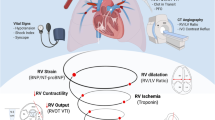
Abstract
Patients with acute symptomatic pulmonary embolism (PE) who present with arterial hypotension or shock have a high risk of death (high-risk PE), and treatment guidelines recommend strong consideration of thrombolysis in this setting. For normotensive patients diagnosed with PE, risk stratification should aim to differentiate the group of patients deemed as having a low risk for early complications (all-cause mortality, recurrent venous thromboembolism, and major bleeding) (low-risk PE) from the group of patients at higher risk for PE-related complications (intermediate-high risk PE), so low-risk patients could undergo consideration of early outpatient treatment of PE and intermediate-high risk patients would undergo close observation and consideration of thrombolysis. Clinicians should also use risk stratification and eligibility criteria to identify a third group of patients that should not undergo escalated or home therapy (intermediate-low risk PE). Such patients should initiate standard therapy of PE while in the hospital. Clinical models [e.g., Pulmonary Embolism Severity Index (PESI), simplified PESI (sPESI)] may accurately identify those at low risk of dying shortly after the diagnosis of PE. For identification of intermediate-high risk patients with acute PE, studies have validated predictive models that use a combination of clinical, laboratory and imaging variables.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
White RH (2003) The epidemiology of venous thromboembolism. Circulation 107:I4–I8
Kasper W, Konstantinides S, Geibel A, Olschewski M, Heinrich F, Grosser KD, Rauber K, Iversen S, Redecker M, Kienast J (1997) Management strategies and determinants of outcome in acute major pulmonary embolism: results of a multicenter registry. J Am Coll Cardiol 30:1165–1171
Kearon C, Akl EA, Comerota AJ, Prandoni P, Bounameaux H, Goldhaber SZ, Nelson ME, Wells PS, Gould MK, Dentali F, Crowther M, Kahn K (2012) Antithrombotic therapy for VTE disease antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of chest physicians. Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest 141:419S–494S
Konstantinides SV, Torbicki A, Agnelli G, Danchin N, Fitzmaurice D, Galiè N, Gibbs JS, Huisman MV, Humbert M, Kucher N, Lang I, Lankeit M, Lekakis J, Maack C, Mayer E, Meneveau N, Perrier A, Pruszczyk P, Rasmussen LH, Schindler TH, Svitil P, Vonk Noordegraaf A, Zamorano JL, Zompatori M, Force Task, Members. Authors (2014) ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism: the task force for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism of the European society of cardiology (ESC) endorsed by the European respiratory society (ERS). Eur Heart J 2014(35):3033–3073
Jaff MR, McMurtry MS, Archer SL, Cushman M, Goldenberg N, Goldhaber SZ, Jenkins JS, Kline JA, Michaels AD, Thistlethwaite P, Vedantham S, White RJ, Zierler BK, American Heart Association Council on Cardiopulmonary, Critical Care, Perioperative and Resuscitation; American Heart Association Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease; American Heart Association Council on Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology (2011) Management of massive and submassive pulmonary embolism, iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Circulation 123:1788–1830
Jiménez D, Aujesky D, Yusen RD (2010) Risk stratification of normotensive patients with acute pulmonary embolism. Br J Haematol 151:415–424
Sánchez D, De Miguel J, Sam A, Wagner C, Zamarro C, Nieto R, García L, Aujesky D, Yusen RD, Jiménez D (2011) The effects of cause of death classification on prognostic assessment of patients with pulmonary embolism. J Thromb Haemost 9:2201–2207
