Abstract
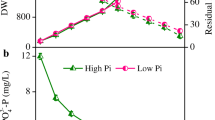
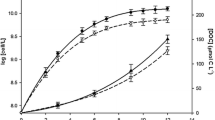
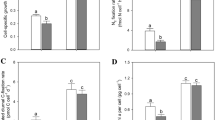
Iron (Fe) is a key element for all living systems, especially for photosynthetic organisms because of its important role in the photosynthetic electron transport chain. Fe limitation in cyanobacteria leads to several physiological and morphological changes. However, the overall metabolic responses to Fe limitation are still poorly understood. In this study, we integrated elemental, stoichiometric, macromolecular, and metabolomic data to shed light on the responses of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803, a non-N2-fixing freshwater cyanobacterium, to Fe limitation. Compared to Synechocystis growing at nutrient replete conditions, Fe-limited cultures had lower growth rates and amounts of chlorophyll a, RNA, RNA:DNA, C, N, and P, and higher ratios of protein:RNA, C:N, C:P, and N:P, in accordance with the growth rate hypothesis which predicts faster growing organisms will have decreased biomass RNA contents and C:P and N:P ratios. Fe-limited Synechocystis had lower amounts Fe, Mn, and Mo, and higher amount of Cu. Several changes in amino acids of cultures growing under Fe limitation suggest nitrogen limitation. In addition, we found substantial increases in stress-related metabolites in Fe-limited cyanobacteria such antioxidants. This study represents an advance in understanding the stoichiometric, macromolecular, and metabolic strategies that cyanobacteria use to cope with Fe limitation. This information, moreover, may further understanding of changes in cyanobacterial functions under scenarios of Fe limitation in aquatic ecosystems.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen MM (1968) Simple conditions for growth of unicellular blue-green algae on plates. J Phycol 4:1–4
Baniulis D, Yamashita E, Zhang H, Hasan SS, Cramer WA (2008) Structure–function of the cytochrome b 6 f complex. Photochem Photobiol 84:1349–1358
Behrenfeld MJ (1999) Widespread iron limitation of phytoplankton in the south Pacific Ocean. Science 283:840–843
Behrenfeld MJ, Milligan AJ (2013) Photophysiological expressions of iron stress in phytoplankton. Annu Rev Mar Sci 5:217–246
Behrenfeld M, Bale A, Kolber Z et al (1996) Confirmation of iron limitation of phytoplankton photosynthesis in the equatorial Pacific-Ocean. Nature 383:508–511
Bellenger J-P, Wichard T, Xu Y, Kraepiel AML (2011) Essential metals for nitrogen fixation in a free-living N2-fixing bacterium: chelation, homeostasis and high use efficiency. Environ Microbiol 13:1395–1411
Bennette NB, Eng JF, Dismukes GC (2011) An LC–MS-based chemical and analytical method for targeted metabolite quantification in the model cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002. Anal Chem 83:3808–3816
Bibby TS, Nield J, Barber J (2001) Iron deficiency induces the formation of an antenna ring around trimeric photosystem I in cyanobacteria. Nature 412:743–745
Bowman WD, Cleveland CC, Halada Ĺ et al (2008) Negative impact of nitrogen deposition on soil buffering capacity. Nat Geosci 1:767–770
Castielli O, De la Cerda B, Navarro JA et al (2009) Proteomic analyses of the response of cyanobacteria to different stress conditions. FEBS Lett 583:1753–1758
Cooley JW, Vermaas WF (2001) Succinate dehydrogenase and other respiratory pathways in thylakoid membranes of Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803: capacity comparisons and physiological function. J Bacteriol 183:4251–4258
da Silva JJRF, Williams RJP (2001) The biological chemistry of the elements: the inorganic chemistry of life. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 1–583. ISBN: 0198508484
Dang TC, Fujii M, Rose AL et al (2012) Characteristics of the freshwater cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa grown in iron-limited continuous culture. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:1574–1583
Dejean S, Gonzalez I, Le Cao K (2013) mixOmics: Omics Data Integration Project. R package version 5.0-1. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=mixOmics
DeLong EF, Karl DM (2005) Genomic perspectives in microbial oceanography. Nature 437:336–342
Elser JJ, Dobberfuhl DR, MacKay NA, Schampel JH (1996) Organism size, life history, and N:P stoichiometry. Bioscience 46:674–684
