhII, and rhIR gene regions were amplified by polymerase chain reaction. Finally, biofilm formed by isolates were observed using a confocal laser scanning microscope. As a result, significant differences were found between hospital services and antibiotic resistance (p < 0.05). Biofilm formation was observed in 76% of the isolates. The production of homoserine lactone, pyocyanin, and elastase were detected in 51%, 65%, 66% of isolates, respectively. The lasI gene was 96% intact and 95% internal, and the lasR was 91% intact and 95% internal for the las system. The rhlI was 91% intact and 90% internal, and the rhlR was 80% intact and 90% internal for the rhl system. According to the microscope results, the isolates with antibiotic resistance formed thicker biofilm layer. Biofilm-positive strains were capable of important virulence factors and developed antibiotic resistance, playing a role in the pathogenesis.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- P. aeruginosa :
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- 3-oxo-C12-HSL:
-
N-(3-oxododecanoyl)-L-homoserine lactone
- EPS:
-
Extracellular polymeric substances
- C4-HSL:
-
N-butanoyl homoserine lactone
- A. tumefaciens :
-
Agrobacterium tumefaciens
- CLSI:
-
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute
- MIC:
-
Minimum inhibitory concentrations
- AHL:
-
N-acylated homoserine lactone
- CLSM:
-
Confocal laser scanning microscope
- ECR:
-
Elastin congo red
- TPZ:
-
Piperacillin-Tazobactam
- LBB:
-
Luria Bertani Broth
- W:
-
Wound
- B:
-
Blood
- AI:
-
Auto inducer
- CN:
-
Gentamicin
- CT:
-
Colistin
- IPM:
-
Imipenem
- LEV:
-
Levofloxacin
- MEM:
-
Meropenem
- TOB:
-
Tobramycin
- CAZ:
-
Ceftazidime
- R:
-
Resistant
- I:
-
Intermediate resistant
- S:
-
Sensitive
- Sp:
-
Sputum
- TA:
-
Tracheal aspirate
- U:
-
Urine
References
Aktepe OC, Aşık G, Çetinkaya Z, Çiftçi IH, Altındiş M (2010) Antimicrobial resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from clinical specimens. Türk Mikrobiyol Cem Derg 40(4):225–231 (http://www.tmc.dergisi.org/pdf/pdf_TMC_392.pdf)
Balasubramanian D, Schneper L, Kumari H, Mathee K (2013) Dynamic and intricate regulatory network determines Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence. Nucleic Acids Res 41(1):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1039
Başaran TI, Berber D, Gökalsın B, Tramice A, Tommonaro G, Abbamondi GR, Hasköylü ME, Öner ET, Iodice C, Sesal NC (2020) Extremophilic natrinema versiforme against Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing. Front Microbiol 11(79):1–10
Behzadi P, Ambrosi C, Scribano D, Zanetti S, Sarshar M, Gajdács M, Donadu MG (2022) Current perspectives on Pseudomonas aeruginosa: epidemiology, virulence and contemporary strategies to combat multidrug-resistant (MDR) pathogens. Front Microbiol 13:975616. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.975616
Cattelan N, Yantorno OM, Deora R (2018) Structural analysis of Bordetella pertussis biofilms by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Bio-Protocol 8(15):1–15. https://doi.org/10.21769/BioProtoc.2953
CLSI. M100-S24 (2014) Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; Twenty-fourth informational supplement. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, p 230. ISBN: 1-56238-897-5
Dave VP, Pathengay A, Nishant K, Pappuru RR, Sharma S, Sharma P, Narayanan R, Jalali S, Mathai A, Das T (2016) Clinical presentations, risk factors and outcomes of ceftazidime-resistant Gram-negative endophthalmitis. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 45(3):254–260. https://doi.org/10.1111/ceo.12833
de Kievit TR, Iglewski BH (2000) Bacterial quorum sensing in pathogenic relationships. Infect Immun 68(9):4839–4849. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.68.9.4839-4849.2000
de Freitas RP, Greatti VR, Alcalde MP, Alcalde MP, Duarte MAH, Weckwerth ACVB, Weckwerth PH (2016) Effect of the association of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory and antibiotic drugs on antibiofilm activity and ph of calcium hydroxide pastes. J Endod 43(1):131–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2016.09.014
Debarbieux L, Leduc D, Maura D, Morello E, Criscuolo A, Grossi O, Balloy V, Touqui L (2010) Bacteriophages can treat and prevent Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infections. J Infect Dis 201(7):1096–1104. https://doi.org/10.1086/651135
Dietrich LEP, Whelan AP, Petersen A, Whıteley M, Newman DK (2006) The phenazine pyocyanin is a terminal signalling factor in the quorum sensing network of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Microbiol 61(5):1308–1321. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05306.x
Diggle SP, Whiteley M (2020) Microbe Profile: Pseudomonas aeruginosa: opportunistic pathogen and lab rat. Microbiology 166(1):30–33. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.000860
