Abstract
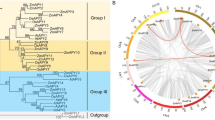
The GRAS gene family performs a variety of functions in plant growth and development processes, and they also play essential roles in plant response to environmental stresses. Medicago truncatula is a diploid plant with a small genome used as a model organism. Despite the vital role of GRAS genes in plant growth regulation, few studies on these genes in M. truncatula have been conducted to date. Using the M. truncatula reference genome data, we identified 68 MtGRAS genes, which were classified into 16 groups by phylogenetic analysis, located on eight chromosomes. The structure analysis indicated that MtGRAS genes retained a relatively constant exon–intron composition during the evolution of the M. truncatula genome. Most of the closely related members in the phylogenetic tree had similar motif compositions. Different motifs distributed in different groups of the MtGRAS genes were the sources of their functional divergence. Twenty-eight MtGRAS genes were expressed in six tissues, namely root, bud, blade, seedpod, nodule, and flower tissues, suggesting their putative function in many aspects of plant growth and development. Nine MtGRAS genes were upregulated under cold, freezing, drought, ABA, and salt stress treatments, indicating that they play vital roles in the response to abiotic stress in M. truncatula. Our study provides valuable information that can be utilized to improve the quality and agronomic benefits of M. truncatula and other plants.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GA:
-
Gibberellic acid
- GAI:
-
Gibberellic acid insensitive
- HAM:
-
Hairy meristem
- Ls:
-
Lateral suppressor
- NSP1:
-
Nodulation signaling pathway 1
- NSP2:
-
Nodulation signaling pathway 2
- PAT:
-
Phytochrome A signal transduction
- RGA:
-
Repressor of GAI
- SCR:
-
Scarecrow
- SCL:
-
Scarecrow-like
- SHR:
-
Short root
- TF:
-
Transcription factor
References
Bailey TL, Elkan C (1994) Fitting a mixture model by expectation maximization to discover motifs in biopolymers. In: International conference on intelligent systems for molecular biology, pp 28–36
Bailey TL, Johnson J, Grant CE, Noble WS (2015) The MEME suite. Nucl Acids Res 43(1):39–49. doi:10.1093/nar/gkv416
Bolle C (2004) The role of GRAS proteins in plant signal transduction and development. Planta 218(5):683–692. doi:10.1007/s00425-004-1203-z
Bolle C, Koncz C, Chua NH (2000) PAT I, a new member of the GRAS family, is involved in phytochrome A signal transduction, Genes Dev 14, 1269-1278. Genes Dev 14(10):1269–1278. doi:10.1101/gad.14.10.1269Genes&Dev.2000
Cannon SB, Mitra A, Baumgarten A, Young ND, May G (2004) The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol 4(1):10–30. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-4-10
Chen K, Li H, Chen Y, Qi Z, Li B, Li Z (2015) TaSCL14, a Novel Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) GRAS gene, regulates plant growth, photosynthesis, tolerance to photooxidative stress, and senescence. J Genet Genom 42(1):21–32. doi:10.1016/j.jgg.2014.11.002
Fambrini M, Mariotti L, Parlanti S, Salvini M, Pugliesi C (2015) A GRAS-like gene of sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) alters the gibberellin content and the axillary meristem outgrowth in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Plant Biol 17(6):1123–1134. doi:10.1111/plb.12358
Fiorilli V, Volpe V, Zanini S, Vallino M, Abbà S, Bonfante P (2015) A rice GRAS gene has an impact on the success of arbuscular mycorrhizal colonization. Am J Plant Sci 6(12):1905–1915. doi:10.4236/ajps.2015.612191
Galovic V, Orlovic S, Fladung M (2015) Characterization of two poplar homologs of the GRAS/SCL gene, which encodes a transcription factor putatively associated with salt tolerance. iForest Biogeosci For 8(6):780–786. doi:10.3832/ifor1330-008
Gao MJ, Parkin I, Lydiate D, Hannoufa A (2004) An auxin-responsive SCARECROW-like transcriptional activator interacts with histone deacetylase. Plant Mol Biol 55(3):417–431. doi:10.1007/s11103-004-0892-9
Goodstein DM, Shu S, Howson R, Neupane R, Hayes RD, Fazo J, Mitros T, Dirks W, Hellsten U, Putnam N (2012) Phytozome: a comparative platform for green plant genomics. Nucl Acids Res 40:1178–1186. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr944
Grimplet J, Agudelo-Romero P, Teixeira RT, Martinez-Zapater JM, Fortes AM (2016) Structural and functional analysis of the GRAS gene family in grapevine indicates a role of GRAS proteins in the control of development and stress responses. Front Plant Sci 7:353–374. doi:10.3389/fpls.2016.00353
