Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the efficacy and safety of Tuina (Chinese therapeutic massage) in the treatment of functional dyspepsia (FD) in children and adults.
Methods
Related articles in PubMed, Excerpta Medica Database (EMBASE), Cochrane Library, Web of Science, China Biology Medicine Disc (CBM), Wanfang Academic Journal Full-text Database (Wanfang), China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), and Chongqing VIP Database (CQVIP) were collected. The retrieval time was from each database’s start to March 2022. Two researchers independently screened the literature, extracted the data, and evaluated the risk of bias in the included studies. A meta-analysis was then performed using the RevMan 5.4 software.
Results
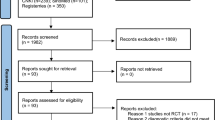
A total of 19 clinical trials were included, 9 of which encompassed studies on adults while 10 were on children with FD, comprising a total of 1 961 patients. The findings of the meta-analysis showed that the effective rate of FD in children and adults treated with Tuina was significantly higher than that in the control group [risk ratio (RR)=1.15, 95% confidence interval (CI) (1.09, 1.21), P<0.001], [RR=1.13, 95%CI (1.06, 1.21), P<0.001]. In addition, the effective rate of FD in children and adults treated with Tuina combined with other treatments was significantly higher than that in the control group [RR=1.14, 95%CI (1.07, 1.21), P<0.001], [RR=1.12, 95%CI (1.02, 1.24), P=0.02]. In terms of single symptoms, Tuina improved epigastric burning sensation score in adults [standardized mean difference (SMD)=-0.41; 95%CI (-0.79, -0.02); Z=2.08; P=0.04] compared with that of the Western medicine group. Compared with children treated with oral Chinese medications (CM) or Chinese patent medicine (CPM), children with FD demonstrated lower scores of epigastric pain [SMD=-0.38, 95%CI (-0.56, -0.19); Z=3.96; P<0.001], postprandial fullness [SMD=-0.30, 95%CI (-0.50, -0.10); Z=2.88; P=0.004], and early satiety [SMD=-0.26, 95%CI (-0.47, -0.06); Z=2.54; P=0.01] after receiving Tuina combined with CM or CPM treatment. No adverse events were reported in the Tuina treatment group, and the follow-up indicated that the symptom scores in the Tuina group improved.
Conclusion
Compared with the control group, both Tuina and Tuina combined with other treatments are shown to have better effective rates, lower incidence of adverse events, and better follow-up outcomes. The study results suggest that Tuina may be a clinically viable complementary therapy. However, due to limitations in the number and quality of the included studies, the above conclusions should be verified by further high-quality studies.
摘要
目的
评价推拿疗法治疗儿童和成人功能性消化不良(FD)的疗效和安全性.
方法
收集PubMed、 荷兰医学文摘(EMBASE)、 Cochrane Library、Web of Science、 中国生物医学文献数据库(CBM)、 万方学术期刊全文数据库(Wanfang)、 中国知网(CNKI)和重庆维普数据库(CQVIP)的相关文章. 检索时间截止到2022年3月. 两名研究人员独立筛选文献, 提取数据, 并评估偏倚风险. 使用RevMan 5.4软件进行meta分析.
结果
共纳入19项临床试验, 其中9项 为成人研究, 10项为儿童研究, 共纳入1 961例患者. 分析结果显示推拿治疗小儿和成人FD的有效率均显著高于对照组[风险比(RR)=1.15, 95%可信区间(CI) (1.09, 1.21), P<0.001], [RR=1.13, 95%CI (1.06,1.21), P<0.001]. 此外, 推拿联合其他疗法治疗小儿及成人FD的有效率均显著高于对照组[RR=1.14, 95%CI (1.07, 1.21), P<0.001], [RR=1.12, 95%CI (1.02, 1.24), P=0.02]. 与口服西药比较, 推拿可降低成人的上腹部烧灼感评分[标准均数差(SMD)=-0.41; 95%CI (-0.79, -0.02); Z=2.08; P=0.04]. 相较口服中药(CM)或中成药(CPM)治疗的FD患儿, 推拿联合CM或CPM治疗后, FD患儿胃脘痛评分降低[SMD=-0.38, 95%CI (-0.56, -0.19); Z=3.96; P<0.001], 餐后饱腹感不适[SMD=-0.30, 95%CI (-0.50, -0.10); Z=2.88; P=0.004], 早期饱腹症状[SMD=-0.26, 95%CI (-0.47, -0.06); Z=2.54; P=0.01]. 推拿治疗组无不良事件报告, 且随访显示推拿组症状评分得到改善.