Ding Y, Teo JWP, Moses DID, Schuster SC, Givskov M, Yang L (2018) Acquisition of resistance to carbapenem and macrolide-mediated quorum sensing inhibition by Pseudomonas aeruginosa via ICETn43716385. Commun Biol 57(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-018-0064-0
Fujimura T, Anan N, Sugimori G, Watanabe T, Jinushi Y, Yoshida I, Yamano Y (2009) Susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates in Japan to doripenem and other antipseudomonal agents. Int J Antimicrob Agents 34(6):523–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2009.07.008
Fuqua WC, Winans SC, Greenberg EP (1994) Quorum sensing in bacteria the LuxR-LuxI family of cell density-response transcriptional regulators. J Bacteriol 176(2):269–275. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.176.2.269-275.1994
Gray KM (1997) Intercellular communication and group behavior in bacteria. Trends Microbiol 5(5):184–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0966-842X(97)01002-0
Hassan A, Usman J, Kaleem F, Omair M, Khalid A, Iqbal M (2011) Evaluation of different detection methods of biofilm formation in the clinical isolates. Braz J Infect Dis 15(4):305–311. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1413-86702011000400002
Jeong SJ, Yoon SS, Bae IK, Jeong SH, Kim JM, Lee K (2014) Risk factors for mortality in patients with bloodstream infections caused by carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa: clinical impact of bacterial virulence and strains on outcome. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 80(2):130–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2014.07.003
Kamali E, Jamali A, Ardebili A, Ezadi F, Mohebbi A (2020) Evaluation of antimicrobial resistance, biofilm forming potential, and the presence of biofilm-related genes among clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. BMC Res Notes 13(27):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-020-4890-z
Karatuna O, Yağcı A (2010) Analysis of quorum sensing-dependent virulence factor production and its relationship with antimicrobial susceptibility in Pseudomonas aeruginosa respiratory isolates. Clin Microbiol Infect 16(12):1770–1775. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-0691.2010.03177.x
Kim SK, Lee JH (2016) Biofilm dispersion in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Microbiol 54(2):71–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-016-5528-7
Kos VN, McLaughlin RE, Gardner HA (2016) Elucidation of mechanisms of ceftazidime resistance among clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by using genomic data. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 60(6):3856–3860. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.03113-15
Kumar A, Naravarjula SS, Das MD (2016) Molecular and immunological characterization of Lp1, the 34 kDa outer membrane lipoprotein of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biologia 71(7):743–747. https://doi.org/10.1515/biolog-2016-0104
Lee J, Zhang L (2015) The hierarchy quorum sensing network in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Protein Cell 6(1):26–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-014-0100-x
Lewis K (2001) Riddle of biofilm resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45(4):999–1007. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.45.4.999-1007.2001
Lopez D, Vlamakis H, Kolter R (2010) Biofilms. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2(7):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a000398
Maura D, Bandyopadhaya A, Rahme LG (2018) Animal models for Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing studies. Methods Mol Biol 1673:227–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7309-5_18
Maurice NM, Bedi B, Sadikot RT (2018) Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms: host response and clinical implications in lung infections. A J Res Cell Mol 58(4):428–439. https://doi.org/10.1165/rcmb.2017-0321TR
Nelson LK, D’Amours GH, Willoughby KMS, Morck DW, Ceri H (2009) Pseudomonas aeruginosa las and rhl quorum sensing systems are important for infection and inflammation in a rat prostatitis model. Microbiol 155(8):2612–2619. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.028464-0
Obritsch MD, Fish DN, MacLaren R, Jung R (2004) National surveillance of antimicrobial resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from intensive care unit patients from 1993 to 2002. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 48(12):4604–4610. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.48.12.4606-4610.2004
Onorato L, Caprio GD, Signoriello S, Coppola N (2019) Efficacy of ceftazidime-avibactam in monotherapy or combination therapy against carbapenem resistant Gram negative organisms: a meta-analysis. Int J Antimicrob Agents 54(6):735–740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2019.08.025
