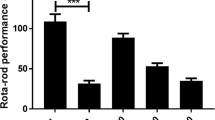
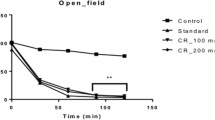
Abstract
Psychological stress and anxiety have been linked to significant impairments of neurobiological functions. There is a wide range of conditions including neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease and use of certain substances or medications that induce stress and anxiety in humans. Confused state of mind, anxiety and psychological stress have been associated with varying degree of disabilities and poor quality of life in humans. Anxiolytic medications are important modulators of CNS that reduce the anxiety and the related psychological effects in patients. Natural product derived drugs such as galantamine have been shown to possess promising neuro-modulatory properties in neurological disorders. Averrhoa carambola is traditionally used for anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, anti-microbial, and anti-ulcerative properties. In this study, we have examined the CNS depressant activity of A. carambola leaves extracts. The neuro-modulatory properties were assessed with the standard protocols that are used to identify such CNS depressant activity and included thiopental sodium-induced sleeping time test, hole cross test, hole board test, and open field test. The extract was found to decrease the motor activity and exploratory behaviour of mice in hole cross, hole board and open field tests. The extract also significantly maximized the duration of sleeping time when administered with thiopental sodium, which also demonstrated the CNS depressant activity. The findings of our study suggest that A. carambola extracts have active CNS depressant and hypnotic properties. However, further studies are warranted for isolation of bioactive constituents and understanding the molecular mechanism and modes of action for such pharmacological effects.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abruzzo PM, Panisi C, Marini M (2021) The alteration of chloride homeostasis/GABAergic signaling in brain disorders: could oxidative stress play a role? Antioxidants 10(8):1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10081316
Ali MS, Dash PR, Nasrin M (2015) Study of sedative activity of different extracts of Kaempferia galanga in Swiss albino mice. BMC Complement Altern Med 15:158. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-015-0670-z
Alzobaidi N, Quasimi H, Emad NA, Alhalmi A, Naqvi M (2021) Bioactive compounds and traditional herbal medicine: promising approaches for the treatment of dementia. Degener Neurol Neuromuscul Dis 11:1–14. https://doi.org/10.2147/DNND.S299589
Amorim EL, Nascimento JE, Monteiro JM, Peixoto Sobrinho TJ, Araújo TA, Albuquerque UP (2008) A simple and accurate procedure for the determination of tannin and flavonoid levels and some applications in ethnobotany and ethnopharmacology. Funct Ecosys Commun 2(1):88–94
Anisuzzman M, Hasan MM, Acharzo AK, Das AK, Rahman S (2017) In vivo and in vitro evaluation of pharmacological potentials of secondary bioactive metabolites of Dalbergia candenatensis leaves. Evid Based Complement Altern Med 2017:5034827. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5034827
Ansari N, Khodagholi F (2013) Natural products as promising drug candidates for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease: molecular mechanism aspect. Curr Neuropharmacol 11(4):414–429. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X11311040005
Astiti NPA, Susdirga SK, Ramona Y (2019) Analysis of phenolic and tannin contents in the methanol extract of sweet and sour star fruit plants (Averrhoa carambola L) leaves commonly used as raw materials of lawar (a Balinese traditional food). Adv Trop Biodivers Environ Sci 3(1):5–7. https://doi.org/10.24843/ATBES.2019.v03.i01.p02
Awaludin A, Kartina K, Maulianawati D, Manalu W, Andriyanto A, Septiana R, Arfandi A, Lalang Y (2020) Phytochemical screening and toxicity of ethanol extract of Sauropus androgynus. Biodiversitas 21:2966–2970. https://doi.org/10.13057/biodiv/d210712
Aziz MA, Barua N, Tareq AM, Alam N, Prova RJ, Mamun MN, Sayeed MA, Chowdhury MA, Emran TB (2020) Possible neuropharmacological effects of Adenia trilobata (Roxb.) in the Swiss albino mice model. Future J Pharm Sci 6(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43094-020-00102-5
Bektas N, Arslan R, Alyu F (2020) The anxiolytic effect of perampanel and possible mechanisms mediating its anxiolytic effect in mice. Life Sci 261:118359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118359