Moores L, Aujesky D, Jiménez D, Díaz G, Gómez V, Martí D, Briongos S, Yusen R (2010) Pulmonary Embolism Severity Index and troponin testing for the selection of low-risk patients with acute symptomatic pulmonary embolism. J Thromb Haemost 8:517–522
Lankeit M, Gómez V, Wagner C, Aujesky D, Recio M, Briongos S, Moores LK, Yusen RD, Konstantinides S, Jiménez D, Instituto Ramón y Cajal de Investigación Sanitaria Pulmonary Embolism Study Group (2012) A strategy combining imaging and laboratory biomarkers in comparison with a simplified clinical score for risk stratification of patients with acute pulmonary embolism. Chest 141:916–922
Jiménez D, Díaz G, Molina J, Martí D, Del Rey J, García-Rull S, Escobar C, Vidal R, Sueiro A, Yusen RD (2008) Troponin I and risk stratification of patients with acute nonmassive pulmonary embolism. Eur Respir J 31:847–853
Vanni S, Nazerian P, Pepe G, Baioni M, Risso M, Grifoni G, Viviani G, Grifoni S (2011) Comparison of two prognostic models for acute pulmonary embolism: clinical vs. right ventricular dysfunction-guided approach. J Thromb Haemost 9:1916–1923
Jiménez D, Lobo JL, Monreal M, Moores L, Oribe M, Barrón M, Otero R, Nauffal D, Rabuñal R, Valle R, Navarro C, Rodriguez-Matute C, Alvarez C, Conget F, Uresandi F, Aujesky DA, Yusen RD, PROTECT investigators (2014) Prognostic significance of multidetector CT in normotensive patients with pulmonary embolism: results of the protect study. Thorax 69:109–115
Aujesky D, Obrosky DS, Stone RA, Auble TE, Perrier A, Cornuz J, Roy PM, Fine MJ (2005) Derivation and validation of a prognostic model for pulmonary embolism. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 172:1041–1046
Aujesky D, Roy PM, Le Manach CP, Verschuren F, Meyer G, Obrosky DS, Stone RA, Cornuz J, Fine MJ (2006) Validation of a model to predict adverse outcomes in patients with pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J 27:476–481
Jiménez D, Yusen RD, Otero R, Uresandi F, Nauffal D, Laserna E, Conget F, Oribe M, Cabezudo MA, Díaz G (2007) Prognostic models for selecting patients with acute pulmonary embolism for initial outpatient therapy. Chest 132:24–30
Donzé J, Le Gal G, Fine MJ, Roy PM, Sanchez O, Verschuren F, Cornuz J, Meyer G, Perrier A, Righini M, Aujesky D (2008) Prospective validation of the pulmonary embolism severity index. A clinical prognostic model for pulmonary embolism. Thromb Haemost 100:943–948
Aujesky D, Roy PM, Verschuren F, Righini M, Osterwalder J, Egloff M, Renaud B, Verhamme P, Stone RA, Legall C, Sanchez O, Pugh NA, N’gako A, Cornuz J, Hugli O, Beer HJ, Perrier A, Fine MJ, Yealy DM (2011) Outpatient versus inpatient treatment for patients with acute pulmonary embolism: an international, open-label, randomised, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 378:41–48
Jiménez D, Aujesky D, Moores L, Gómez V, Lobo JL, Uresandi F, Otero R, Monreal M, Muriel A, Yusen RD, RIETE Investigators (2010) Simplification of the pulmonary embolism severity index for prognostication in patients with acute symptomatic pulmonary embolism. Arch Intern Med 170:1383–1389
Zondag W, Mos IC, Creemers-Schild D, Hoogerbrugge AD, Dekkers OM, Dolsma J, Eijsvogel M, Faber LM, Hofstee HM, Hovens MM, Jonkers GJ, van Kralingen KW, Kruip MJ, Vlasveld T, de Vreede MJ, Huisman MV; Hestia Study Investigators (2011) Outpatient treatment in patients with acute pulmonary embolism: the Hestia study. J Thromb Haemost 9:1500–1507
Kohn CG, Meanrs EL, Parker MW, Hernandez AW, Coleman CI (2014) Prognostic accuracy of clinical prediction rules for early post-pulmonary embolism all-cause mortality: a bivariate meta-analysis. Chest. doi:10.1378/chest.14-1888
