Abstract
Objective
To observe the effect of herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion on the expressions of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MEK1/2) and extracellular regulatory protein kinase (ERK1/2) in gastric tissues of rats with spleen deficiency syndrome, and to explore the possible mechanisms of herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion in treating spleen deficiency syndrome.
Methods
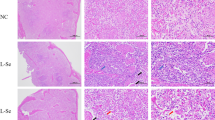
Sixty Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were randomly divided into a blank control group (group A), a model group (group B), a ranitidine group (group C), and a herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion group (group D) by random digit, 15 rats in each group. Rat models of spleen deficiency syndrome were made by intragastric administration of 4 °C 200% concentrated Da Huang (Radix et Rhizoma Rhei). After successful modeling, the rats in group C were treated with 25 mg/(kg·bw) ranitidine by intragastric adminstration and rats in group D were treated with herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion at Zusanli (ST 36) and Zhongwan (CV 12), for 8 d. Excepted for rats in group A, all the other rats were treated with indomethacin at 5 mg/(kg·bw) at 8:00 a.m. on the second day after finishing all the intervention and sacrificed 7 h later to isolate the stomach. Histopathological changes of the gastric tissues were observed under light microscope after hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining. The protein expressions of MEK1/2 and ERK1/2 in the gastric tissues were detected by immunohistochemistry.
Results
After intervention, the gastric mucosal injury in group B was significantly severer than that in group A, with large breakage and ablating; the damage of gastric mucosa was decreased in group C compared with group B; the gastric mucosal surface remained relatively complete, and the status of breakage and ablating was significantly improved. After intervention, compared with group A, the protein expressions of MEK1/2 and ERK1/2 in gastric tissues of the other groups were significantly higher (P<0.01). Compared with group B, the protein expressions of MEK1/2 and ERK1/2 in group C and D were significantly higher (all P<0.01). Compared with group C, the protein expressions of MEK1/2 and ERK1/2 in group D were significantly higher (P<0.01).
Conclusion
Herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion promotes the repair of gastric mucosa in rats with spleen deficiency syndrome, via improving protein expressions of MEK1/2 and ERK1/2 in gastric tissues, as well as activating MEK/ERK signaling pathway.
摘要
目的
通过观察隔药饼灸对脾虚证大鼠胃组织分裂原活化蛋白激酶(MEK1/2)及细胞外调节蛋白激酶(ERK1/2) 蛋白表达的影响, 探讨隔药饼灸治疗脾虚证的可能作用机制。
方法
将60 只SPF 级Sprague-Dawley (SD)大鼠按随 机数字表法分为空白对照组(A 组)、模型组(B 组)、雷尼替丁组(C 组)和隔药饼灸组(D 组), 每组15 只。通过200% 的大黄浓缩液4 ℃灌胃制作脾虚证大鼠模型。造模成功后, C 组按25 mg/(kg·bw)灌胃给药, D 组接受隔药饼灸足三 里和中脘治疗, 连续治疗8 d。除A 组外, 其余组大鼠于治疗完成的第二天上午8:00 接受消炎痛5 mg/(kg·bw)灌 胃, 7 h 后处死动物, 取胃。应用苏木精-伊红(HE)染色, 光镜下观察大鼠胃组织病理学改变, 采用免疫组化法检测 大鼠胃组织MEK1/2 及ERK1/2 蛋白表达。
结果
干预结束后, 与A 组相比, B 组大鼠胃黏膜损伤明显, 可见较大的 破损、脱落; 与B 组比较, C 组大鼠胃黏膜表面有部分脱落, 破损情况改善, D 组大鼠胃黏膜表面较完整, 脱落及破 损明显改善。干预结束后, 与A 组比较, 其他各组大鼠胃组织MEK1/2 及ERK1/2 蛋白表达明显升高(均P<0.01); 与B 组比较, C 组和D 组大鼠胃组织MEK1/2 及ERK1/2 蛋白表达升高(均P<0.01); 与C 组比较, D 组胃组织MEK1/2 及ERK1/2 蛋白表达升高(P<0.01)。
结论
隔药饼灸通过提高胃组织MEK1/2 及ERK1/2 蛋白表达, 激活MEK/ERK 信 号转导通路, 进而促进脾虚证大鼠胃黏膜的修复。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li C, Wang CJ. Comparative study on gastric mucosa damage in three different models of spleen-deficiency syndrome. Zhongguo Zhongxiyi Jiehe Xiaohua Zazhi, 2013, 21(3): 127–130.
Feng D, Liu J, Qu XJ, Zhang Y, Xu L, Qu JL, Zhu ZT, Liu YP. Mechanism and the sensitivity of MEK/ERK inhibitor to 5-FU in gastric cancer cells. Zhonghua Zhongliu Fangzhi Zazhi, 2011, 18(5): 321–324.