Bruce RD (1985) An up-and-down procedure for acute toxicity testing. Fundam Appl Toxicol 5(1):151–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/0272-0590(85)90059-4
Bruni O, Ferini-Strambi L, Giacomoni E, Pellegrino P (2021) Herbal remedies and their possible effect on the GABAergic system and sleep. Nutrients 13(2):530. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13020530
Castañeda R, Cáceres A, Velasquez D, Rodriguez C, Morales D, Castillo A (2021) Medicinal plants used in traditional Mayan medicine for the treatment of central nervous system disorders: an overview. J Ethnopharmacol 283:114746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2021.114746
Chandrasekhar Y, Ramya EM, Navya K, Phani Kumar G, Anilakumar KR (2017) Antidepressant like effects of hydrolysable tannins of Terminalia catappa leaf extract via modulation of hippocampal plasticity and regulation of monoamine neurotransmitters subjected to chronic mild stress (CMS). Biomed Pharmacother 86:414–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.12.031
Chau CF, Chen CH, Lee MH (2004a) Characterization and physiochemical properties of some potential fibers derived from Averrhoa carambola. Nahrung 48(1):43–46. https://doi.org/10.1002/food.200300354
Chau CF, Huang YL, Lee MH (2004b) Effect of novel pomace fiber on lipid and cholesterol metabolism in the hamster. Nutr Res 24:337–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nutres.2004.01.003
Chopade AR, Pol RP, Patil PA, Dharanguttikar VR, Naikwade NS, Dias RJ, Mali SN (2021) Pharmacological and in-silico investigations of anxiolytic-like effects of Phyllanthus fraternus: a probable involvement of GABA-A receptor. Curr Enzym Inhib 17(1):42–48. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573408016999201026200650
Chung KS, Paul PH, Kimura T (1996) International collation of traditional and folk medicine: Northeast Asia. World Scientific Publishing Company, Singapore
Creaven AM, Healy A, Howard S (2018) Social connectedness and depression: is there added value in volunteering? J Soc Person Relation 35(10):1400–1417. https://doi.org/10.1177/0265407517716786
da Silva TC, da Silva JM, Ramos MA (2018) What factors guide the selection of medicinal plants in a local pharmacopoeia? A case study in a rural community from a historically transformed Atlantic forest landscape. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2018:2519212. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2519212
Das BN, Ahmed M (2012) Analgesic activity of fruit extract of Averrhoa carambola. Int J Life Sci Biotech Pharm Res 1(3):22–26
Di Lorenzo A, Sobolev AP, Nabavi SF, Sureda A, Moghaddam AH, Khanjani S, Di Giovanni C, Xiao J, Shirooie S, Sokeng AJ, Baldi A (2019) Antidepressive effects of a chemically characterized maqui berry extract (Aristotelia chilensis (Molina) Stuntz) in a mouse model of post-stroke depression. Food Chem Toxicol 129:434–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2019.04.023
Doyno CR, White CM (2019) Sedative-hypnotic agents that impact gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors: focus on flunitrazepam, gamma-hydroxybutyric acid, phenibut, and selank. J Clin Pharmacol 61:S114–S128. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcph.1922
Ebert B, Wafford KA, Deacon S (2006) Treating insomnia: current and investigational pharmacological approaches. Pharmacol Ther 112(3):612–629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2005.04.014
Edeoga HO, Okwu DE, Mbaebie BO (2005) Phytochemical constituents of some Nigerian medicinal plants. Afr J Biotechnol 4(7):685–688. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB2005.000-3127
Egbuna C, Nadia S, Jabeen NS (2018) Pharmacognosy and prehistoric uses of medicinal plants. In: Egbuna C, Kumar S, Ifemeje JC, Kurhekar JV (eds) Phytochemistry. Apple Academic Press, New York, pp 3–16
Emon NU, Alam S, Rudra S, Chowdhury S, Rajbangshi JC, Ganguly A (2020) Evaluation of pharmacological potentials of the aerial part of Achyranthes aspera L.: in vivo, in vitro and in silico approaches. Adv Trad Med 25:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-020-00528-5
Emon NU, Alam S, Rudra S, Riya SR, Paul A, Hossen SM, Kulsum U, Ganguly A (2021) Antidepressant, anxiolytic, antipyretic, and thrombolytic profiling of methanol extract of the aerial part of Piper nigrum: in vivo, in vitro, and in silico approaches. Food Sci Nutr 9(2):833–846. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.2047
Fitzgerald M, Heinrich M, Booker A (2020) Medicinal plant analysis: a historical and regional discussion of emergent complex techniques. Front Pharmacol 10:1480. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.01480
