Abstract
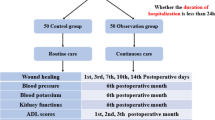
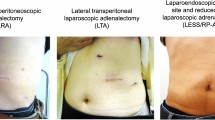
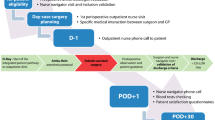
The objective of this study is to compare the satisfaction of patients undergoing robot-assisted retroperitoneal laparoscopy adrenalectomy under the ambulatory mode and conventional mode. Basic information and clinical data of patients who underwent robotic-assisted posterior laparoscopic adrenalectomy between June 2020 and June 2023 were queried from our case system. The Outpatient and Ambulatory Surgery Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems Survey (OAS CAHPS®) was used to investigate patient satisfaction with preoperative preparation, discharge counseling, postoperative instructions, postoperative pain, and satisfaction with nursing work. The stats R package was used to select the appropriate statistic for the statistics based on the characteristics of the data. A total of 311 patients who underwent robot-assisted posterior laparoscopic adrenalectomy were enrolled in our case system. There were no statistical differences between the two groups in gender, age, body mass index, ASA classification, laterality, maximum tumor diameter, type of resection, hormonal activity, disease type, pathological classification, duration of surgery, estimated intraoperative bleeding, postoperative complications and follow-up period that were compared between the two groups of patients. There were no significant differences in preoperative preparation score, discharge counseling score, postoperative guidance score and nursing care satisfaction score (P > 0.05). Postoperative hospitalization, peristalsis time, defecation time, time to first postoperative mobilization, duration of indwelling drain and hospitalization costs in patients in the ambulatory model group were significantly less than patients in the conventional model group (P < 0.001). Patients in the ambulatory model group had significantly higher postoperative pain relief scores than patients in the conventional model group. In conclusion, our data suggest that patient satisfaction is equal between the conventional and ambulatory mode of performing robotic-assisted adrenalectomy. Patient satisfaction was probably associated with shorter hospitalization days, adequate preoperative preparation and standardized, high-quality post-discharge information and guidance.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
Suhonen RA, Iivonen MK, Valimaki MA (2007) Day-case surgery patients’ health-related quality of life. Int J Nurs Pract 13(2):121–129
Uludag M, Aygun N, Isgor A (2020) Surgical Indications and Techniques for Adrenalectomy. Sisli Etfal Hastan Tip Bul 54(1):8–22
Bancos I, Prete A (2021) Approach to the Patient with Adrenal Incidentaloma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 106(11):3331–3353
Ren X, Shang JW, Ren RM et al (2020) Analysis of the influencing factors for postoperative chronic kidney insufficiency in patients with primary aldosteronism. Chin J Urol 41(10):731–735
Piazza L, Caragliano P, Scardilli M et al (1999) Laparoscopic robot-assisted right adrenalectomy and left ovariectomy (case reports). Chir Ital 51(6):465–466
Giron F, Rey CC, Rodriguez L et al (2022) Postoperative outcomes of minimally invasive adrenalectomy: do body mass index and tumor size matter? A single-center experience. BMC Surg 22(1):280
Sada A, Mckenzie TJ (2023) Surgical approaches to the adrenal gland. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 30(3):161–166
Vatansever S, Nordenstrom E, Raffaelli M et al (2022) Robot-assisted versus conventional laparoscopic adrenalectomy: Results from the EUROCRINE Surgical Registry. Surgery 171(5):1224–1230
Gan L, Peng L, Li J et al (2022) Comparison of the effectiveness and safety of robotic-assisted and laparoscopic in adrenalectomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg 105:106853
Moughnyeh M, Lindeman B, Porterfield JR et al (2020) Outpatient robot-assisted adrenalectomy: Is it safe? Am J Surg 220(2):296–297
Gartland RM, Fuentes E, Fazendin J et al (2021) Safety of outpatient adrenalectomy across 3 minimally invasive approaches at 2 academic medical centers. Surgery 169(1):145–149
Yao X, Luo XY, Xie YY et al (2021) Application effect of continuous nursing in patients with adrenal aldosterone tumor after day operation. Chin Nurs Res 35(21):3924–3927
Tanner D, Morgan H (2022) An Evaluation of Timing of Discharge Instruction and the Impact on Patient Satisfaction. J Perianesth Nurs 37(1):29–33
Shariq OA, Bews KA, Mckenna NP et al (2021) Is same-day discharge associated with increased 30-day postoperative complications and readmissions in patients undergoing laparoscopic adrenalectomy? Surgery 169(2):289–297
Ragavan N, Bafna S, Thangarasu M et al (2021) Day-case robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery: Feasibility and safety. Turk J Urol 47(1):30–34
Graves CE (2022) Clinical Judgment and Experience Remain Critical Factors in the Safety of Minimally Invasive Adrenalectomy: Commentary on "Outpatient Adrenalectomy: A Framework for Assessment and Institutional Protocol. Ann Surg 275(2):e543
Su D, Zhang Z, Xia F et al (2023) The safety, benefits and future development of overnight and outpatient thyroidectomy. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 14:1110038
Wang K, Yao X, Liu P et al (2021) Feasibility and safety of retroperitoneal laparoscopic adrenalectomy in day surgery mode. J Clin Urol 36(10):802–805
Kang E, Gillespie BM, Tobiano G et al (2018) Discharge education delivered to general surgical patients in their management of recovery post discharge: A systematic mixed studies review. Int J Nurs Stud 87:1–13
Pigg RA, Fazendin JM, Porterfield JR et al (2022) Patient Satisfaction is Equivalent for Inpatient and Outpatient Minimally-Invasive Adrenalectomy. J Surg Res 269:207–211
Kelly MP, Calkins TE, Culvern C et al (2018) Inpatient Versus Outpatient Hip and Knee Arthroplasty: Which Has Higher Patient Satisfaction? J Arthroplasty 33(11):3402–3406
Asamrew N, Endris AA, Tadesse M (2020) Level of Patient Satisfaction with Inpatient Services and Its Determinants: A Study of a Specialized Hospital in Ethiopia. J Environ Public Health 2020:2473469
Funding
This research is financially supported by project from Natural Science Research in Shanxi Province (202203021211072).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X.Y. completed the conception and design of the study. X.Y.L completed the acquisition of clinical data. Y.H.T and K.W. completed the data analysis and interpretation. Y.H.T completed the drafting of manuscript and critical revision. J.W.S completed the approval of final version of manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Yao Xue, Luo Xiaoyan, Tai Yanghao, Wang Kang, and Shang Jiwen have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, Y., Xiaoyan, L., Yanghao, T. et al. Patient satisfaction analysis of robot-assisted minimally invasive adrenalectomy: a single-center retrospective study. J Robotic Surg 18, 39 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-023-01755-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-023-01755-z