Abstract
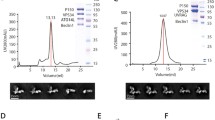
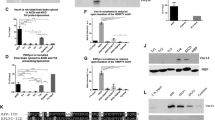
Specific protein-phosphoinositide (PI) interactions are known to play a key role in the targeting of proteins to specific cellular membranes. Investigation of these interactions would be greatly facilitated if GFP-fusion proteins expressed in mammalian cells and used for their subcellular localization could also be employed for in vitro lipid binding. In this study, we found that lysates of cells overexpressing GFP-fusion proteins could be used for in vitro protein-PI binding assays. We applied this approach to examine the PI-binding properties of Aplysia Sec7 protein (ApSec7) and its isoform ApSec7(VPKIS), in which a VPKIS sequence is inserted into the PH domain of ApSec7. EGFP-ApSec7 but not EGFP-ApSec7(VPKIS) did specifically bind to PI(3,4,5)P3 in an in vitro lipid-coated bead assay. Overexpression of EGFP-ApSec7 but not EGFP-ApSec7(VPKIS) did induce neurite outgrowth in Aplysia sensory neurons. Structure modeling analysis revealed that the inserted VPKIS caused misfolding around the PI(3,4,5)P3-binding pocket of ApSec7 and disturbed the binding of PI(3,4,5)P3 to the pleckstrin homology (PH) domain. Our data indicate that plasma membrane localization of EGFP-ApSec7 via the interaction between its PH domain and PI(3,4,5)P3 might play a key role in neurite outgrowth in Aplysia.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ApSec7:
-
Aplysia Sec7 protein
- PH:
-
Pleckstrin homology
- PI:
-
Phosphoinositide
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- OSBP:
-
Oxysterol-binding protein
- FAPP1/2:
-
PI4P adaptor protein ½
- CERT:
-
Ceramide transfer protein
- TGN:
-
Trans-Golgi network
- PLC:
-
Phospholipase
- GEF:
-
GDP/GTP exchange factor
- ARF:
-
ADP ribosylation factor
- ARNO:
-
ARF binding site opener
- FRB:
-
Rapamycin-binding domain of mTOR
- FKBP:
-
FK506 binding protein 12
- PJ:
-
Pseudojanin
- INPP5E:
-
Polyphosphate 5-phosphatase E
- PAO:
-
Phenylarsine oxide
- PI4K:
-
PI4 kinase
- MD:
-
Molecular dynamics
References
Di Paolo G, De Camilli P (2006) Phosphoinositides in cell regulation and membrane dynamics. Nature 443:651–657
Lemmon MA (2008) Membrane recognition by phospholipid-binding domains. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:99–111
Jang DJ, Park SW, Kaang BK (2009) The role of lipid binding for the targeting of synaptic proteins into synaptic vesicles. BMB Rep 42:1–5
Godi A, Di Campli A, Konstantakopoulos A, Di Tullio G, Alessi DR, Kular GS, Daniele T, Marra P, Lucocq JM, De Matteis MA (2004) FAPPs control Golgi-to-cell-surface membrane traffic by binding to ARF and PtdIns(4)P. Nat Cell Biol 6:393–404
Levine TP, Munro S (2002) Targeting of Golgi-specific pleckstrin homology domains involves both PtdIns 4-kinase-dependent and -independent components. Curr Biol 12:695–704
Hanada K, Kumagai K, Yasuda S, Miura Y, Kawano M, Fukasawa M, Nishijima M (2003) Molecular machinery for non-vesicular trafficking of ceramide. Nature 426:803–809
Lemmon MA, Ferguson KM, O’Brien R, Sigler PB, Schlessinger J (1995) Specific and high-affinity binding of inositol phosphates to an isolated pleckstrin homology domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:10472–10476
Garcia P, Gupta R, Shah S, Morris AJ, Rudge SA, Scarlata S, Petrova V, McLaughlin S, Rebecchi MJ (1995) The pleckstrin homology domain of phospholipase C-delta 1 binds with high affinity to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in bilayer membranes. Biochemistry 34:16228–16234
Franke TF, Kaplan DR, Cantley LC, Toker A (1997) Direct regulation of the Akt proto-oncogene product by phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate. Science 275:665–668
Jang DJ, Park SW, Lee JA, Lee C, Chae YS, Park H, Kim MJ, Choi SL, Lee N, Kim H, Kaang BK (2010) N termini of apPDE4 isoforms are responsible for targeting the isoforms to different cellular membranes. Learn Mem 17:469–479
Wang X, Li W, Zhao D, Liu B, Shi Y, Chen B, Yang H, Guo P, Geng X, Shang Z, Peden E, Kage-Nakadai E, Mitani S, Xue D (2010) Caenorhabditis elegans transthyretin-like protein TTR-52 mediates recognition of apoptotic cells by the CED-1 phagocyte receptor. Nat Cell Biol 12:655–664
Fairn GD, Ogata K, Botelho RJ, Stahl PD, Anderson RA, De Camilli P, Meyer T, Wodak S, Grinstein S (2009) An electrostatic switch displaces phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinases from the membrane during phagocytosis. J Cell Biol 187:701–714
