Abstract
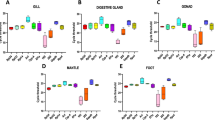
The green mirid bug Cyrtorhinus lividipennis (Hemiptera: Miridae), known as a predator, plays an important role in modulating the population density of planthoppers and leafhoppers in rice ecosystem. To understand the molecular mechanisms underlying many physiological processes of C. lividipennis research on gene expression are required, and reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) is the most commonly used method to quantify the expression of target genes. However, there are no previous reports on reliable reference genes in C. lividipennis. Here, we evaluated the stability of eight candidate reference genes (RPL32, β-Tub, SDHA, RPL9, GAPDH, EF1α, β-Act and α-Act) under different conditions with five algorithms (ΔCt method, BestKeeper, GeNorm, NormFinder and RefFinder). Results have indicated that RPL32 and RPL9 are suitable reference genes across nymphal stages, RPL32 and RPL9 are the suggested reference genes in different developmental stages of adult females, RPL32, RPL9 and β-Tub are suitable reference genes for all developmental stages, β-Tub, GAPDH, RPL9 and β-Act are reliable reference genes in different tissues of 5th instar females, EF1α, RPL9, RPL32 and β-Tub are stable reference genes in different tissues of one-day-old adult females, β-Tub, EF1α, RPL9, RPL32 and β-Act are suitable reference genes in all samples. These results highlight the importance of identifying reference genes under different experimental treatments. Our study will facilitate further phylogenetic and physiological mechanism research at the transcriptional level in C. lividipennis.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 18S :
-
rRNA 18 S ribosomal RNA.
- Act :
-
Actin.
- cDNA:
-
Complementary deoxyribonucleic acid.
- ClJHAMT :
-
Cyrtorhinus lividipennis juvenile hormone acid methyl transferase.
- ClJHE :
-
Cyrtorhinus lividipennis juvenile hormone esterase.
- ClKr-h1 :
-
Cyrtorhinus lividipennis Krüppel homolog 1.
- ClSPATA13 :
-
Cyrtorhinus lividipennis spermatogenesis-associated protein 13.
- ClVg :
-
Cyrtorhinus lividipennis vitellogenin.
- Ct:
-
Threshold cycle.
- ddH2O:
-
Double distilled water.
- EF1α :
-
Eukaryotic elongation factor 1-alph.
- GAPDH :
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
- NCBI:
-
National Center for Biotechnology Information.
- qPCR:
-
Quantitative polymerase chain reaction.
- RH:
-
Relative humidity.
- RNA:
-
Ribonucleic Acid.
- RPL32 :
-
Ribosomal protein L32.
- RPL9 :
-
Ribosomal protein L9.
- RPS15 :
-
Ribosomal protein S15.
- RT-qPCR:
-
Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction.
- SD:
-
Standard deviation.
- SDHA :
-
Succinate dehydrogenase complex flavoprotein subunit A.
- SV:
-
Stability value.
- TOR:
-
target of rapamycin.
- α-Act :
-
alph-Actin.
- β-Act :
-
beta-Actin.
- β-Tub :
-
beta-Tubin.