Elser JJ, Sterner RW, Gorokhova E et al (2008) Biological stoichiometry from genes to ecosystems. Ecol Lett 3:540–550
Farkas E, Csóka H, Micera G, Dessi A (1997) Copper(II), nickel(II), zinc(II), and molybdenum(VI) complexes of desferrioxamine B in aqueous solution. J Inorg Biochem 65:281–286
Ferreira F, Straus NA (1994) Iron deprivation in cyanobacteria. J Appl Phycol 6:199–210
Fiehn O (2002) Metabolomics - the link between genotypes and phenotypes. Plant Mol Biol 48:155–171
Flores E, Frías JE, Rubio LM, Herrero A (2005) Photosynthetic nitrate assimilation in cyanobacteria. Photosynth Res 83:117–133
Fox J, Weisberg S (2011) An R companion to applied regression. R package, 2nd edn. Sage, Thousand Oaks CA. http://socserv.socsci.mcmaster.ca/jfox/Books/Companion
Gargallo-Garriga A, Sardans J, Pérez-Trujillo M et al (2014) Opposite metabolic responses of shoots and roots to drought. Sci Rep 4:6829
Gargallo-Garriga A, Sardans J, Pérez-Trujillo M et al (2015) Warming differentially influences the effects of drought on stoichiometry and metabolomics in shoots and roots. New Phytol 207:591–603
Gründel M, Scheunemann R, Lockau W, Zilliges Y (2012) Impaired glycogen synthesis causes metabolic overflow reactions and affects stress responses in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Microbiology 158:3032–3043
Hagemann M (2011) Molecular biology of cyanobacterial salt acclimation. FEMS Microbiol Rev 35:87–123
Hasunuma T, Kikuyama F, Matsuda M et al (2013) Dynamic metabolic profiling of cyanobacterial glycogen biosynthesis under conditions of nitrate depletion. J Exp Bot 64:2943–2954
Hernández-Prieto MA, Schön V, Georg J et al (2012) Iron deprivation in Synechocystis: inference of pathways, non-coding RNAs, and regulatory elements from comprehensive expression profiling. G3 (Bethesda) 2:1475–1495
Houshyani B, Kabouw P, Muth D et al (2012) Characterization of the natural variation in Arabidopsis thaliana metabolome by the analysis of metabolic distance. Metabolomics 8:131–145
Huege J, Goetze J, Schwarz D et al (2011) Modulation of the major paths of carbon in photorespiratory mutants of synechocystis. PLoS One 6:e16278
Jones OAH, Maguire ML, Griffin JL et al (2013) Metabolomics and its use in ecology. Austral Ecol 38:713–720
Kaneko T, Sato S, Kotani H et al (1996) Sequence analysis of the genome of the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC6803. II. Sequence determination of the entire genome and assignment of potential protein-coding regions. DNA Res 3:109–136
Katoh H, Hagino N, Grossman AR, Ogawa T (2001a) Genes essential to iron transport in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803. J Bacteriol 183:2779–2784
Katoh H, Hagino N, Ogawa T (2001b) Iron-binding activity of FutA1 subunit of an ABC-type iron transporter in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803. Plant Cell Physiol 42:823–827
Kellom M, Poret-Peterson AT, Rivas-Ubach A et al (2018) Transcriptomics of iron limitation without growth media chelation in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 (Submitted)
Keren N, Aurora R, Pakrasi HB (2004) Critical roles of bacterioferritins in iron storage and proliferation of cyanobacteria. Plant Physiol 135:1666–1673
Knoop H, Gründel M, Zilliges Y et al (2013) Flux balance analysis of cyanobacterial metabolism: the metabolic network of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. PLoS Comput Biol 9:e1003081
Kopf M, Klähn S, Scholz I et al (2014) Comparative analysis of the primary transcriptome of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. DNA Res 21:527–539
Kranzler C, Lis H, Finkel OM et al (2014) Coordinated transporter activity shapes high-affinity iron acquisition in cyanobacteria. ISME J 8:409–417
Krieg N, Parte A, Ludwig W et al (2010) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 4. The Bacteroidetes, Spirochaetes, Tenericutes (Mollicutes), Acidobacteria, Fibrobacteres, Fusobacteria, Dictyoglomi, Gemmatimonadetes, Lentisphaerae, Verrucomicrobia, Chlamydiae, and Planctomycetes. Springer, New York
Latifi A, Ruiz M, Zhang C-C (2009) Oxidative stress in cyanobacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 33:258–278
Lee DY, Fiehn O (2013) Metabolomic response of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii to the inhibition of target of rapamycin (TOR) by rapamycin. J Microbiol Biotechnol 23:923–931