Lee SH, Shim J, Choi SL, Lee N, Lee CH, Bailey CH, Kandel ER, Jang DJ, Kaang BK (2012) Learning-related synaptic growth mediated by internalization of Aplysia cell adhesion molecule is controlled by membrane phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate synthetic pathway. J Neurosci 32:16296–16305
Frank S, Upender S, Hansen SH, Casanova JE (1998) ARNO is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for ADP-ribosylation factor 6. J Biol Chem 273:23–27
Venkateswarlu K, Oatey PB, Tavare JM, Cullen PJ (1998) Insulin-dependent translocation of ARNO to the plasma membrane of adipocytes requires phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Curr Biol 8:463–466
Santy LC, Casanova JE (2001) Activation of ARF6 by ARNO stimulates epithelial cell migration through downstream activation of both Rac1 and phospholipase D. J Cell Biol 154:599–610
Lee YS (2014) Genes and signaling pathways involved in memory enhancement in mutant mice. Mol Brain 7:43
Choi JH, Park P, Baek GC, Sim SE, Kang S, Lee Y, Ahn SH, Lim CS, Lee YS, Collingridge GL, Kaang BK (2014) Effects of PI3K inverted question mark overexpression in the hippocampus on synaptic plasticity and spatial learning. Mol Brain 7:78
Huh M, Han JH, Lim CS, Lee SH, Kim S, Kim E, Kaang BK (2003) Regulation of neuritogenesis and synaptic transmission by msec7-1, a guanine nucleotide exchange factor, in cultured Aplysia neurons. J Neurochem 85:282–285
Raucher D, Stauffer T, Chen W, Shen K, Guo S, York JD, Sheetz MP, Meyer T (2000) Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate functions as a second messenger that regulates cytoskeleton-plasma membrane adhesion. Cell 100:221–228
Balla A, Kim YJ, Varnai P, Szentpetery Z, Knight Z, Shokat KM, Balla T (2008) Maintenance of hormone-sensitive phosphoinositide pools in the plasma membrane requires phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase IIIalpha. Mol Biol Cell 19:711–721
Lee JA, Kim HK, Kim KH, Han JH, Lee YS, Lim CS, Chang DJ, Kubo T, Kaang BK (2001) Overexpression of and RNA interference with the CCAAT enhancer-binding protein on long-term facilitation of Aplysia sensory to motor synapses. Learn Mem 8:220–226
Kaang BK (1996) Parameters influencing ectopic gene expression in Aplysia neurons. Neurosci Lett 221:29–32
Roy A, Levine TP (2004) Multiple pools of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate detected using the pleckstrin homology domain of Osh2p. J Biol Chem 279:44683–44689
Yeung T, Gilbert GE, Shi J, Silvius J, Kapus A, Grinstein S (2008) Membrane phosphatidylserine regulates surface charge and protein localization. Science 319:210–213
Kim KH, Jun YW, Park Y, Lee JA, Suh BC, Lim CS, Lee YS, Kaang BK, Jang DJ (2014) Intracellular membrane association of the Aplysia cAMP phosphodiesterase long and short forms via different targeting mechanisms. J Biol Chem 289:25797–25811
Suh BC, Inoue T, Meyer T, Hille B (2006) Rapid chemically induced changes of PtdIns(4,5)P2 gate KCNQ ion channels. Science 314:1454–1457
Ferguson KM, Lemmon MA, Schlessinger J, Sigler PB (1995) Structure of the high affinity complex of inositol trisphosphate with a phospholipase C pleckstrin homology domain. Cell 83:1037–1046
Klarlund JK, Tsiaras W, Holik JJ, Chawla A, Czech MP (2000) Distinct polyphosphoinositide binding selectivities for pleckstrin homology domains of GRP1-like proteins based on diglycine versus triglycine motifs. J Biol Chem 275:32816–32821
Ogasawara M, Kim SC, Adamik R, Togawa A, Ferrans VJ, Takeda K, Kirby M, Moss J, Vaughan M (2000) Similarities in function and gene structure of cytohesin-4 and cytohesin-1, guanine nucleotide-exchange proteins for ADP-ribosylation factors. J Biol Chem 275:3221–3230
Suh BC, Hille B (2008) PIP2 is a necessary cofactor for ion channel function: how and why? Annu Rev Biophys 37:175–195
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Basic Science Research Program through NRF (2014-R1A1A2012804) funded by the Ministry of Education (D.-J. J), Science and Technology, and by the National Honor Scientist Program of Korea (D.-J. J & B.-K. K). S.K and I.C are supported by the MIREBraiN program of DGIST and the National Creative Research Initiatives (Center for Proteome Biophysics) of National Research Foundation, Korea (No. 2008-0061984).
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Jun, YW., Kim, S., Kim, KH. et al. Analysis of Phosphoinositide-Binding Properties and Subcellular Localization of GFP-Fusion Proteins. Lipids 50, 427–436 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-015-3994-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-015-3994-z