结论
与对照组相比, 推拿治疗和推拿联合其他疗法均有更好的有效率、 更低的不良事件发生率和更好的随访结局. 对于成人, 与口服西药治疗相比, 推拿疗法可降低上腹部烧灼感评分. 对于FD患儿, 与单服CPM相比, 推拿联合CPM治疗可降低患儿上腹部疼痛、餐后饱胀不适感和早饱症状评分. 本研究结果提示推拿可能是一种临床可行的补充疗法. 但是由于所纳研究的数量和质量的限制, 上述结论需要更多高质量研究的补充验证.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data supporting this research article are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
DROSSMAN D A, HASLER W L. Rome IV-functional GI disorders: disorders of gut-brain interaction. Gastroenterology, 2016, 150(6): 1257–1261.
FORD A C, MARWAHA A, SOOD R, MOAYYEDI P. Global prevalence of, and risk factors for, uninvestigated dyspepsia: a meta-analysis. Gut, 2015, 64(7): 1049–1057.
FORD A C, MARWAHA A, LIM A, MOAYYEDI P. What is the prevalence of clinically significant endoscopic findings in subjects with dyspepsia? Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2010, 8(10): 830–837. e1-e2.
FORD A C, MAHADEVA S, CARBONE M F, LACY B E, TALLEY N J. Functional dyspepsia. Lancet, 2020, 396(10263): 1689–1702.
ROBIN S G, KELLER C, ZWIENER R, HYMAN P E, NURKO S, SAPS M, DI LORENZO C, SHULMAN R J, HYAMS J S, PALSSON O, VAN TIBURG M A L. Prevalence of pediatric functional gastrointestinal disorders utilizing the Rome IV criteria. J Pediatr, 2018, 195: 134–139
SUGANA K, TACK J, KUIPERS E J, GRAHAM D Y, ELOMAR E M, MIURA S, HARUMA K, ASAKA M, UEMURA N, MALFERTHEINER P. Kyoto global consensus report on Helicobacter pylori gastritis. Gut, 2015, 64(9): 1353–1367.
RODRÍGUEZ-GARCÍA J L, CARMONA-SÁNCHEZ R. Functional dyspepsia and dyspepsia associated with Helicobacter pylori infection: do they have different clinical characteristics?. Rev Gastroenterol Mex, 2016, 81(3): 126–133.
VAN OUDENHOVE L, CROWELL M D, DROSSMAN D A, HALPERT A D, KEEFER L, LACKNER J M, MURPHY T B, NALIBOFF B D, LEVY R L. Biopsychosocial aspects of functional gastrointestinal disorders. Gastroenterology, 2016, 150(6): 1355–1367. e2.
ARO P, TALLEY N J, JOHANSSON S E, AGREUS L, RONKAINEN J. Anxiety is linked to new-onset dyspepsia in the Swedish population: a 10-year follow-up study. Gastroenterology, 2015, 148(5): 928–937.
VAN OUDENHOVE L, AZIZ Q. The role of psychosocial factors and psychiatric disorders in functional dyspepsia. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2013, 10(3): 158–167.
CASSAR M P. Handbook of Clinical Massage: A Complete Guide for Student and Practitioners. 2nd Edition. New York: Churchill Livingstone, 2004.
MOYER C A, ROUNDS J, HANNUM J W. A metaanalysis of massage therapy research. Psychol Bull, 2004, 130(1): 3–18.
UYSAL N, EESR I, AKPINAR H. The effect of abdominal massage on gastric residual volume: a randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterol Nurs, 2012, 35(2): 117–123.
ZHU H, LI Y, WANG Y W, LIU C, PANG Y. Clinical effects of abdominal massage combined with fluid infusion in treatment of infantile diarrhea. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi, 2016, 24(7): 1124.