Leiss KA, Cristofori G, van Steenis R et al (2013) An eco-metabolomic study of host plant resistance to Western flower thrips in cultivated, biofortified and wild carrots. Phytochemistry 93:63–70
Lengeler J, Drews G, Schlegel H (1999) Biology of the prokaryotes. Wiley-Blackwell, Hoboken, pp 1–984
Macel M, Van Dam NM, Keurentjes JJB (2010) Metabolomics: the chemistry between ecology and genetics. Mol Ecol Resour 10:583–593
Mackey KRM, Post AF, McIlvin MR et al (2015) Divergent responses of Atlantic coastal and oceanic Synechococcus to iron limitation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:9944–9949
Maeda H, Sakuragi Y, Bryant DA, Dellapenna D (2005) Tocopherols protect Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 from lipid peroxidation. Plant Physiol 138:1422–1435
Mari A, Lyon D, Fragner L et al (2013) Phytochemical composition of Potentilla anserina L. analyzed by an integrative GC–MS and LC–MS metabolomics platform. Metabolomics 9:599–607
Ogawa T, Bao DH, Katoh H et al (2002) A two-component signal transduction pathway regulates manganese homeostasis in Synechocystis 6803, a photosynthetic organism. J Biol Chem 277:28981–28986
Oksanen J, Guillaume-Blanchet F, Kindt R et al (2013) vegan: community ecology package. R package version 2.0-9. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan
Orr JC, Fabry VJ, Aumont O et al (2005) Anthropogenic ocean acidification over the twenty-first century and its impact on calcifying organisms. Nature 437:681–686
Osanai T, Oikawa A, Shirai T et al (2014) Capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry reveals the distribution of carbon metabolites during nitrogen starvation in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Environ Microbiol 16:512–524
Papageorgiou GC, Murata N (1995) The unusually strong stabilizing effects of glycine betaine on the structure and function of the oxygen-evolving Photosystem II complex. Photosynth Res 44:243–252
Peñuelas J, Sardans J (2009) Ecological metabolomics. Chem Ecol 25:305–309
Pluskal T, Castillo S, Villar-Briones A, Orešič M (2010) MZmine 2: modular framework for processing, visualizing, and analyzing mass spectrometry-based molecular profile data. BMC Bioinform 11:395
R Core Team (2013) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R package
Raven JA, Evans MCW, Korb RE (1999) The role of trace metals in photosynthetic electron transport in O2-evolving organisms. Photosynth Res 60:111–150
Richardson DJ (2000) Bacterial respiration: a flexible process for a changing environment. Microbiology 146(Pt 3):551–571
Rivas-Ubach A, Sardans J, Pérez-Trujillo M et al (2012) Strong relationship between elemental stoichiometry and metabolome in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109:4181–4186
Rivas-Ubach A, Pérez-Trujillo M, Sardans J et al (2013) Ecometabolomics: optimized NMR-based method. Methods Ecol Evol 4:464–473
Rivas-Ubach A, Gargallo-Garriga A, Sardans J et al (2014) Drought enhances folivory by shifting foliar metabolomes in Quercus ilex trees. New Phytol 202:874–885
Rivas-Ubach A, Barbeta A, Sardans J et al (2016a) Topsoil depth substantially influences the responses to drought of the foliar metabolomes of Mediterranean forests. Perspect Plant Ecol Evol Syst 21:41–54
Rivas-Ubach A, Sardans J, Hódar JA et al (2016b) Similar local but different systemic metabolomic responses of closely related pine subspecies to folivory by caterpillars of the processionary moth. Plant Biol 18:484–494
Rivas-Ubach A, Hódar JA, Sardans J et al (2016c) Are the metabolic responses to folivory of closely related plant species linked to macroevolutionary and plant-folivore coevolutionary processes? Ecol Evol 6:4372–4386
Rivas-Ubach A, Sardans J, Hódar JA et al (2017) Close and distant: contrasting the metabolism of two closely related subspecies of Scots pine under the effects of folivory and summer drought. Ecol Evol. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.3343
Ryan-Keogh TJ, Macey AI, Cockshutt AM et al (2012) The cyanobacterial chlorophyll-binding-protein IsiA acts to increase the in vivo effective absorption cross-section of psi under iron limitation. J Phycol 48:145–154
