Abstract
Objective
To observe the effect of electroacupuncture (EA) on Janus kinase 2/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (JAK2/STAT3) pathway in knee joint synovial tissues of rats with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and to explore the action mechanism of EA on RA.
Methods
Twelve of the 48 SPF male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were assigned to a normal group by the random number table method. The remaining 36 rats were subjected to RA model preparation by intradermal injection of the Freund’s complete adjuvant into the right hind foot pad of each rat under sterile conditions. After the model was successfully prepared, rats were then divided into a model group, a drug group and an EA group according to a random number table method (n=12). Rats in the drug group were treated with 2 mL aqueous solution of tripterygium glycosides [8.1 mg/(kg·bw)]; rats in the EA group were treated with EA at bilateral Yanglingquan (GB 34) and Zusanli (ST 36), for 30 min each time; rats in the normal group and the model group were placed in a special rat fixation tank for 30 min each time, and received the same dose of normal saline as those in the drug group. Rats in all groups received intervention once a day for 4 weeks. Diameter of rat ankle joint and rat arthritis index were measured before and after the intervention. At the end of the experiment, the expressions of phospho-JAK2 and phospho-STAT3 were determined by immunohistochemistry. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) was used to detect JAK2 and STAT3 mRNAs expressions.
Results
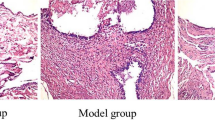
After the model was produced, the arthritis index <2 was considered successful in model preparation. Compared with the model group, the ankle joint diameters and arthritis indexes of rats in the drug group and the EA group were significantly lower (all P>0.01); immunohistochemical staining cells with phospho-JAK2 and phospho-STAT3 were significantly decreased (all P>0.01); the expression levels of JAK2 and STAT3 mRNAs were decreased with statistical differences (all P>0.01). There were no significant differences between the EA group and the drug group (all P<0.05).
Conclusion
EA can alleviate the inflammatory response of RA rats, improve their pathological conditions, reduce the expressions of phospho-JAK2 and phospho-STAT3 in the synovial tissue of knee joint, and decrease the expressions of JAK2 and STAT3 mRNAs. The therapeutic effect of EA is comparable to that of the tripterygium glycosides. The mechanism of EA treatment may be related to the inactivation of the JAK2/STAT3 pathway.
摘要
目的
观察电针对类风湿关节炎(RA)大鼠膝关节滑膜组织非受体型酪氨酸激酶2/信号转导和转录激活因子3(JAK2/STAT3)通路的影响, 探讨电针治疗RA的作用机制。
方法
采用随机数字表法从48只SPF级雄性SD大鼠中取12只为正常组, 其余36只大鼠无菌条件下右后足跖皮内注射弗氏完全佐剂复制RA模型, 造模成功后再按照数字表随机分为模型组、药物组和电针组, 每组12只。 药物组大鼠接受2 m L雷公藤多苷片水溶液灌胃[8.1 mg/(kg·bw)]; 电针组大鼠接受电针双侧阳陵泉和足三里治疗, 电针刺激每次持续30 min。 正常组和模型组大鼠被置于特制大鼠固定筒中, 每次持续30 min, 并接受与药物组同等剂量的生理盐水灌胃。 每组大鼠每天干预1次, 连续干预4周。 在干预前后检测大鼠踝关节直径数值和大鼠关节炎指数。 实验结束后免疫组化法观察磷酸化JAK2(phospho-JAK2)和磷酸化STAT3(phospho-STAT3)的表达, 实时荧光定量聚合酶链反应(RT-qPCR)法检测JAK2和STAT3 mRNA表达。
结果
模型复制后, 关节炎指数大于2视为模型制备成功。 与模型组比较, 药物组和电针组大鼠踝关节直径数值和关节炎指数明显降低, 组间具有统计学差异(均P<0.01); phospho-JAK2及phospho-STAT3免疫组化阳性染色细胞减少, 组间具有统计学差异(均P<0.01); JAK2和STAT3 mRNA表达量下降, 组间具有统计学差异(均P<0.01)。 电针组与药物组比较, 均无统计学差异(均P>0.05)。
结论
电针可以减轻 RA 大鼠的炎性反应, 改善其病理状况, 减少膝关节滑膜组织 phospho-JAK2 和 phospho-STAT3 的表达, 降低 JAK2 及 STAT3 mRNA 表达量, 其治疗作用与雷公藤多苷片相当, 电针治疗作用机制可能与抑制 JAK2/STAT3 通路激活有关。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Negrei C, Bojinca V, Balanescu A, Bojinca M, Baconi D, Spandidos DA, Tsatsakis AM, Stan M. Management of rheumatoid arthritis: impact and risks of various therapeutic approaches. Exp Ther Med, 2016, 11(4): 1177–1183.
Li QH, Xie WX, Li XP, Huang KT, Du ZH, Cong WJ, Zhou LH, Ye TS, Chen JF. Adenosine A2A receptors mediate anti-inflammatory effects of electroacupuncture on synovitis in mice with collagen-induced arthritis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2015, 2015: 809560.
Ding SS, Hong SH, Zhang K, Xu Y, Zhao X, Li Q, Wang SJ, Wang C, Guo Y. Platform for studying effect of manual acupuncture on inflammatory pain model induced by completed Freund’s adjuvant. Liaoning Zhongyi Zazhi, 2016, 43(12): 2483–2487.
Zhang R, Guo LH, Yin Y, Chen TW, Ma WZ. Effect of electroacupuncture on serum TNF-α, IL-β and intercellular adhesion molecule 1 levels in rheumatoid arthritis rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu, 2016, 41(2): 51–54.