Wang CG, Yang ZB, Zuo BR, Xie YF, Liu Q. Expression of the proliferation signaling pathway on the gastric mucosa cells in rats with acute gastric mucosa injury treated by acupuncture. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Zazhi, 2014, 29(9): 2797–2799.
Yi Z, Chang XR, Yi SX, Yan J, Xie H, Lin YP, Song J, Peng F. Evidence-based medicine analysis of clinical studies survey on the acupuncture-moxibustion treatment of spleen-stomach vacuity cold. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Xuekan, 2010, 28(9): 1866–1868.
Shi J, Zhang GS, Liu M, Liu WA, Liu JZ, Chang XR. Influence of smog moxibustion and non-smog moxibustion on serum SOD and MDA in rats with acute gastric mucosal injury. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi, 2013, 21(16): 1516–1521.
Liu M, Lei YJ, Pan SA, Guo LN, Zhao Z, Yan HF, Wang C, Chang XR. Effects of moxibustion preconditioning on protective factors in rats with stress-induced gastric mucosal lesions. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Xuekan, 2015, 33(9): 2068–2071.
Peng Y, Peng F, Yi SX, Lin YP, Chang XR, Long YW, Zhang HG. Effect of moxibustion on motility, absorption and content of ATP in small intestine of spleen-deficiency rats. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu, 2012, 32(3): 246–250.
Li ZR. Experimental Acupuncture Science. 2nd Edition. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2007: 253.
Zhao SY, Jiang W, Wang CJ. Spleen-deficiency and the barrier function of gastrointestinal mucosa. Zhongguo Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi, 2012, 20(11): 523–525.
Chang XR, Liu M, Yan J, Yi SX, Yue ZH, Zhang GS, Liu ML, Sun GJ, Wang LL, Hu L, Wu HG. Research on mechanisms and principles of warm-unblock and warmtonic effects on moxibustion. Shijie Zhongyiyao, 2013, 8(8): 875–879.
Zhao SY, Wang CJ. Influence of Sijunzi decoction on gastric PCD and Caspase-3 expression in spleen deficient rats. Zhongguo Yike Daxue Xuebao, 2014, 43(1): 31–33.
Lin YP, Yi SX, Wu F, Xiang ZY, Yan J, Chang XR. Effect of Shenque (CV 8) acupoint drug cake-separated moxibustion on the lesion of gastric mucosa in stress rats. Zhongguo Linchuang Kangfu, 2005, 9(15): 138–139.
Gao X, Zhang ZY, Wu HL, Hu KW, Jiang ZD, Yang XB, Wang JS. Protective effect of mosapride on acute gastric mucosal lesions induced by aspirin in rats. Gastroenterology, 2012, 17(9): 550–554.
Guo H, Ji FZ, Zhao XF, Gong JN, Qu JL. Effect of peiminine on MEK1/2, ERK1/2 and the phosphorylation in lung tissue of pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Nanjing Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao, 2016, 32(3): 170–175.
Liu XL, Wang RJ, Fu QS. Effect of Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang on expression of MEK/ERK mRNA in gastric mucosa of rats with spleen-deficiency. Zhongyao Yaoli Yu Linchuang, 2013, 29(1): 5–8.
Zhang H, Guo H, Zhang YC, Liu M, Ai K, Su YM, Li MH, Li TL. Effect of moxibustion intervention on expression of gastric epidermal growth factor receptor and extracellular signal regulated kinase 1/2 expression in rats with gastric ulcer. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu, 2014, 39(5): 351–357.
Aliaga JC, Deschênes C, Beaulieu JF, Calvo EL, Rivard N. Requirement of the MAP kinase cascade for cell cycle progression and differentiation of human intestinal cells. Am J Physiol, 1999, 277(3 Pt 1): G631–G641.
Li TL, Su YM, Qi F, Ni W, Zhang H, Zhang YC, Guo H. Effect of moxibustion on serum TFF and gastric mucosa ERK1/2 and PCNA in gastric ulcer model rats with spleen deficiency symptom. Hunan Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao, 2015, 35(2): 49–51.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, 国家重点基础研究发展 计划, No. 2015CB554502); Fund Project of Hunan Province Education Office (湖南省教育厅科研计划项目, No.13C685); Graduate Student Research Innovation Project of Hunan Province (湖南省研究生科研创新项目, No. CX2016B351).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bi, Dy., Liu, Q., Yi, Z. et al. Effect of herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion on MEK1/2 and ERK1/2 expressions of gastric tissues in rats with spleen deficiency syndrome. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 15, 305–310 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-017-1019-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-017-1019-6
Keywords
- Moxibustion Therapy
- Indirect Moxibustion
- Point
- Zusanli (ST 36)
- Point
- Zhongwan (CV 12)
- Research on Acupoints
- Gastric Mucosal Damage
- Spleen Deficiency Syndrome
- Rats