Pang Z, Raudonis R, Glick BR, Lin TJ, Cheng Z (2019) Antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: mechanisms and alternative therapeutic strategies. Biotechnol Adv 37(1):177–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2018.11.013
Qin S, Xiao W, Zhou C, Pu Q, Deng X, Lan L, Liang H, Song X, Wu M (2022) Pseudomonas aeruginosa: pathogenesis, virulence factors, antibiotic resistance, interaction with host, technology advances and emerging therapeutics. Signal Transduct Target Ther 7(199):1–27. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-022-01056-1
Rust L, Messing CR, Iglewski BH (1994) Elastase assays. Methods Enzymol 235:554–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(94)35170-8
Schaber JA, Carty NL, McDonald NA, Graham ED, Cheluvappa R, Griswold JA, Hamood AN (2004) Analysis of quorum sensing-deficient clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Med Microbiol 53(9):841–853. https://doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.45617-0
Schlafer S, Meyer RL (2017) Confocal microscopy imaging of the biofilm matrix. J Microbiol Methods 138:50–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2016.03.002
She P, Wang Y, Liu Y, Tan F, Chen L, Luo Z, Wu Y (2019) Effects of exogenous glucose on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation and antibiotic resistance. Microbiologyopen 8(12):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1002/mbo3.933
Stepanovic S, Vukovic D, Dakic I, Savic B, Svabic-Vlahovic M (2000) Modified microtiter-plate test for quantification of staphylococcal biofilm formation. J Microbiol Methods 40(2):175–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-7012(00)00122-6
Sultan M, Arya R, Kim KK (2021) Roles of two-component systems in Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence. Int J Mol Sci 22(22):12152. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212152
Tınaz GB, Ulusoy S, Arıdogan B, Eroğlu F, Kaya S (2005) N-butanoyl-L-homoserine lactone (BHL) deficient Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from an intensive care unit. Microbiol Res 160(4):399–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2005.03.005
Wagner T, Soong G, Sokol S, Saiman L, Prince A (2005) Effects of azithromycin on clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from cystic fibrosis patients. Chest 128(2):912–919. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.128.2.912
Walkty A, Baxter M, Adam H, Karlowsky JA, Wiens PL, Hoban DJ, Zhanel GG (2012) Antimicrobial susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates obtained from patients in canadian hospitals: CANWARD 2008–2011. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 73(4):361–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2012.05.007
Waters CM, Bassler BL (2005) Quorum sensing: cell-to-cell communication in bacteria. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 21:319–346. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.cellbio.21.012704.131001
Wei Q, Ma LZ (2013) Biofilm matrix and its regulation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int J Mol Sci 14(10):20983–21005. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141020983
Whitehead NA, Barnard AML, Slater H, Simpson NJL, Salmond GPC (2001) Quorum-sensing in Gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 25(4):365–404. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2001.tb00583.x
Williams P, Camara M, Hardman A, Swift S, Milton D, Hope VJ, Winzer K, Middleton B, Pritchard DI, Bycroft BW (2000) Quorum sensing and the population-dependent control of virulence. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 355:667–680. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2000.0607
Xiong J, Deraspe M, Iqbal N, Krajden S, Chapman W, Dewar K, Roy PH (2017) Complete genome of a panresistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain, isolated from a patient with respiratory failure in a canadian community hospital. Genome Announc 5(22):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00458-17
Yuan Y, Qu K, Tan D, Li X, Wang L, Cong C, Xiu Z, Xu Y (2019) Isolation and characterization of a bacteriophage and its potential to disrupt multi-drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Microb Pathog 128:329–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2019.01.032
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Anadolu University Research Foundation [Project Code: 1403F090].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the Clinical Research Ethical Committee of Ondokuz Mayıs University, Turkey (OMÜ KAEK 2014/577).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Başkan, C., Yıldırım, T., Bilgin, M. et al. Determination of biofilm formation, antibiotic susceptibility profiles and quorum sensing mediated virulence factors in ceftazidime resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biologia 78, 2881–2893 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-023-01429-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-023-01429-z