Heckmann AB, Lombardo F, Miwa H, Perry JA, Bunnewell S, Parniske M, Wang TL, Downie JA (2006) Lotus japonicus nodulation requires two GRAS domain regulators, one of which is functionally conserved in a non-legume. Plant Physiol 142(4):1739–1750. doi:10.1104/pp.106.089508
Hirsch S, Oldroyd GE (2009) GRAS-domain transcription factors that regulate plant development. Plant Signal Behav 4(8):698–700. doi:10.4161/psb.4.8.9176
Hirsch S, Kim J, Muñoz A, Heckmann AB, Downie JA, Oldroyd GED (2009) GRAS proteins form a DNA binding complex to induce gene expression during nodulation signaling in Medicago truncatula. Plant Cell 21(21):545–557. doi:10.1105/tpc.108.064501
Hu B, Jin J, Guo AY, Zhang H, Luo J, Gao G (2015) GSDS 2.0: an upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 31(8):1296–1297. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btu817
Huang W, Xian Z, Xia K, Tang N, Li Z (2015) Genome-wide identification, phylogeny and expression analysis of GRAS gene family in tomato. BMC Plant Biol 15(1):209–226. doi:10.1186/s12870-015-0590-6
Johnson LS, Eddy SR, Portugaly E (2010) Hidden Markov model speed heuristic and iterative HMM search procedure. BMC Bioinf 11:431–438. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-11-431
Kaló P, Gleason C, Edwards A, Marsh J, Mitra RM, Hirsch S, Jakab J, Sims S, Long SR, Rogers J (2005) Nodulation signaling in legumes requires NSP2, a member of the GRAS family of transcriptional regulators. Science 308(5729):1786–1789. doi:10.1126/science.110951
Krzywinski M, Schein J, Birol İ, Connors J, Gascoyne R, Horsman D, Jones SJ, Marra MA (2009) Circos: an information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res 19(9):1639–1645. doi:10.1101/gr.092759.109
Lee MH, Kim B, Song SK, Heo JO, Yu NI, Lee SA, Kim M, Dong GK, Sohn SO, Lim CE (2008) Large-scale analysis of the GRAS gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 67(6):659–670. doi:10.1007/s11103-008-9345-1
Letunic I, Doerks T, Bork P (2012) SMART 7: recent updates to the protein domain annotation resource. Nucl Acids Res 40:302–305. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr931
Li J, Yu C, Hua W, Luo Z, Bo O, Long C, Zhang J, Ye Z (2015) Knockdown of a JmjC domain-containing gene JMJ524 confers altered gibberellin responses by transcriptional regulation of GRAS protein lacking the DELLA domain genes in tomato. J Exp Bot 66(5):1413–1426. doi:10.1093/jxb/eru493
Li W, Xu H, Liu Y, Song L, Guo C, Shu Y (2016) Bioinformatics analysis of MAPKKK family genes in Medicago truncatula. Genes 7(4):13–29. doi:10.3390/genes7040013
Liu X, Widmer A (2014) Genome-wide comparative analysis of the GRAS gene family in populus, Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Mol Biol Rep 32(6):1129–1145. doi:10.1007/s11105-014-0721-5
Liu Y, Zhang J, Li W, Guo C, Shu Y (2015) In silico identification, phylogeny and expression analysis of expansin superfamily in Medicago truncatula. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 1:1–7. doi:10.1080/13102818.2015.1093919
López M, Herrera-Cervera JA, Iribarne C, Tejera NA, Lluch C (2008) Growth and nitrogen fixation in Lotus japonicus and Medicago truncatula under NaCl stress: nodule carbon metabolism. J Plant Physiol 165(6):641–650. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2007.05.009
Lu J, Wang T, Xu Z, Sun L, Zhang Q (2015) Genome-wide analysis of the GRAS gene family in Prunus mume. Mol Genet Genom 290(1):303–317. doi:10.1007/s00438-014-0918-1
Ma HS (2010) The salt- and drought-inducible poplar GRAS protein SCL7 confers salt and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 61(14):4011–4019. doi:10.1093/jxb/erq217
Mayrose M, Ekengren SK, Melech-Bonfil S, Martin GB, Sessa G (2006) A novel link between tomato GRAS genes, plant disease resistance and mechanical stress response. Mol Plant Pathol 7(6):593–604. doi:10.1111/j.1364-3703.2006.00364.x
Mbe ESK, Fotsin HB, Kengne J, Woafo P (2014) A nuclear factor Y interacting protein of the GRAS family is required for nodule organogenesis, infection thread progression, and lateral root growth. Plant Physiol 164(3):1430–1442. doi:10.1104/pp.113.230896
Morohashi K, Minami M, Takase H, Hotta Y, Hiratsuka K (2003) Isolation and characterization of a novel GRAS gene that regulates meiosis-associated gene expression. J Biol Chem 278(23):20865–20873. doi:10.1074/jbc.M301712200
Navarro L, Bari R, Achard P, Lisón P, Nemri A, Harberd NP, Jones JD (2008) DELLAs control plant immune responses by modulating the balance of jasmonic acid and salicylic acid signaling. Curr Biol 18(9):650–655. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2008.03.060
Punta M, Coggill PC, Eberhardt RY, Mistry J, Tate J, Boursnell C, Pang N, Forslund K, Ceric G, Clements J, Heger A, Holm L, Sonnhammer Erik L L, Eddy SR, Bateman A, Finn RD (2012) The Pfam protein families database. Nucl Acids Res 40:290–301. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr1065