Paiva LV, Providencia RC, Barra SN, Faustino AC, Botelho AM, Marques AL (2013) Cardiovascular risk assessment of pulmonary embolism with the GRACE risk score. Am J Cardiol 111:425–431
Aujesky D, Obrosky DS, Stone RA, Auble TE, Perrier A, Cornuz J, Roy PM, Fine MJ (2006) A prediction rule to identify low-risk patients with pulmonary embolism. Arch Intern Med 166:169–175
Jimenez D, Kopecna D, Tapson V, Briese B, Schreiber D, Lobo JL, Monreal M, Aujesky D, Sanchez O, Meyer G, Konstantinides S, Yusen RD, On Behalf Of The Protect Investigators (2014) Derivation and validation of multimarker prognostication for normotensive patients with acute symptomatic pulmonary embolism. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 189:718–726
Wood KE (2002) Major pulmonary embolism: review of a pathophysiologic approach to the golden hour of hemodynamically significant pulmonary embolism. Chest 121:877–905
Ribeiro A, Lindmarker P, Juhlin-Dannfelt A, Johnsson H, Jorfeldt L (1997) Echocardiography Doppler in pulmonary embolism: right ventricular dysfunction as a predictor of mortality rate. Am Heart J 134:479–487
Grifoni S, Olivotto I, Cecchini P, Pieralli F, Camaiti A, Santoro G, Conti A, Agnelli G, Berni G (2000) Short term clinical outcome of patients with pulmonary embolism, normal blood pressure and echocardiographic right ventricular dysfunction. Circulation 101:2817–2822
Lobo JL, Holley A, Tapson V, Moores L, Oribe M, Barron M, Otero R, Nauffal D, Valle R, Monreal M, Yusen RD (2014) Jimenez D; PROTECT and RIETE investigators. Prognostic significance of tricuspid annular displacement in normotensive patients with acute symptomatic pulmonary embolism. J Thromb Haemost 12:1020–1027
Sanchez O, Trinquart L, Colombet I, Durieux P, Huisman MV, Chatellier G, Meyer G (2008) Prognostic value of right ventricular dysfunction in patients with haemodynamically stable pulmonary embolism: a systematic review. Eur Heart J 29:1569–1577
Becattini C, Agnelli G, Vedovati MC, Pruszczyk P, Casazza F, Grifoni S, Salvi A, Bianchi M, Douma R, Konstantinides S, Lankeit M, Duranti M (2011) Multidetector computed tomography for acute pulmonary embolism: diagnosis and risk stratification in a single test. Eur Heart J 32:1657–1663
Schoepf UJ, Kucher N, Kipfmueller F, Quiroz R, Costello P, Goldhaber SZ (2004) Right ventricular enlargement on chest computed tomography: a predictor of early death in acute pulmonary embolism. Circulation 110:3276–3280
Trujillo J, den Exter P, Gómez V, Castillo H, Moreno C, van der Hulle T, Huisman M, Monreal M, Yusen RD, Jimenez D (2013) Computed tomography-assessed right ventricular dysfunction and risk stratification of patients with acute non-massive pulmonary embolism: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Thrombosis Haemost 11:1823–1832
Janata K, Holzer M, Laggner AN, Müllner M (2003) Cardiac troponin T in the severity assessment of patients with pulmonary embolism: cohort study. BMJ 326:312–313
Lankeit M, Friesen D, Aschoff J, Dellas C, Hasenfuß G, Katus H, Konstantinides S, Giannitsis E (2010) Highly sensitive troponin T assay in normotensive patients with acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J 31:1836–1844
Dellas C, Puls M, Lankeit M, Schafer K, Cuny M, Berner M, Hasenfuss G, Konstantinides S (2010) Elevated heart-type fatty acid-binding protein levels on admission predict an adverse outcome in normotensive patients with acute pulmonary embolism. J Am Coll Cardiol 55:2150–2157
