Abstract
Objective
To observe the effect of Anrou-pressing and kneading Hegu (LI 4) and Sanyinjiao (SP 6) on uterine inertia during painless parturition.
Methods
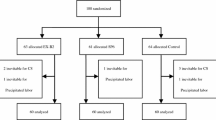
A total of 100 cases of patients with uterine inertia during painless parturition were randomized into an acupoint group and a medicine group by the SPSS programming, with 50 cases in each group. Patients in the acupoint group received the treatment of Anrou-pressing and kneading bilateral Hegu (LI 4) and Sanyinjiao (SP 6), while patients in the medicine group received intravenous oxytocin. The labor time and maternal-child safety were evaluated, and the labor stage was compared.
Results
The latent and active phases in the 1st labor stage and the 2nd labor stage in the acupoint group were substantially shorter than those in the medicine group, and the between-group comparisons showed statistical significance (all P<0.05). The between-group comparison of the 3rd labor stage showed no statistical significance (P>0.05). The postpartum hemorrhage amount in both groups was within the safe range, and the between-group comparison showed no statistical significance (P>0.05). The newborn 1 min Apgar score was ranged 8–10 points, and the between-group comparison showed no statistical significance (P>0.05). The between-group comparison of the labor stage efficacy showed statistical significance (P<0.01), with a better progression in the acupoint group.
Conclusion
Anrou-pressing and kneading Hegu (LI 4) and Sanyinjiao (SP 6) is both effective and safe for uterine inertia during painless parturition.
摘要
目的
观察按揉合谷和三阴交对无痛分娩产程中宫缩乏力的影响。
方法
应用SPSS 编程法将100 例无痛 分娩产程中宫缩乏力的产妇随机分为穴位组和药物组, 每组50 例。穴位组按揉双侧合谷和三阴交, 药物组静滴 缩宫素。对两组的产程时间及母婴安全进行评价, 并比较两组产妇产程进展疗效。
结果
穴位组第1 产程潜伏期、 第1 产程活跃期和第2 产程时间均明显短于药物组, 组间差异均有统计学意义(均P<0.05); 第3 产程两组差异无 统计学意义(P>0.05)。 两组产妇分娩后出血量均在正常范围, 组间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。 两组新生儿1 min 内Apgar评分均在8~10 分, 组间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。 两组产妇产程进展疗效差异有统计学意义(P<0.01), 穴位组的产程进展情况优于药物组。
结论
按揉合谷和三阴交穴治疗无痛分娩产程中宫缩乏力的疗效肯定, 安全 性高。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yin CY, Zhou JZ, Lü XY, Huang XP, He GH, Chen JF. Characteristics of uterine contraction and stages of labor under continuous epidural block anesthesia. Nanfang Yike Daxue Xuebao, 2006, 26(11): 1563–1567.
Xie X, Gou WL. Obstetrics and Gynecology. 8th Edition. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 2013: 188.
Lin HS, Xia SJ. SPSS was applied to design the randomization of experiments. Zhongguo Weisheng Tongji, 2005, 22(6): 397–398.
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Nomenclature and Location of Acupuncture Points (GB/T 12346-2006). Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2006.
Zhen XX. Gynaecology and Obstetrics Nursing. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 2006: 61, 154.
Han Y. Clinical Observation of the Effect of Electroacupuncture at Hegu (LI 4) on Oxytocic Function in Maternal with Uterine Inertia. Beijing: Master Thesis of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, 2006: 37.
Le J. Obstetrics and Gynecology. 6th Edition. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 2004: 197–198.
Liu XH, Wu LL, Yi W. Clinical research of analgesic for labor with acupoint injection and electroacupuncture. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu, 2015, 35(11): 1155–1158.
Zhao Y, Zhu CP, Cheng XH. Application and security observation of acupuncture in labor analgesia. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2017, 36(8): 905–909.
Wang R, Li H, Zhang O. Analysis on abortion mechanism of Hegu (LI 4) and Sanyinjiao (SP 6). Tianjin Zhongyiyao, 2009, 26(1): 41–42.
Zhang YF, Li MJ. Warm needling for preventing postpartum hemorrhage based on syndrome differentiation. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2011, 30(10): 675–676.
Jiang QY, Gao Y, Tang QL, Li YL, Mo HX. The clinical observation with analgesia on first of labor after using acupoint massage at Hegu (LI 4). Anmo Yu Kangfu Yixue, 2011, 2(12): 4–5.
Zhu J, Wan MQ, Zhang LF, Sun X, Liang J. Effects on uterine contraction of puncturing Hegu (LI 4) and Sanyinjiao (SP 6) with electric needles in the rats in pregnancy at late stage. Beijing Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao, 2003, 26(2): 73–75.
Ma SX, Wu FW, Cui JM, Jin ZH, Kong LJ. Effect on moxibustion at Sanyinjiao (SP 6) for uterine contraction pain in labor: a randomized controlled trail. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu, 2010, 30(8): 623–626.
Jin ZH, Ma SX. Effect of moxibusting at Sanyinjiao (SP 6) on the active period of the first stage of labor and the delivery analgesia. Zhongguo Quanke Yixue, 2010, 13(28): 3229–3230.
Jin ZH, Zhang P, Ma SX. Effect of moxibustion at Sanyinjiao (SP 6) on stages of labor and the safety of mothers and infants. Zhongguo Quanke Yixue, 2010, 13(25): 2879–2881.
Ma WZ, Zhou PJ, Zhang Y, Yuan Y, Wu Y, Zhao CH, Xia YL. Clinical observation on the effect of electroacupuncture at Sanyinjiao (SP 6) on labor. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu, 2010, 35(3): 217–221.
Li P, Liu XW. The clinical and mechanism study on acupuncture for relieving the labor pain. Tianjin Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao, 2006, 25(2): 74–76.
Ma ZH, Yan F, Zhao YY, Jiao BJ, Qu M, Mao SH. Clinical study on transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation plus remifentanil for labor analgesia. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2018, 37(5): 526–530.
Zhu QS, Wang FY, Sun XY. Acupuncture analgesia in childbirth, the efficacy and mechanism. Jichu Yixue Yu Linchuang, 2011, 31(6): 679–682.
Fang JQ, Shao XM. New trains of thoughts about acupuncture analgesia: acupuncture analgesia may involve multi-dimensional regulation of pain. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu, 2017, 42(1): 85–89.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Traditional Chinese Medicine Science Research Planning Project of Hunan Province (湖南省中医药科研计划项目, No. 2019138).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
There is no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Statement of Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zan, Y., Wei, Z. Effect of Anrou-pressing and kneading Hegu (LI 4) and Sanyinjiao (SP 6) on uterine inertia during painless parturition. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 19, 67–71 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-020-1220-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-020-1220-x
Keywords
- Acupoint Therapy
- Acupoint Pressure Therapy
- Point, Hegu (LI 4)
- Point, Sanyinjiao (SP 6)
- Analgesia, Obstetrical
- Uterine Inertia
- Parturition