Schumacher K, Theres K (1999) The Lateral suppressor (Ls) gene of tomato encodes a new member of the VHIID protein family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(1):290–295
Shen C, Yue R, Sun T, Zhang L, Xu L, Tie S, Wang H, Yang Y (2015) Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of auxin response factor gene family in Medicago truncatula. Front Plant Sci 6(11):73–84. doi:10.3389/fpls.2015.00073
Shu Y, Liu Y, Zhang J, Song L, Guo C (2016) Genome-wide analysis of the AP2/ERF superfamily genes and their responses to abiotic stress in Medicago truncatula. Front Plant Sci 6(676):1247–1263. doi:10.3389/fpls.2015.01247
Song XM, Liu TK, Duan WK, Ma QH, Ren J, Wang Z, Li Y, Hou XL (2014) Genome-wide analysis of the GRAS gene family in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis). Genomics 103(1):135–146. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2013.12.004
Song L, Jiang L, Chen Y, Shu Y, Bai Y, Guo C (2016) Deep-sequencing transcriptome analysis of field-grown Medicago sativa L. crown buds acclimated to freezing stress. Funct Integr Genom 16(5):495–511. doi:10.1007/s10142-016-0500-5
Sun X, Xue B, Jones WT, Rikkerink E, Dunker AK, Uversky VN (2011) A functionally required unfoldome from the plant kingdom: intrinsically disordered N-terminal domains of GRAS proteins are involved in molecular recognition during plant development. Plant Mol Biol 77(3):205–223. doi:10.1007/s11103-011-9803-z
Sun X, Jones WT, Rikkerink EH (2012) GRAS proteins: the versatile roles of intrinsically disordered proteins in plant signalling. Biochem J 442(1):1–12. doi:10.1042/BJ20111766
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28(10):2731–2739. doi:10.1093/molbev/msr121
Tian C, Ping W, Sun S, Li J, Chen M (2004) Genome-wide analysis of the GRAS gene family in rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 54(4):519–532. doi:10.1023/B:PLAN.0000038256.89809.57
Trapnell C, Pachter L, Salzberg SL (2009) TopHat: discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics 25(9):1105–1111. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp120
Trapnell C, Williams BA, Pertea G, Mortazavi A, Kwan G, Baren MJV, Salzberg SL, Wold BJ, Pachter L (2010) Transcript assembly and abundance estimation from RNA-Seq reveals thousands of new transcripts and switching among isoforms. Nat Biotechnol 28(5):511–515. doi:10.1038/nbt.1621
Untergasser A, Cutcutache I, Koressaar T, Ye J, Faircloth BC, Remm M, Rozen SG (2012) Primer3—new capabilities and interfaces. Nucl Acids Res 40(15):115–126. doi:10.1093/nar/gks596
Wei Y, Shi H, Xia Z, Tie W, Ding Z, Yan Y, Wang W, Hu W, Li K (2016) Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the WRKY gene family in cassava. Front Plant Sci 7:211–228. doi:10.3389/fpls.2016.00025
Wickham H (2009) ggplot2: elegant graphics for data analysis. Springer Publishing Company, Berlin
Xin S, Xie Z, Cheng Z, Wu W, Wang B, Fang J (2016) A characterization of grapevine of GRAS domain transcription factor gene family. Funct Integr Genom 97(4):541–548. doi:10.1007/s10142-016-0479-y
Xu K, Chen S, Li T, Ma X, Liang X, Ding X, Liu H, Luo L (2015) OsGRAS23, a rice GRAS transcription factor gene, is involved in drought stress response through regulating expression of stress-responsive genes. BMC Plant Biol 15(1):141. doi:10.1186/s12870-015-0532-3
Yuan Y, Fang L, Karungo SK, Zhang L, Gao Y, Li S, Xin H (2016) Overexpression of VaPAT1, a GRAS transcription factor from Vitis amurensis, confers abiotic stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep 35(3):655–666. doi:10.1007/s00299-015-1910-x
Zhang LL, Zhao MG, Tian QY, Zhang WH (2011) Comparative studies on tolerance of Medicago truncatula and Medicago falcata to freezing. Planta 234(3):445–457. doi:10.1007/s00425-011-1416-x
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the MOST 863 project (2013AA102607-5); Key Scientific and Technological Project of Heilongjiang Province of China (GA15B105-1); the Natural and Science Foundation of China (No. 31470571); the Graduate Innovation Fund of Harbin Normal University (HSDBSCX2014-04); the National Major Project for Cultivation of Transgenic Crops (#2011ZX08004-002-003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. Hajduch.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, L., Tao, L., Cui, H. et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the GRAS family proteins in Medicago truncatula . Acta Physiol Plant 39, 93 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-017-2393-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-017-2393-x