Abstract
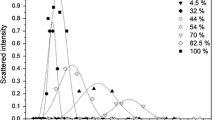
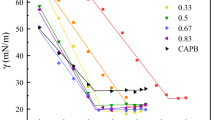
A series of surfactants derived from l-Proline, the free amine esters, the ester hydrochlorides and the quaternary ammonium compounds with varying chain lengths (C8–C14) were synthesised. The physicochemical and biological properties were determined in both single and sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS) mixed systems with a view of enhancing the properties of the individual surfactants as potential ingredients in detergent formulations. The mode of action of the proline surfactants were investigated by their ability to form mixed micelles with the phospholipid 1,2-dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphatidylcholine (DMPC). The presence of a quaternary ammonium moiety and an increase in alkyl chain length were found to enhance the antibacterial activity of the proline QUAT derivatives. The SDS-C14 QUAT mixed system displayed good antibacterial activity with optimum activity at mole fractions αQUAT: 0.4 and 0.6. The antibacterial activity of the mixed system was found to be governed by the monomers rather than the micelles. The SDS-C14 QUAT mixed system also showed moderate irritancy which makes them potential candidates as detergents.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scheibel JJ. The evolution of anionic surfactant technology to meet the requirements of the laundry detergent industry. J Surfact Deterg. 2004;7:319–28.
Yu Y, Zhao J, Andrew EB. Development of surfactants and builders in detergent formulations. Chin J Chem Eng. 2008;16:517–27.
Rakutani K, Onda Y, Inaoka T. Surfactants derived from secondary alcohols. In: Karsa DR, editor. Industrial applications of surfactants IV. Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry; 1999.
Johnson JR, Chirash W. Softener, bleach and anti-cling composition. US Pat 4203852 A. 1980.
Tamura T, Iihara T, Nishida S, Ohta S. Cleaning performance and foaming properties of lauroylamidopropylbetaine/non-ionic mixed systems. J Surfact Deterg. 1999;2:207–11.
Infante MR, Perez L, Pinazo A, Clapes P, Moran MC, Angelet M, Garcia MT, Vinardell MP. Amino acid-based surfactants. Comptes Rendues Chimi. 2004;250:583–92.
Holmberg K. Preparation, application and biodegradability, 2nd edition, surfactant science series. New York: Marcel Dekker; 2004.
Pinazo A, Pons R, Perez L, Infante MR. Amino acids as raw material for biocompatible surfactants. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2011;50:4805–17.
Chandra N, Tyagi VK. Synthesis, properties and applications of amino acid based surfactants: a review. J Dispers Sci Technol. 2013;34:800–8.
Moran MC, Pinazo A, Perez L, Clapes P, Angelet M, Garcia MT, Vinardell MP, Infante MR. Green amino acid-based surfactants. Green Chem. 2004;6:233–40.
Castillo JA, Pinazo A, Carilla J, Infante MR, Alsina MA, Haro I, Clapes. Interaction of antimicrobial arginine-based cationic surfactants with liposomes and lipid monolayers. Langmuir. 2004;20:3379–87.
Lukac M, Lacko I, Bukovsky M, Kyselova Z, Karlovsta J, Horvath B, Devinsky F. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of a series of optically active quaternary ammonium salts derived from phenylalanine. Cent Eur J Chem. 2010;8:194–201.
Perez L, Pinazo A, Garcia MT, Lozano M, Manresa A, Angelet M, Vinardell MP, Mitjans M, Pons R, Infante MR. Cationic surfactants from lysine: synthesis, micellization and biological evaluation. Eur J Med Chem. 2009;44:1884–92.
Joondan N, Jhaumeer-Laulloo S, Caumul P. A study of the antibacterial activity of l-Phenylalanine and l-Tyrosine esters in relation to their CMCs and their interactions with 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine, DPPC as model membrane. Microbiol Res. 2014;169:675–85.
Joondan N, Caumul P, Akerman M, Jhaumeer-Laulloo S. Synthesis, micellisation and interaction of novel quaternary ammonium compounds derived from l-Phenylalanine with 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine as model membrane in relation to their antibacterial activity, and their selectivity over human red blood cells. Bioorg Chem. 2015;58:117–29.
