Abstract
Objective
To observe the efficacy of acupoint sticking with Jianpi Tongjing Zhitong ointment in the treatment of functional dyspepsia due to liver-qi stagnation and spleen deficiency and its effect on serum 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) and ghrelin contents.
Methods
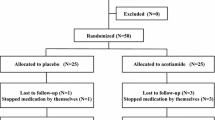
One hundred patients with functional dyspepsia due to liver-qi stagnation and spleen deficiency were divided into a treatment group and a control group by the random number table method, with 50 cases in each group. The treatment group received acupoint sticking with Jianpi Tongjing Zhitong ointment and the control group was treated with mosapride citrate orally. Patients were treated for 4 weeks as a course. The therapeutic efficacy was compared after one-course treatment and the differences in gastric emptying rate, and serum 5-HT and ghrelin contents between groups were compared before and after treatment.
Results
The total effective rate was 79.6% in the control group and 89.4% in the treatment group, showing significantly different between groups (P<0.05). After treatment, the gastric emptying rate and serum ghrelin content of the two groups increased significantly, and the serum 5-HT content decreased significantly, the intra-group differences were significant (all P<0.01). After treatment, the gastric emptying rate and serum ghrelin content were significantly higher in the treatment group than those in the control group, while the serum 5-HT was significant lower in the treatment group, the inter-group differences were significant (all P<0.05). A negative correlation (r=−0.59) was observed between serum 5-HT content and gastric emptying rate, and a positive correlation (r=0.64) was observed between serum ghrelin content and gastric emptying rate, showing statistical significance (all P<0.01).
Conclusion
Acupoint sticking with Jianpi Tongjing Zhitong ointment has a remarkable clinical efficacy in treating patients with functional dyspepsia due to liver-qi stagnation and spleen deficiency and is able to influence the secretion of serum 5-HT and ghrelin. Improving the gastrointestinal motility through the regulation of related brain-gut peptides is suggested as an underlying mechanism for this therapy.
摘要
目的
观察健脾通经止痛膏穴位贴敷治疗肝郁脾虚型功能性消化不良的临床疗效及对血清中5-羟色胺 (5-HT)和胃促生长素(Ghrelin)含量的影响。
方法
将100例肝郁脾虚型功能性消化不良患者按随机数字表法分为治疗 组和对照组, 每组50例。治疗组予健脾通经止痛膏穴位贴敷治疗, 对照组予枸橼酸莫沙必利片口服治疗。4周为1个 疗程, 1个疗程后比较两组的临床疗效及治疗前后患者胃排空率、血清5-HT和Ghrelin的含量。
结果
对照组总有效 率为79.6%, 治疗组为89.4%, 两组比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。两组治疗后胃排空率和血清Ghrelin含量显著升 高, 血清5-HT含量明显降低, 组内差异均有统计学意义(均P<0.01)。治疗组胃排空率和血清Ghrelin含量明显高于对 照组, 血清5-HT含量明显低于对照组, 组间差异均有统计学意义(均P<0.05)。血清5-HT水平与胃排空率呈负相关 (r=−0.59), 血清Ghrelin水平与胃排空率呈正相关(r=0.64), 具有统计学意义(均P<0.01)。
结论
健脾通经止痛膏穴位贴 敷治疗肝郁脾虚型功能性消化不良临床疗效显著, 并能影响患者血清5-HT和Ghrelin的分泌; 通过调节脑肠肽的分泌, 从而影响胃肠道运动,可能是其治疗功能性消化不良的潜在作用机制。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu BY, Zhang FC, Liang LX. Epidemiology of functional dyspepsia. Weichangbingxue He Ganbingxue Zazhi, 2013, 22(1): 85–90.
Ghoshal UC, Singh R, Chang FY, Hou X, Wong BC, Kachintorn U; Functional Dyspepsia Consensus Team of the Asian Neurogastroenterology and Motility Association and the Asian Pacific Association of Gastroenterology. Epidemiology of uninvestigated and functional dyspepsia in Asia: facts and fiction. J Neurogastroenterol Motil, 2011, 17(3): 235–244.
Kong WG, Duan YX, He T. Clinical observation of acupoint paste application effect on sleep quality of functional dyspepsia with anxiety insomnia patients. Neimenggu Zhongyiyao, 2017, 36(7): 84–85.
Wang J, Zhong ZS, Lü L, Ye ZH, Huang SP. Study on the efficacy of the spleen strengthening and qi regulating method in treating functional dyspepsia due to spleen deficiency and qi stagnation and its effect on 5-HT, MTL and ghrelin levels. Shizhen Guoyi Guoyao, 2016, 27(11): 2670–2672.