STEIN D J. Massage acupuncture, moxibustion, and other forms of complementary and alternative medicine in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol Clin North Am, 2017, 46(4): 875–880.
TURAN N, AŞT T A. The effect of abdominal massage on constipation and quality of life. Gastroenterol Nurs, 2016, 39(1): 48–59.
BIRIMOGLU OKUYAN C, BILGILI N. Effect of abdominal massage on constipation and quality of life in older adults: a randomized controlled trial. Complement Ther Med, 2019, 47: 102219.
TANG Y, TANG M W, LOU X X, CUI Y H, QIN S. Advances in TCM treatment of functional dyspepsia. Zhongyi Xuebao, 2020, 35(2): 299–303.
YOU Y, GAO J J, XIE M D, YANG H R, WANG Z, LI J, ZHOU Y F. Research progress of treating functional dyspepsia by massage. Zhongyi Yanjiu, 2021, 34(11): 60–64.
TALLEY N J, STANGHELLINI V, HEADING R C, KOCH K L, MALAGELADA J R, TYTGAT G N. Functional gastroduodenal disorders. Gut, 1999, 45(Suppl 2): ii37–ii42.
TACK J, TALLEY N J, CAMILLER M, HOLTMANN G, Hu P, MALAGELADA J R, STANGHELLINI V. Functional gastroduodenal disorders. Gastroenterology, 2006, 130(5): 1466–1479.
HIGGINS J P, THOMPSON S G, DEEKS J J, ALTMAN D G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ, 2003, 327(7414): 557–560.
DERSIMONIAN R, LAIRD N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials, 1986, 7(3): 177–188.
CHALMERS T C. Meta-analysis in clinical medicine. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc, 1988, 99: 144–150.
LI J L. Clinical Observation of the Therapeutic Effect of Spleen Nourishing and Qi Regulating Massage in the Treatment for Spleen Deficiency Qi Stagnation Type of Postprandial Distress Syndrome. Tianjin: Master Thesis of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020.
NING J J, YU J, LI W. Observation on clinical effect of Tuina plus Western medication for functional dyspepsia due to liver Qi stagnation and spleen deficiency. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2018, 16(2): 109–114.
NING X. Clinical study on treatment of functional dyspepsia with massage along meridian points combined with cisapride. Xiandai Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi, 2010, 19(23): 2895–2896.
SUN Y, GAI Y H. Clinical study of functional dyspepsia treated with omeprazole combined with Tuina. Zhongguo Shiyong Yiyao, 2009, 4(29): 124–125.
CHEN Y Y, BAO A, WANG H T, LI J L, FAN Q, WANG J G. Clinical effect observation of abdominal massage on functional dyspepsia of liver-stagnation and spleendeficiency based on “mediating Zhongjiao” theory. Tianjin Zhongyiyao, 2021, 38(10): 1268–1272.
WANG C Y, ZHANG Y Q, ZHANG Z Y, XU J Y, DOU Y B, FAN S, HAN X X. Efficacy evaluation of massaging Jiaji acupoint treating functional dyspepsia of postprandial distress syndrome. Anmo Yu Kangfu Yixue, 2016, 7(3): 41–42.
YE F W, SONG J L, LIN L Q. Clinical analysis of abdominal Tuina in the treatment of functional dyspepsia. Shoudu Shipin Yu Yiyao, 2015, 22(16): 86–87.
ZHANG D S, XUE W G, LI J H. Clinical observation of abdominal Tuina in the treatment of functional dyspepsia. Beijing Zhongyiyao, 2010, 29(8): 619–621.
TAI X T, AI J. Effect of selective spinal Tuina therapy on the elderly patients with functional dyspepsia of dynamic obstacles type. Laonian Yixue Yu Baojian, 2010, 16(16): 380–382.
XU F, FAN C H. Clinical analysis of tonifying spleen promoting digestion and unblocking Qi therapy combined with abdominal massage therapy in treating 47 cases of functional dyspepsia in children with spleen deficiency and Qi stagnation type. Zhongyi Erke Zazhi, 2015, 11(4): 61–63.
SHEN L X. Clinical study on Tuina in children with functional dyspepsia. Xiandai Yangsheng, 2019, 8: 125–126.