Faustino CMC, Calado ART, Garcia-Rio L. Mixed micelle formation between amino-acid based surfactants and phospholipids. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2011;329:493–8.
Ohta A, Toda K, Morimoto Y, Asakawa T, Miyagishi S. Effect of the side chain of N-acyl amino acid surfactants on micelle formation: an isothermal titration calorimetry study. Colloid Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp. 2008;317:316–22.
Jadhav V, Maiti S, Dasgupta A, Das PK, Dias RS, Miguel MG, Lindman B. Effect of head group geometry of amino acid based cationic surfactants on interaction with plasmid DNA. Biomacromolecules. 2008;9:1852–9.
Dasgupta A, Das PK, Dias RS, Miguel MG, Lindman B, Jadhav VM, Gnanamani M, Maiti S. Effect of headgroup on DNA-cationic surfactant interactions. J Phys Chem B. 2007;111:8502–8.
Bauer AW, Kirby WMM, Sherris JC, Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966;45:493–6.
Fait ME, Garrote GL, Clapes P, Tanco S, Lorenzo J, Morcelle SR. Biocatalytical synthesis, antimicrobial properties and toxicity studies of arginine derivative surfactants. Amino Acids. 2015;47:1465–77.
Li H, Yu C, Chen R, Li J, Li J. Novel inic liquid-type Gemini surfactants: synthesis, surface active property and antimicrobialo activity. Colloid Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp. 2012;395:116–24.
Yang Y, Yang X, Xue J, Curren R, Huang J, Tan X, Xie X, Xiong X, et al. Altex Proceedings, 1/12, Proceedings of WC8, 139–143
Holland PM, Rubingh DN. Mixed surfactant systems—an overview. ACS Symp Ser. 1992;501:2–30.
Ong CP, Ng CL, Lee HK, Li SFY. The use of mixed surfactants in micellar electrokinetic chromatography. Electrophoresis. 1994;15:1273–5.
Chen LG, Bermudez H. Charge screening between anionic and cationic surfactants in ionic liquids. Langmuir. 2013;29:2805–8.
Clint JH. Surfactant aggregation. New York: Chapman and Hall; 1992.
Bakshi MS, Sachar S, Mahajan N, Kaur I, Kaur G, Singh N, Sehgal P, Doe H. Mixed-micelle formation by strongly interacting surfactant binary mixtures: effect of head-group modification. Colloid Polym Sci. 2002;280:990–1000.
Silva BFB, Marques EF. Thermotropic behavior of asymmetric chain length catanionic surfactants: the influence of the polar head group. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2005;290:267–74.
Ghosh S, Ghatak C, Banerjee C, Mandal S, Kuchlyan J, Sarkar N. Spontaneous transition of micelle-vesicle-micelle in a mixture of cationic surfactants and anionic surfactant-like ionic liquid: a pure nonlipid small unilamellar vesicular template used for solvent and rotational relaxation study. Langmuir. 2013;29:10066–76.
Jing-Liang L, Bing-Hung C. Surfactant-mediated biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Materials. 2009;2:76–94.
Lozano N, Perez L, Pons R, Luque-Ortega JR, Fernandez-Reyes M, Rivas L, Pinazo A. Interaction studies of diacyl glycerol arginine-based surfactants with DPPC and DMPC monolayers, relation with antimicrobial activity. Colloid Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp. 2008;319:196–203.
Pape WJW, Hopper U. Standardization of an in vitro red blood cell test for evaluating the acute cytotoxic potential of tensides. Drug Res. 1990;4:498–502.
Acknowledgements
One of the authors is thankful to Tertiary Education Commission (TEC) of Mauritius for the grant of a scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Joondan, N., Caumul, P. & Jhaumeer-Laulloo, S. Investigation of the physicochemical and biological properties of proline-based surfactants in single and mixed surfactant systems. J Surfact Deterg 20, 103–115 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11743-016-1895-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11743-016-1895-7