Sharon S, Salomon E, Kranzler C et al (2014) The hierarchy of transition metal homeostasis: iron controls manganese accumulation in a unicellular cyanobacterium. Biochim Biophys Acta 1837:1990–1997
Shcolnick S, Keren N (2006) Metal homeostasis in cyanobacteria and chloroplasts. Balancing benefits and risks to the photosynthetic apparatus. Plant Physiol 141:805–810
Shcolnick S, Summerfield TC, Reytman L et al (2009) The mechanism of iron homeostasis in the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 and its relationship to oxidative stress. Plant Physiol 150:2045–2056
Shi D, Xu Y, Hopkinson BM, Morel FMM (2010) Effect of ocean acidification on iron availability to marine phytoplankton. Science 327:676–679
Shi D, Kranz SA, Kim J-M, Morel FMM (2012) Ocean acidification slows nitrogen fixation and growth in the dominant diazotroph Trichodesmium under low-iron conditions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:E3094–E3100
Singh AK, Chakravarthy D, Singh TPK, Singh HN (1996) Evidence for a role for l-proline as a salinity protectant in the cyanobacterium Nostoc muscorum. Plant Cell Environ 19:490–494
Singh AK, Li H, Sherman LA (2004) Microarray analysis and redox control of gene expression in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Physiol Plant 120:27–35
Sterner R, Elser J (2002) Ecological stoichiometry: the biology of elements from molecules to the biosphere. Princeton University Press, Princeton, pp 1–439. ISBN: 0691074909
Steuer R, Kurths J, Fiehn O, Weckwerth W (2003) Observing and interpreting correlations in metabolomic networks. Bioinformatics 19:1019–1026
Sumner LW, Amberg A, Barrett D et al (2007) Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis. Metabolomics 3:211–221
Szabados L, Savouré A (2010) Proline: a multifunctional amino acid. Trends Plant Sci 15:89–97
t’Kindt R, De Veylder L, Storme M et al (2008) LC–MS metabolic profiling of Arabidopsis thaliana plant leaves and cell cultures: optimization of pre-LC–MS procedure parameters. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 871:37–43
Tovar-Sanchez A, Sañudo-Wilhelmy SA, Garcia-Vargas M et al (2003) A trace metal clean reagent to remove surface-bound iron from marine phytoplankton. Mar Chem 82:91–99
Vitousek PM, Aber JD, Howarth RW et al (1997) Human alteration of the global nitrogen cycle: sources and cosequences. Ecol Appl 7:737–750
Vrede T, Tranvik LJ (2006) Iron constraints on planktonic primary production in oligotrophic lakes. Ecosystems 9:1094–1105
Wilson A, Boulay C, Wilde A et al (2007) Light-induced energy dissipation in iron-starved cyanobacteria: roles of OCP and IsiA proteins. Plant Cell 19:656–672
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Laia Mateu-Castell, Laura Steger, Zarraz Lee, Jessica Corman, Krist Rouypirom, Zureyma Martinez, Matthew Kellom, Wei Deng, and Jennifer Learned for their laboratory support. Thanks to Ravi Vannela for providing Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 and Wim Vermaas for the helpful discussion of the data. ARU appreciates the financial support of the research fellowship (JAE) from the CSIC. This research was supported by the Spanish Government Project CGL2013-48074-P and the Catalan Government Project SGR 2014-274, the European Research Council (Synergy Grant SyG-2013-610028, IMBALANCE-P), and the NASA Astrobiology Institute at Arizona State University (Follow the Elements; NAI5-0018). A portion of the research was performed using EMSL, a DOE Office of Science User Facility sponsored by the Office of Biological and Environmental Research at the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory. MO and OU were supported by the Ministry of Education, the National Sustainability Program I (NPU I), grants LO1415 and LM2015061, and by CzeCOS ProCES project num. CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/16_013/0001609. ATPP and JJE were supported by the ASU NASA Astrobiology Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by R. Baczek-Kwinta.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rivas-Ubach, A., Poret-Peterson, A.T., Peñuelas, J. et al. Coping with iron limitation: a metabolomic study of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Acta Physiol Plant 40, 28 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-018-2603-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-018-2603-1