Abstract
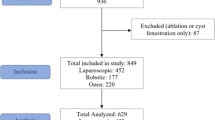
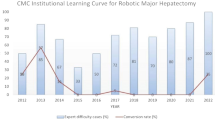
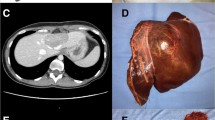
The transition from open hepatectomy to minimally invasive techniques has reduced morbidity and mortality. However, laparoscopic liver resection (LLR) requires substantial expertise. Robotic liver resection (RLR) combines minimal invasiveness with open surgical precision. It may facilitate complex procedures without the learning required for LLR. We evaluated RLR outcomes in a limited resource setting and assessed its efficacy and practicality. This retrospective study analyzed 67 robotic hepatectomies conducted from 2020 to 2023. Demographic, perioperative factors, and surgical outcomes were analyzed. Major hepatectomies were required in 46/67 (68.7%) patients who underwent RLR. No open conversions, 30-day mortalities, or readmissions occurred. Complications occurred in 7.4% of patients; major complications occurred in 5.9%. Learning curve analysis showed a negative correlation between operation sequence and operative time. Effective use of robotic technology combined with the expertise of well-trained surgeons facilitates successful execution of RLR with feasible surgical outcomes, even at smaller centers.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Wakabayashi T, Cacciaguerra AB, Abe Y, Bona ED, Nicolini D, Mocchegiani F et al (2022) Indocyanine green fluorescence navigation in liver surgery: a systematic review on dose and timing of administration. Ann Surg 275(6):1025–1034
Ban D, Tanabe M, Kumamaru H, Nitta H, Otsuka Y, Miyata H et al (2021) Safe dissemination of laparoscopic liver resection in 27,146 cases between 2011 and 2017 from the National Clinical Database of Japan. Ann Surg 274(6):1043–1050
Sucandy I, Giovannetti A, Ross S, Rosemurgy A (2020) Institutional first 100 case experience and outcomes of robotic hepatectomy for liver tumors. Am Surg 86(3):200–207
Gravetz A, Sucandy I, Wilfong C, Patel N, Spence J, Ross S et al (2019) Single-institution early experience and learning curve with robotic liver resections. Am Surg 85(1):115–119
Wang ZY, Chen QL, Sun LL, He SP, Luo XF, Huang LS et al (2019) Laparoscopic versus open major liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma: systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative cohort studies. BMC Cancer 19(1):1047
Guro H, Cho JY, Han HS, Yoon YS, Choi Y, Kim S et al (2018) Outcomes of major laparoscopic liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Surg Oncol 27(1):31–35
Kingham TP, Leung U, Kuk D, Gönen M, D’Angelica MI, Allen PJ et al (2016) Robotic liver resection: a case-matched comparison. World J Surg 40:1422–1428
Choi GH, Chong JU, Choi JS, Lee WJ (2017) Robotic hepatectomy: the Korean experience and perspective. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr 6(4):230–238
Morel P, Jung M, Cornateanu S, Buehler L, Majno P, Toso C et al (2017) Robotic versus open liver resections: a case-matched comparison. Int J Med Robot 13(3):e1800
Liu L, Wang Y, Wu T, Lin J, Deng L, Jiang J et al (2022) Robotic versus laparoscopic major hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma: short-term outcomes from a single institution. BMC Surg 22(1):432
Conticchio M, Delvecchio A, Ferraro V, Stasi M, Casella A, Filippo R et al (2023) Robotic liver resection: report of institutional first 100 cases. Surg Tech Dev 12(4):176–187
Yang HY, Rho SY, Choi JS, Choi GH (2021) Robotic major liver resections: surgical outcomes compared with open major liver resections. Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 25(1):8–17
Liu R, Wakabayashi G, Kim HJ, Choi GH, Yiengpruksawan A, Fong Y et al (2019) International consensus statement on robotic hepatectomy surgery in 2018. World J Gastroenterol 25(12):1432–1444
Chen PD, Wu CY, Hu RH, Chou WH, Lai HS, Liang JT et al (2017) Robotic versus open hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma: a matched comparison. Ann Surg Oncol 24(4):1021–1028
McCarron FN, Vrochides D, Martinie JB (2023) Current progress in robotic hepatobiliary and pancreatic surgery at a high-volume center. Ann Gastroenterol Surg 7(6):863–870