References
Ahmed T, Zhang T, Wang Z, He K, Bai S (2016) Identification and expression pattern analysis of chemosensory receptor genes in the Macrocentrus cingulum (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) antennae. Eur J Entomol 113:76–83. https://doi.org/10.14411/eje.2016.009
Ali MP, Rahman M, Nowrin F, Haque S, Qin X, Uddin M, Landis D, Howlader M (2021) Salinity influences plant-pest-predator tritrophic Interactions. J Econ Entomol 114(4). https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/toab133
Andersen CL, Jensen JL, Orntoft TF (2004) Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: A model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res 64(15):5245–5250. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0496
Chang YW, Chen JY, Lu MX, Yuan G, Tian ZH, Gong WR, Wei Z, Du YZ, Gao Y (2017) Selection and validation of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR analysis under different experimental conditions in the leafminer Liriomyza trifolii (Diptera: Agromyzidae). PLoS ONE 12(7):e0181862. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0181862
Dzaki N, Ramli KN, Azlan A, Ishak IH, Azzam G (2017) Evaluation of reference genes at different developmental stages for quantitative real-time PCR in Aedes aegypti. Sci Rep 7:43618. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep43618
Flavia F, Tommaso M, Roberta P (2021) Selection and validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR normalization in different tissues of milk thistle (Silybum marianum, Gaert.). Gene 768:145272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2020.145272
Florence PP, Mathieu C, Annabel W, Mathieu J, Violaine L (2016) Selection of valid reference genes for reverse transcription quantitative PCR analysis in Heliconius numata (Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae). J Insect Sci 16(1):50. https://doi.org/10.1093/jisesa/iew034
Foquet B, Song H (2020) There is no magic bullet: the importance of testing reference gene stability in RT-qPCR experiments across multiple closely related species. PeerJ 8:e9618. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.9618
Fu W, Wen X, Zhang Z, Wang S, Zhang Y (2013) Exploring valid reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR analysis in Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). Int J Biol Sci 9(8):792–802. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.5862
Ge L, Jiang L, Zheng S, Zhou Y, Wu Q, Liu F (2020) Frizzled 2 functions in the regulation of TOR-mediated embryonic development and fecundity in Cyrtorhinus lividipennis Reuter. Front Physiol 11:579233. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2020.579233
Heong KL, Bleih S, Lazaro AA (1990) Predation of Cyrtorhinus lividipennis Reuter on eggs of the green leafhopper and brown planthopper in rice. Res Popul Ecol 32(2):255–262. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02512561
Hu K, Tian P, Yang L, Tang Y, Qiu L, He H, Ding W, Li Y (2020) Molecular characterization of the Krüppel-homolog 1 and its role in ovarian development in Sogatella furcifera (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Mol Biol Rep 47(2):1099–1106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-019-05206-7
Jing Y, Yue G, Zhongfang L, Junjiao L, Yuying Z, Pengjiu Z, Jianbin F, Xuguo Z, Renjun F (2019) Selection of reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis under intrinsic conditions in the hawthorn spider mite, Amphitetranychus viennensis (Acarina: Tetranychidae). Front Physiol 10:1427. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.01427
Li F, Li Y, Wang T, Li T, Zhu S, Pei P, Tang G (2020) Screening potential reference genes for reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction normalization in Atrijuglans hetaohei (Lepidoptera: Gelechioidea). Entomol Res 50(6):317–326. https://doi.org/10.1111/1748-5967.12444
Liu S, Zhao J, Hamada C, Cai W, Khan M, Zou Y, Hua H (2019) Identification of attractants from plant essential oils for Cyrtorhinus lividipennis, an important predator of rice planthoppers. J Pest Sci 92(2):769–780. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-018-1054-1
Lü J, Yang C, Zhang Y, Pan H (2018) Selection of reference genes for the normalization of RT-qPCR data in gene expression studies in insects: A systematic review. Front Physiol 9:1560. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.01560
Lu W, Xu Q, Zhu J, Liu C, Ge L, Yang G, Liu F (2017) Inductions of reproduction and population growth in the generalist predator Cyrtorhinus lividipennis (Hemiptera: Miridae) exposed to sub-lethal concentrations of insecticides. Pest Manag Sci 73(8):1709–1718. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.4518