GBD 2019 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators (2020) Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. Lancet 396(10258):1204–1222. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30925-9
Goncalves ST, Baroni S, Fernando A, Cortez DAG, Melo Gessilda AN (2006) Preliminary studies on gastric anti-ulcerogenic effects of Averrhoa carambola in rats. Acta Farm Bonaer 25(2):245–247
Ham HJ, Lee YS, Yun J, Han SB, Son DJ, Hong JT (2020) Anxiolytic-like effects of the ethanol extract of Magnolia obovata leaves through its effects on GABA-benzodiazepine receptor and neuroinflammation. Behav Brain Res 383:112518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2020.112518
Han KS, Kim L, Shim I (2012) Stress and sleep disorder. Exp Neurobiol 21(4):141–150
Holanda DK, Wurlitzer NJ, Dionisio AP, Campos AR, Moreira RA, de Sousa PH, de Brito ES, Ribeiro PR, Iunes MF, Costa AM (2020) Garlic passion fruit (Passiflora tenuifila Killip): assessment of eventual acute toxicity, anxiolytic, sedative, and anticonvulsant effects using in vivo assays. Food Res Int 128:108813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2019.108813
Hong-liang ZH, Xia JI, Tian-min HU, Yue QI, Guang-ming HU, Ren-bin HU, Zhen-guang HU (2021) Study on the mechanism of the root of Averrhoa carambola L. in the treatment of diabetic kidney disease based on network pharmacology. Nat Prod Res Dev (NPRD) 33(4):647. https://doi.org/10.16333/j.1001-6880.2021.4.015
Horowitz M (2017) Antidepressant and anxiolytic-like, sedation and hypnosis. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 28(2):91–92. https://doi.org/10.1515/jbcpp-2017-0022
Hritcu L, Ionita R, Postu PA et al (2017) Antidepressant flavonoids and their relationship with oxidative stress. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2017:5762172. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5762172
Kalmbach DA, Anderson JR, Drake CL (2018) The impact of stress on sleep: pathogenic sleep reactivity as a vulnerability to insomnia and circadian disorders. J Sleep Res 27(6):e12710. https://doi.org/10.1111/jsr.12710
Krause J, Tobin G (2013) Discovery, development, and regulation of natural products. In Kulka M (ed) Using old solutions to new problems-natural drug discovery in the 21st century. IntechOpen, London, pp 1-35. https://doi.org/10.5772/56424
Kumar AR, Subburathinam KM, Prabakar G (2007) Phytochemical screening of selected medicinal plants of Asclepiadaceae family. Asian J Microbiol Biotechnol Environ Sci 9(1):177–180
Lakmal K, Yasawardene P, Jayarajah U, Seneviratne SL (2021) Nutritional and medicinal properties of star fruit (Averrhoa carambola): a review. Food Sci Nutr 9(3):1810–1823. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.2135
Lopresti AL, Smith SJ, Hood SD, Drummond PD (2019) Efficacy of a standardised saffron extract (affron®) as an add-on to antidepressant medication for the treatment of persistent depressive symptoms in adults: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Psychopharmacol 33(11):1415–1427. https://doi.org/10.1177/0269881119867703
Luan F, Peng L, Lei Z, Jia X, Zou J, Yang Y, He X, Zeng N (2021) Traditional uses, phytochemical constituents and pharmacological properties of Averrhoa carambola L.: a review. Front Pharmacol 12:699899. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.699899
Masum M, Rahman S, Begum K, Begum B, Rashid A (2007) Phytochemical and biological studies of Averrhoa carambola. J Pharm Sci 6(2):125–128. https://doi.org/10.3329/dujps.v6i2.688
Mendelson S (2019) Herbal treatment of major depression: scientific basis and practical use. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Milan R, Vasiliadis HM (2020) The association between side effects and adherence to antidepressants among primary care community-dwelling older adults. Aging Mental Health 24(8):1229–1236. https://doi.org/10.1080/13607863.2019.1594165
Nabavi SM, Daglia M, Braidy N, Nabavi SF (2017) Natural products, micronutrients, and nutraceuticals for the treatment of depression: a short review. Nutr Neurosci 20(3):180–194. https://doi.org/10.1080/1028415X.2015.1103461
Najmi A, Javed SA, Al Bratty M, Alhazmi HA (2022) Modern approaches in the discovery and development of plant-based natural products and their analogues as potential therapeutic agents. Molecules 27(2):349. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27020349
Nimgampalle M, Devanathan V, Saxena A (2021) Importance of in silico studies on the design of novel drugs from medicinal plants against 21st-century pandemics: past, present, and future. In: Viswanath B (ed) Pandemic outbreaks in the 21st century 2021. Academic Press, Cambridge, pp 211–223