Peng CY, Luo L, Hu L, Song XG, Tang ZL, Wu ZJ, Cai RL, Hao F, Hu WB. Effect of different Freund’s complete adjuvant dose on duplicating rheumatoid arthritis rat model. Zhongguo Yiyao Zhinan, 2012, 10(1): 1–3.
Li PP, Xie GX, Song SS, Huang B, Wu YJ, Wang Q, Tong CY, Zhang YF, Zhou AW, Liu LH, Zhang LL, Wei W. Clinical manifestations and the main evaluation method on adjuvant-induced arthritis model in rats. Zhongguo Mianyixue Zazhi, 2012, 28(5): 453–457.
Li ZR. Experimental Acupuncture Science. 2nd Edition. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2007: 242, 245, 257.
Liu L, Qi F, Li YL, Ai K, Cai X, Li X, Zhang H. Effects of electroacupuncture on TAK1 expression in articular synovial cell of rats with adjuvant-induced arthritis. Hunan Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao, 2017, 37(1): 65–69.
Li WX, Huang YR, Lei LD, Li N. Effects of electroacupuncture and manual acupuncture interventions on contents of serum inflammatory cytokines in rats with chronic adjuvant arthritis. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu, 2012, 37(4): 271–276.
Yu WJ, Chen B, Chen ZL, Xing LY, Li NC, Wang TT, Li MY. Analysis of influencing factors of acupuncture analgesia, anti-inflammatory effect on treating adjuvant arthritis of rat model. Liaoning Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao, 2017, 19(9): 107–109.
Fan W, Yang J, Xia LN, Wu P. Synergistic effect of anti-inflammatory treatment by moxibustion on Yanglingquan (GB 34) in AA rats based on theory of Shaoyang governing bones. Liaoning Zhongyi Zazhi, 2017, 44(4): 852–854.
Kelly S, Bombardieri M, Humby F, Ng N, Marrelli A, Riahi S, DiCicco M, Mahto A, Zou L, Pyne D, Hands RE, Pitzalis C. Angiogenic gene expression and vascular density are reflected in ultrasonographic features of synovitis in early rheumatoid arthritis: an observational study. Arthritis Res Ther, 2015, 17(1): 58.
Isozaki T, Amin MA, Arbab AS, Koch AE, Ha CM, Edhayan G, Haines GK, Ruth JH. Inhibitor of DNA binding 1 as a secreted angiogenic transcription factor in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther, 2014, 16(2): R68.
Novikova DS, Popkova TV, Lukina GV, Luchikhina EL, Karateev DE, Volkov AV, Novikov AA, Aleksandrova EN, Nasonov EL. The effects of rituximab on lipids, arterial stiffness and carotid intima-media thickness in rheumatoid arthritis. J Korean Med Sci, 2016, 31(2): 202–207.
Li N, Wang JC, Liang TH, Zhu MH, Wang JY, Fu XL, Zhou JR, Zheng SG, Chan P, Han J. Pathologic finding of increased expression of interleukin-17 in the synovial tissue of rheumatoid arthritis patients. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2013, 6(7): 1375–1379.
Tas SW, Maracle CX, Balogh E, Szekanecz Z. Targeting of proangiogenic signaling pathways in chronic inflammation. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 2016, 12(2): 111–122.
Walker JG, Ahern MJ, Coleman M, Weedon H, Papangelis V, Beroukas D, Roberts-Thomson PJ, Smith MD. Expression of JAK3, STAT1, STAT4 and STAT6 in inflammatory arthritis: unique JAK3 and STAT4 expression in dendritic cells in seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Reum Dis, 2006, 65(2): 149–156.
Thomas SJ, Snowden JA, Zeidler MP, Danson SJ. The role of JAK/STAT signaling in the pathogenesis, prognosis and treatment of solid tumours. Br J Cancer, 2015, 113(3): 365–371.
Malemud CJ. The PI3K/Akt/PTEN/mTOR pathway: a fruitful target for inducing cell death in rheumatoid arthritis? Future Med Chem, 2015, 7(9): 1137–1147.
Ding H, Hong C, Wang Y, Liu J, Zhang N, Shen C, Wei W, Zheng F. Calreticulin promotes angiogenesis via activating nitric oxide signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol, 2014, 178(2): 236–244.
Waters MJ, Brooks AJ. JAK2 activation by growth hormone and other cytokines. Biochem J, 2015, 466(1): 1–11.
Xie MY, Zhang H, Wang YL, Li ZH, Huang JM, Hou YW. Research of analgesia and anti-inflammatory mechanism of rheumatoid arthritis treated with acupuncture and moxibustion based on cell pathway. Zhongyiyao Linchuang Zazhi, 2017, 29(10): 1586–1588.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Research Fund Project for Introduced Talents of Yijishan Hospital (弋矶山医院引进人才科研基金项目, No. YR201809).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
The authors declared that there was no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Statement of Human and Animal Rights
The treatment of animals conformed to the ethical criteria.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, Wm., Zhao, Cj. Effect of electroacupuncture on JAK2/STAT3 pathway in synovial tissues of rats with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 17, 223–230 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-019-1121-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-019-1121-z
Keywords
- Acupuncture Therapy
- Electroacupuncture
- Point, Yanglingquan (GB 34)
- Point, Zusanli (ST 36)
- Arthritis, Rheumatoid
- Janus Kinase 2/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (JAK2/STAT 3) Pathway
- Rats