Jiménez D, Uresandi F, Otero R, Lobo JL, Monreal M, Martí D, Zamora J, Muriel A, Aujesky D, Yusen RD (2009) Troponin-based risk stratification of patients with nonmassive pulmonary embolism: systematic review and metaanalysis. Chest 136:974–982
Jiménez D, Aujesky D, Díaz G, Monreal M, Otero R, Martí D, Marín E, Aracil E, Sueiro A, Yusen RD, RIETE Investigators (2010) Prognostic significance of deep vein thrombosis in patients presenting with acute symptomatic pulmonary embolism. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 181:983–991
Meinel FG, Nance JW, Schoepf UJ, Hoffmann VS, Thierfelder KM, Costello P, Goldhaber SZ, Bamberg F (2015) Predictive value of computed tomography in acute pulmonary embolism: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Med 128:747–759
Jiménez D, Aujesky D, Moores L, Gómez V, Martí D, Briongos S, Monreal M, Barrios V, Konstantinides S, Yusen RD (2011) Combinations of prognostic tools for identification of high-risk normotensive patients with acute symptomatic pulmonary embolism. Thorax 66:75–81
Binder L, Pieske B, Olschewski M, Geibel A, Klostermann B, Reiner C, Konstantinides S (2005) N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide or troponin testing followed by echocardiography for risk stratification of acute pulmonary embolism. Circulation 112:1573–1579
Scridon T, Scridon C, Skali H, Alvarez A, Goldhaber SZ, Solomon SD (2005) Prognostic significance of troponin elevation and right ventricular enlargement in acute pulmonary embolism. Am J Cardiol 96:303–305
Sanchez O, Trinquart L, Planquette B, Couturaud F, Verschuren F, Caille V, Meneveau N, Pacouret G, Roy PM, Righini M, Perrier A, Bertoletti L, Parent F, Lorut C, Meyer G (2013) Echocardiography and pulmonary embolism severity index have independent prognostic roles in pulmonary embolism. Eur Respir J 42:681–688
Sanchez O, Trinquart L, Caille V, Couturaud F, Pacouret G, Meneveau N, Verschuren F, Roy PM, Parent F, Righini M, Perrier A, Lorut C, Tardy B, Benoit MO, Chatellier G, Meyer G (2010) Prognostic factors for pulmonary embolism: the PREP study, a prospective multicenter cohort study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 181:168–173
Bova C, Sanchez O, Prandoni P, Lankeit M, Konstantinides S, Vanni S, Jimenez D (2014) Identification of intermediate-risk patients with acute symptomatic pulmonary embolism: analysis of individual participants’ data from six studies. Eur Respir J 44:694–703
Fernandez C, Bova C, Sanchez O, Prandoni P, Lankeit M, Konstantinides S, Vanni S, Fernandez-Golfin C, Yusen RD, Jimenez D (2015) Validation of a model for identification of patients at intermediate to high risk for complications associated with acute symptomatic pulmonary embolism. Chest. doi:10.1378/chest.14-2551
Meyer G, Vicaut E, Danays T, Agnelli G, Becattini C, Beyer-Westendorf J, Bluhmki E, Bouvaist H, Brenner B, Couturaud F, Dellas C, Empen K, Franca A, Galiè N, Geibel A, Goldhaber SZ, Jimenez D, Kozak M, Kupatt C, Kucher N, Lang IM, Lankeit M, Meneveau N, Pacouret G, Palazzini M, Petris A, Pruszczyk P, Rugolotto M, Salvi A, Schellong S, Sebbane M, Sobkowicz B, Stefanovic BS, Thiele H, Torbicki A, Verschuren F, Konstantinides SV, PEITHO Investigators (2014) Fibrinolysis for patients with intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med 370:1402–1411
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement of human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiménez, D., Lobo, J.L., Barrios, D. et al. Risk stratification of patients with acute symptomatic pulmonary embolism. Intern Emerg Med 11, 11–18 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-015-1388-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-015-1388-0