Ramadan NS, Wessjohann LA, Mocan A, Vodnar DC, El-Sayed NH, El-Toumy SA, Abdou Mohamed D, Abdel Aziz Z, Ehrlich A, Farag MA (2020) Nutrient and sensory metabolites profiling of Averrhoa carambola L.(starfruit) in the context of its origin and ripening stage by GC/MS and chemometric analysis. Molecules 25(10):2423. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102423
Roell KR, Reif DM, Motsinger-Reif AA (2017) An introduction to terminology and methodology of chemical synergy-perspectives from across disciplines. Front Pharmacol 8:158. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2017.00158
Shah NA, Raut BA, Baheti A, Kuchekar BS (2011) In-vitro anthelmintic activity of leaf extract of Averrhoa carambola against Pheretima posthuma. Pharmacogyonline 1:524527
Sheikh BY, Zihad SMNK, Sifat N et al (2016) Comparative study of neuropharmacological, analgesic properties and phenolic profile of Ajwah, Safawy and Sukkari cultivars of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera). Orient Pharm Exp Med 16:175–183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-016-0239-5
Sheth A (2005) The Herbs of Ayurveda. Vol. 1. Sheth Publisher, Gujrat
Shui G, Leong LP (2006) Residue from starfruit as valuable source for functional food ingredients and nutraceuticals. Food Chem 97:277–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.03.048
Soncini R, Santiago MB, Orlandi L, Moraes GO, Peloso AL, dos Santos MH, Alves-da-Silva G, Paffaro VA Jr, Bento AC, Giusti-Paiva A (2011) Hypotensive effect of aqueous extract of Averrhoa carambola L. (Oxiladaceae) in rats: an in-vivo and in-vitro approach. J Ethnopharmacol 133(2):3537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2010.10.001
Sripanidkulchai B, Tattawasart U, Laupattarakasem P, Wongpanich V (2002) Antiinflammatory and bactericidal properties of elected indigenous medicinal plants used for dysuria. Thai J Pharm Sci 26(12):33–38
Suetani S, Stubbs B, McGrath JJ, Scott JG (2019) Physical activity of people with mental disorders compared to the general population: a systematic review of longitudinal cohort studies. Soc Psychiatr Epidemiol 1:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-019-01760-4
Süntar I (2020) Importance of ethnopharmacological studies in drug discovery: role of medicinal plants. Phytochem Rev 19(5):1199–1209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-019-09629-9
Tadros SH, Sleem AA (2004) Pharmacognostical and biological study of the stem and leaf of Avehrroa carambola L. Bull Fac Pharm 42:225–246
Uddin SJ, Shilpi JA, Rahman MT, Ferdous M, Rouf R, Sarker SD (2006) Assessment of neuropharmacological activities of Pandanus foetidus (Pandanaceae) in mice. Pharmazie 61:362–364
Vargas-Madriz AF, Kuri-García A, Vargas-Madriz H, Chávez-Servín JL, Ayala-Tirado RA (2021) Phenolic profile and antioxidant capacity of fruit Averrhoa carambola L.: a review. Food Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1590/fst.69920
Weich S, Pearce HL, Croft P, Singh S, Crome I, Bashford J (2014) Frisher M (2014) effect of anxiolytic and hypnotic drug prescriptions on mortality hazards: retrospective cohort study. BMJ 348:g1996. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.g1996
Welcome MO (2020) Neuroinflammation in CNS diseases: molecular mechanisms and the therapeutic potential of plant derived bioactive molecules. Pharma Nutrition 11:100176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phanu.2020.100176
Zangrossi H Jr, Del Ben CM, Graeff FG, Guimarães FS (2020) Serotonin in panic and anxiety disorders. In: Müller CP, Cunningham KA (eds) Handbook of behavioural neuroscience, Vol 31. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 611–633
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the department of pharmacy, Daffodil International University for providing necessary support to conduct the research.
Funding
This work was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR), King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia under grant no. (KEP-1-141-41). The authors, therefore, acknowledge with thanks DSR technical and financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akter, A., Islam, F., Bepary, S. et al. CNS depressant activities of Averrhoa carambola leaves extract in thiopental-sodium model of Swiss albino mice: implication for neuro-modulatory properties. Biologia 77, 1337–1346 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-022-01057-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-022-01057-z