GAO Y F, XU W P. Clinical effect of Xiao Er Xiao Shi granule combined with Tuina on functional dyspepsia in children. Zhongguo Zhongyiyao Keji, 2019, 26(6): 934–935.
LU T, ZHANG X J. Effect of Tuina combined with conventional medicine on functional dyspepsia in children. Anmo Yu Kangfu Yixue, 2019, 10(15): 24–26.
YANG Y. Effect of Simo decoction combined with massage on pediatric functional dyspepsia. Linchuang Yixue Yanjiu Yu Shijian, 2019, 4(17): 123–124.
YU N H. Analysis of clinical effective rate of infantile Tuina in treating functional dyspepsia. Guoji Yiyao Weisheng Daobao, 2019, 25(8): 1286–1288.
YUAN G H, CHEN M J, LIU S N, ZHANG K, HE H S. Clinical study on chiropractic combined with massage for the treatment of children with functional dyspepsia. Neike, 2021, 16(3): 402–404.
ZHOU H Y, XU X M. Effect of Tuina along meridians on functional dyspepsia in children and its influence on appetite regulating factors. Hunan Zhongyi Zazhi, 2021, 37(6): 106–107, 119.
LI S, TIAN G. Study on the value of infantile Tuina in treating functional dyspepsia. Jiankang Dashiye, 2019, 18: 123–124.
CAI H P. Evaluation of therapeutic effect of Tuina on functional dyspepsia in children. Zhongguo Fuyou Baojian, 2018, 33(9): 2136–2139.
ZHANG Y D, LIU C L. Functional dyspepsia and the brain-gut axis. Weichangbingxue Yu Ganbingxue Zazhi, 2019, 28(8): 939–941, 946.
LUO X F, ZHAO N, LIU S W, LI H N, ZHANG W, WANG Q S, WANG J H. Effects of abdominal massage on the structure of ENS-ICC-SMC in constipated irritable bowel syndrome rabbits. Zhongguo Jichu Yixue Zazhi, 2020, 26(6): 777–780, 811.
MOSIIENKO H P. Role of gastrointestinal hormones in pathogenesis of functional diseases of the digestive system in adolescent. Lik Sprava, 2008, (7-8): 47–50.
ZHANG W, LI H N, HAI X H, WANG H T, LI D H, WANG J G. Clinical study on the effect of abdominal Tuina on the level of plasma brain-gut peptide in patients with constipation and irritable bowel syndrome. Sichuan Zhongyi, 2015, 33(11): 164–166.
MAO L F, WANG L D, ZHANG H W, LIU J L, DU X J, PENG Z H. Functional dyspepsia and brain-gut peptides. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi, 2015, 23(4): 570–576.
DÍAZ-CABIALE Z, FLORES-BURGESS A, PARRADO C, NARVÁEZ M, MILLÓN C, PUIGCERVER A, COVEÑAS R, FUXE K, NARVÁEZ J A. Galanin receptor/neuropeptide Y receptor interactions in the central nervous system. Curr Protein Pept Sci, 2014, 15(7): 666–672.
SAAD M F, RIAD-GABRIEL M G, KHAN A, SHARMA A, MICHAEL R, JINAGOUDA S D, BOYADJIAN R, STEIL G M. Diurnal and ultradian rhythmicity of plasma leptin: effects of gender and adiposity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 1998, 83(2): 453–459.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the International (Regional) Cooperation and Exchange Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China [国家自然科学基金国际(地 区)合作与交流项目, No. 81820108033]. The registration number of this study in International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews is CRD42022321222.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WEI Wei was responsible for the design and conception of this study. TAO Zijing and CAO Zeng conducted statistical analysis, graph drawing, and manuscript writing; LIU Qian, ZHANG Gezhi, FANG Shuangshuang, YANG Yang, and DU Sijing were responsible for searching databases, screening documents, extracting data, and evaluating methodological quality; all authors critically revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tao, Z., Cao, Z., Liu, Q. et al. Tuina treatment for children and adults with functional dyspepsia: a meta-analysis and systematic review of randomized controlled trials. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 21, 413–426 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-023-1400-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-023-1400-6