Long ZT, Li HJ, Liang H, Wu YC, Ameer S, Qu XL et al (2024) Robotic versus laparoscopic liver resection for liver malignancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of propensity score-matched studies. Surg Endosc 38(1):56–65
Reddy SK, Barbas AS, Turley RS, Steel JL, Tsung A, Marsh JW et al (2011) A standard definition of major hepatectomy: resection of four or more liver segments. HPB (Oxford) 13(7):494–502
Berber E, Akyildiz HY, Aucejo F, Gunasekaran G, Chalikonda S, Fung J (2010) Robotic versus laparoscopic resection of liver tumours. HPB (Oxford) 12(8):583–586
Troisi RI, Patriti A, Montalti R, Casciola L (2013) Robot assistance in liver surgery: a real advantage over a fully laparoscopic approach? Results of a comparative bi-institutional analysis. Int J Med Robot 9(2):160–166
Strasberg SM (2005) Nomenclature of hepatic anatomy and resections: a review of the Brisbane 2000 system. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 12(5):351–355
Durán M, Briceño J, Padial A, Anelli FM, Sánchez-Hidalgo JM, Ayllón MD et al (2022) Short-term outcomes of robotic liver resection: an initial single-institution experience. World J Hepatol 14(1):224–233
Jang EJ, Kim KW, Kang SH (2022) Early experience of pure robotic right hepatectomy for liver donors in a small-volume center. JSLS 26(4):e2022.00063
Charlson ME, Carrozzino D, Guidi J, Patierno C (2022) Charlson Comorbidity Index: a critical review of clinimetric properties. Psychother Psychosom 91(1):8–35
Mao B, Zhu S, Li D, Xiao J, Wang B, Yan Y (2023) Comparison of safety and effectiveness between robotic and laparoscopic major hepatectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg 109(12):4333–4346
Chen A, Tsai KY, Wang WY, Chen HA, Huang MT (2023) Robotic versus laparoscopic hepatectomy: a single-center, propensity score- matched study. Asian J Surg 46(9):3593–3600
Rayman S, Sucandy I, Ross SB, Crespo K, Syblis C, Rosemurgy A (2023) A propensity score matched analysis of robotic and open hepatectomy for treatment of liver tumors. Clinical outcomes, oncological survival, and costs comparison. J Robot Surg 17(5):2399–2407
Lin ZY, Zhang XP, Zhao GD, Li CG, Wang ZH, Liu R et al (2023) Short-term outcomes of robotic versus open hepatectomy among overweight patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a propensity score-matched study. BMC Surg 23(1):153
Chen PD, Wu CY, Hu RH, Chen CN, Yuan RH, Liang JT et al (2017) Robotic major hepatectomy: Is there a learning curve? Surgery 161(3):642–649
McCarron F, Cochran A, Ricker A, Mantha R, Driedger M, Beckman M et al (2023) 10 years, 100 robotic major hepatectomies: a single-center experience. Surg Endosc 38(2):902–907
Lee B, Choi Y, Cho JY, Yoon Y-S, Han H-S (2021) Initial experience with a robotic hepatectomy program at a high-volume laparoscopic center: single-center experience and surgical tips. Ann Transl Med 9(14):1132
Funding
This work was supported by the Dong-A University Research Fund. The Dong-A University research fund had no part in the design, execution, analysis, or writing of the study or the decision to submit for publication. No other entity had a role in funding, writing, designing, analyzing, or sponsoring the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: EJJ; Methodology: EJJ; Formal analysis and investigation: SHK, KWK; Writing—original draft preparation: EJJ; Writing—review and editing: SHK, KWK; Funding acquisition: EJJ, Approved final script: EJJ, SHK, KWK.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the ethics committee of Dong-A University Hospital (IRB No. DAUH IRB-24-022). The requirement for informed consent was waived because of the retrospective nature of this study. The study was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent to participate
The requirement for informed consent was waived because of the retrospective nature of this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jang, E.J., Kang, S.H. & Kim, K.W. Exploring the feasibility of robotic liver resection in a limited resource setting. J Robotic Surg 18, 187 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-024-01901-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-024-01901-1