Zhang W, Chen Y. Effect of acupuncture on psychological factors and serum ghrelin levels in patients with functional dyspepsia. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2018, 37(1): 37–41.
Put commission of Rome. Roman III functional gastrointestinal disease diagnostic criteria. Weichangbingxue, 2006, 11(12): 761–765.
Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China. Guiding Principles for Clinical Study of New Chinese Medicines. Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2002: 134–139.
Mi YH, Mi YX, Wang YB, Li SL, Pei XJ, Wang DZ, Wang XJ. Effect of Weishu formula on the gastric emptying rate, motilin and nitric oxide in patients with functional dyspepsia. Hebei Zhongyi, 2016, 38(2): 191–193.
Wang LD, Du XJ, Liu JH, Mao LF. Discussion on treatment of functional dyspepsia by smoothing liver and invigorating spleen based on brain-gut interactions. Zhongyi Yanjiu, 2019, 32(4): 1–3.
Yang GZ, Gao S. An analysis of point selection and medication law of acupoint application for functional dyspepsia based on data mining. Henan Zhongyi, 2019, 39(11): 1767–1770.
Zhu YN. Study on law of selecting acupoints in treating functional dyspepsia with acupuncture based on data mining. Shanxi Zhongyi, 2019, 35(1): 53–55.
Fan MM, Zhang XL, Liu JX, Wang S. Research progress in functional dyspepsia relevant to traditional Chinese medicine based on the theory of brain-gut axis. Zhongnan Daxue Xuebao (Yixue Ban), 2019, 44(11): 1300–1305.
Liu J, Li F, Tang XD, Ma J, Ma X, Ge DY, Li GM, Wang Y. Xiangshaliujunzi decoction alleviates the symptoms of functional dyspepsia by regulating brain-gut axis and production of neuropeptides. BMC Complement Altern Med, 2015, 15: 387.
Zhang YD, Liu CL. Functional dyspepsia and the brain-gut axis. Weichangbingxue He Ganbingxue, 2019, 28(8): 939–941.
Chua AS, Keeling PW, Dinan TG. Role of cholecystokinin and central serotonergic receptors in functional dyspepsia. World J Gastroenterol, 2006, 12(9): 1329–1335.
Yagi T, Asakawa A, Ueda H, Miyawaki S, Inui A. The role of ghrelin in patients with functional dyspepsia and its potential clinical relevance (review). Int J Mol Med, 2013, 32(3): 523–531.
Lin LB, Shen YT, Que RY, Chen YR, Zhou ME, Li Y. Effect of Shugan Jianpi Yangxin therapy on serum 5-HT, SP, VIP and NPY in the patients with functional dyspepsia complicated with anxiety and depression. Shijie Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi, 2019, 14(7): 966–969.
Liu XC, Sun XP, Sui YU, Zhang HG. Efficacy of Xiangsha Yangwei decoction in the adjuvant treatment of FD and its effect on traditional Chinese medicine syndromes scores, gastric motility and serum levels of leptin, gastrin and ghrelin. Sichuan Zhongyi, 2019, 37(9): 89–92.
Leng JC, Zhang W, Li SY, Tian Z, Li Y. Bi-directional regulation of acupuncture therapy for functional bowel disorders and brain-gut interaction. Liaoning Zhongyi Zazhi, 2015, 42(5): 1142–1145.
Ma XX, Wang FY, Fu JJ, Tang XD. Discussion on material basis and scientific connotation of spleen governing transportation and transformation from the aspect of brain-gut interaction. Zhongyi Zazhi, 2016, 57(12): 996–999.
Ni HH. Clinical study of neuromodulation in the treatment of functional dyspepsia. Zhongguo Shiyong Yiyao, 2019, 14(21): 112–114.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Research Project of Health and Family Planning Commission of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (内蒙古自治区卫生和计划生育委员 会科研项目, No. 201703065).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Author
Kong Wei-guang, M.M., associate chief physician
Conflict of Interest
There was no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Statement of Informed Consent
This trial had been approved by the Ethics Committee of Inner Mongolia Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Approval No. nmgzy-2017-08). Informed consent was obtained from the patients in this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei-guang, K., Tian-feng, H. Efficacy and effect on related brain-gut peptides of acupoint sticking therapy for functional dyspepsia. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 19, 384–388 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-021-1270-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-021-1270-8
Keywords
- Acupoint Sticking Therapy
- Emplastrum Therapy
- Dyspepsia
- Liver-qi Stagnation and Spleen Deficiency
- Brain-gut Peptide
- 5-hydroxytryptamine
- Ghrelin