Luo J, Wang A, Cheng Y, Rong H, Guo L, Peng Y, Xu L (2020) Selection and validation of suitable reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis in Apolygus lucorum (Hemiptera: Miridae). J Econ Entomol 113(1):451–460. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/toz301
Matsumura M, Urano S, Suzuki Y (2005) Evaluating augmentative releases of the mirid bug Cyrtorhinus lividipennis to suppress brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens in open paddy fields. In: Toriyama K, Heong KL, Hardy B (eds) Rice is Life: Scientific Perspectives for the 21st Century International Rice Research Institute, Manila, Philippines, pp 473–475 https:// www. cabdi rect. org/ cabdi rect/ FullT extPDF/ 2005/ 20053 159947. pdf
Sarwar MB, Ahmad Z, Anicet BA, Sajid M, Rashid B, Hassan S, Ahmed M, Husnain T (2020) Identification and validation of superior housekeeping gene(s) for qRT-PCR data normalization in Agave sisalana (a CAM-plant) under abiotic stresses. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 26:567–584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-020-00760-y
Narsai R, Ivanova A, Ng S, Whelan J (2010) Defining reference genes in Oryza sativa using organ, development, biotic and abiotic transcriptome datasets. BMC Plant Biol 10:56. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-10-56
Pan H, Yang X, Siegfried BD, Zhou X (2015) A comprehensive selection of reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis in a predatory lady beetle, Hippodamia convergens (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). PLoS ONE 10(4):e0125868. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0125868
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29(9):e45. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/29.9.e45
Radonić A, Thulke S, Mackay IM, Landt O, Siegert W, Nitsche A (2004) Guideline to reference gene selection for quantitative real-time PCR. Biochem Bioph Res Co 313(4):856–862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.11.177
Roy S, Saha TT, Zou Z, Raikhel AS (2018) Regulatory pathways controlling female insect reproduction. Annu Rev Entomol 63:489–511. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ento-020117-043258
Sigsgaard L (2007) Early season natural control of the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens: the contribution and interaction of two spider species and a predatory bug. Bull Entomol Res 97(5):533–544. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0007485307005196
Silver N, Best S, Jiang J, Thein SL (2006) Selection of housekeeping genes for gene expression studies in human reticulocytes using real-time PCR. BMC Mol Biol 7(1):33. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2199-7-33
Sousa FCBd N, CSd M, Araújo MdS, Barbosa RdS, Bayão LT, Sousa GFV KRS (2021) Selection of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR normalization in European quail tissues. Mol Biol Rep 48(1):67–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-06134-7
Tang B, Dai W, Zhang C (2019) Selection of reference genes for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction normalization in Bradysia odoriphaga (Diptera: Sciaridae). Entomol Sci 22(4):422–436. https://doi.org/10.1111/ens.12383
Tang Y, He H, Qu X, Cai Y, Ding W, Qiu L, Li Y (2020) RNA interference-mediated knockdown of the transcription factor Krüppel homologue 1 suppresses vitellogenesis in Chilo suppressalis. Insect Mol Biol 29(2):183–192. https://doi.org/10.1111/imb.12617
Tian P, Qiu L, Zhou A, Chen G, He H, Ding W, Li Y (2019) Evaluation of appropriate reference genes for investigating gene expression in Chlorops oryzae (Diptera: Chloropidae). J Econ Entomol 112(5):2207–2214. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/toz142
Upadhyay SK, Singh H, Dixit S, Mendu V, Verma PC (2016) Molecular characterization of vitellogenin and vitellogenin receptor of Bemisia tabaci. PLoS ONE 11(5):e0155306. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0155306
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Speleman F (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3(7):RESEARCH0034. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2002-3-7-research0034
Wang GY, Zhu JL, Zhou WW, Liu S, Khairul QM, Ansari NA, Zhu ZR (2018) Identification and expression analysis of putative chemoreception genes from Cyrtorhinus lividipennis (Hemiptera: Miridae) antennal transcriptome. Sci Rep 8(1):12981. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-31294-9
Wang GY, Zhu MF, Jiang YD, Zhou WW, Liu S, Heong KL, Cheng J, Zhu ZR (2017) Identification of candidate odorant-binding protein and chemosensory protein genes in Cyrtorhinus lividipennis (Hemiptera: Miridae), a key predator of the rice planthoppers in Asia. Environ Entomol 46(3):654–662. https://doi.org/10.1093/ee/nvx075
Wang X, Kong X, Liu S, Huang H, Chen Z, Xu Y (2020) Selection of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR in Chrysoperla nipponensis (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae) under tissues in reproduction and diapause. J Insect Sci 20(4):20. https://doi.org/10.1093/jisesa/ieaa079
Wang Z, Meng Q, Zhu X, Sun S, Liu A (2019) Evaluation and validation of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR in Helopeltis theivora Waterhouse (Hemiptera: Miridae). Sci Rep 9(1):13291. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-49479-1
Xie F, Xiao P, Chen D, Xu L, Zhang B (2012) miRDeepFinder: a miRNA analysis tool for deep sequencing of plant small RNAs. Plant Mol Biol 80(1):75–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-012-9885-2
Xu J, Lu MX, Cui YD, Du YZ (2017) Selection and evaluation of reference genes for expression analysis using qRT-PCR in Chilo suppressalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). J Econ Entomol 110(2): 683–691. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/tow297
Xu J, Welker DL, James RR (2021) Variation in expression of reference genes across life stages of a bee, Megachile rotundata. Insects 12(1):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12010036
Yadav PK, Sharma S, Sharma A (2021) Management trends of rice insect pests in South Asia: A Review. Rev Food Agri (RFNA) 2(2):46–53. https://doi.org/10.26480/rfna.02.2021.46.53
Yan X, Zhang Y, Xu K, Wang Y, Yang W (2021) Selection and validation of reference genes for gene expression analysis in Tuta absoluta Meyrick (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae). Insects 12(7):589. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12070589
Yang XJ, Zheng HL, Liu YY, Li HW, Jiang YH, Lin LB, Deng XY, Zhang QL (2020) Selection of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR in Aquatica leii (Coleoptera: Lampyridae) under five different experimental conditions. Front Physiol 11:555233. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2020.555233
Yu B, Lv YN, Zeng M, Jia PY, Lu HN, Zhu YB, Li S, Cui YY, Luan YX (2020) Selection of reference genes for normalization of gene expression in Thermobia domestica (Insecta: Zygentoma: Lepismatidae). Genes 12(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12010021
Zhang X, Liao X, Mao K, Zhang K, Wan H, Li J (2016) Insecticide resistance monitoring and correlation analysis of insecticides in field populations of the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) in China 2012–2014. Pestic Biochem Phys 132:13–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2015.10.003
Zheng C, Zhao D, Xu Y, Shi F, Zong S, Tao J (2020a) Reference gene selection for expression analyses by qRT-PCR in Dendroctonus valens. Insects 11(6):326. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11060328
Zheng W, Meng Q, Zhu X, Sun S, Liu A, Gao S, Gou Y (2020b) Identification and evaluation of reference genes for normalization of gene expression in developmental stages, sexes, and tissues of Diaphania caesalis (Lepidoptera, Pyralidae). J Insect Sci 20(1):6. https://doi.org/10.1093/jisesa/iez130
Zhu H, Zheng S, Xu J, Wu Q, Song Q, Ge L (2020a) The amino acid-mediated TOR pathway regulates reproductive potential and population growth in Cyrtorhinus lividipennis Reuter (Hemiptera: Miridae). Front Physiol 11:617237. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2020.617237
Zhu J, Li Y, Tang Y, Liu J, Chen Y, LV Z, Liu F (2020b) Juvenile hormone-mediated reproduction induced by a sublethal concentration of imidacloprid in Cyrtorhinus lividipennis (Hemiptera: Miridae). J Asia-Pac Entomol 23(1):98–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aspen.2019.10.018
Zhu P, Lu Z, Heong K, Chen G, Zheng X, Xu H, Yang Y, Nicol HI, Gurr GM (2014) Selection of nectar plants for use in ecological engineering to promote biological control of rice pests by the predatory bug, Cyrtorhinus lividipennis. PLoS ONE 9(9):e108669. Heteroptera: Miridaehttps://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0108669
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 32001894 and 31872928).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, K., Chen, K., Fu, B. et al. Reliable reference genes for qPCR normalization in females of the mirid predator, Cyrtorhinus lividipennis (Hemiptera: Miridae). Biologia 77, 2383–2392 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-022-01093-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-022-01093-9