Abstract
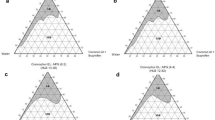
Aim of the current study was to prepare and estimate capsaicin loaded microemulgel (CaP-ME) for the treatment of inflammation. The preparation of CaP-ME was based on the pseudo ternary phase diagram by the phase titration method using various oils such as clove oil, cinnamon oil, turpent oil. To the CaP-ME, different combination of gelling agents was incorporated. CaP-ME was prepared by incorporating different gelling agent such as aerosil and chitosan in to a CaP-MEs. Various preparations were assessed for pH, physical appearance, spreadability, in vitro release and particle size (PS), etc. The results obtained from the preparation of CaP-ME exhibited globule size of 31.6 ± 1.11 nm, polydisperse index (0.441 ± 0.02), % transmittance, and drug content (95.5 ± 8.16%) were within in the range. From the performed pseudo ternary phase diagrams using various oils, 3 pseudo ternary phase diagram was selected based on the area of ME for the further formulation of MEs. Three MEs (F1, F2, F3) were prepared and the F3 shown the better results in all the parameters. The chitosan (G1)-based CaP-ME (F3) gel had a good transparency, better spreadability, extrudability, pH and in vitro release (94.76 ± 5.09%). Hence, it was concluded that turpentine oil is the best oil phase for the preparation of CaP-MEs when compared with other oils like clove oil and cinnamon oil and chitosan-based gel exhibits their efficient topical delivery.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data that support the findings of this study are included within the article (and any supplementary files).
Change history
15 February 2024
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-024-03348-y
References
Ahmad J, Amin S, Kohli K, Mir SR (2013) Construction of pseudoternary phase diagram and its evaluation: development of self-dispersible oral formulation. Int J Drug Dev Res 5:84–90
Ahmad F, Al-Subaie AM, Gayasuddin M, Mohamed JM, Krishnaraju V (2020) Review on the medicinal uses and pharmacological aspects of Plectranthus tenuiflorus from the Labiatae family of Saudi Arabia. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res 64(2):43–48
Alkilani AZ, McCrudden MT, Donnelly RF (2015) Transdermal drug delivery: innovative pharmaceutical developments based on disruption of the barrier properties of the stratum corneum. Pharmaceutics 7(4):38–70
Alqahtani A, Raut B, Khan S, Mohamed JMM, Fatease AA, Alqahtani T, Alamri A, Ahmad F, Krishnaraju V (2021) The unique carboxymethyl fenugreek gum gel loaded itraconazole self-emulsifying nanovesicles for topical onychomycosis treatment. Polymers (basel) 14(2):325
Bhalke RD, Kulkarni SS, Kendre PN, Pande VV, Giri MA (2020) A facile approach to fabrication and characterization of novel herbal microemulsion-based UV shielding cream Futur. J Pharm Sci 6:76
Chintalapudi R, Murthy TE, Lakshmi KR, Manohar GG (2015) Formulation, optimization, and evaluation of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems of nevirapine. Int J Pharm Investig 5(4):205–13
Dantas MG, Reis SA, Damasceno CM, Rolim LA, Rolim-Neto PJ, Carvalho FO, Quintans-Junior LJ, Almeida JR (2016) Development and evaluation of stability of a gel formulation containing the monoterpene borneol. Sci World J 2016:7394685
Fida S, Jalil A, Habib R, Akhlaq M, Mahmood A, Minhas MU, Khan KU, Nawaz A (2022) Development of mucus-penetrating iodine loaded self-emulsifying system for local vaginal delivery. Plos One 17:e0266296
Ghadi A, Mahjoub S, Tabandeh F, Talebnia F (2014) Synthesis and optimization of chitosan nanoparticles: potential applications in nanomedicine and biomedical engineering. Caspian J Intern Med 5(3):156–161
Leanpolchareanchai J, Teeranachaideekul V (2023) Topical microemulsions: skin irritation potential and anti-inflammatory effects of herbal substances. Pharmaceuticals (basel) 16(7):999
Mohamed JMM, Alqahtani A, Ahmad F, Krishnaraju V, Kalpana K (2020) Stoichiometrically governed curcumin solid dispersion and its cytotoxic evaluation on colorectal adenocarcinoma cells. Drug Des Devel Ther 14:4639–4719
Mohamed JM, Alqahtani A, Ahmad F, Krishnaraju V, Kalpana K (2021) Pectin co-functionalized dual layered solid lipid nanoparticle made by soluble curcumin for the targeted potential treatment of colorectal cancer. Carbohydr Polym 252:117180
Mohamed JMM, Khan BA, Rajendran V, El-Sherbiny M, Othman G, Hussamuldin ABA, Al-Serwi RH (2022a) Polymeric ethosomal gel loaded with nimodipine: optimisation pharmacokinetic and histopathological analysis. Saud Pharm J 30(11):1603–1611
Mohamed JMM, Elhassan GO, Khan J, Nachiya RAMJ, Kayarohanam S, Janakiraman AK (2022b) Studies on poly herbal powder shampoo for the treatment of pediculosis capitis and pityriasis capitis infestations. Int J Appl Pharm 14:127–134
Moideen MMJ, Alqahtani A, Venkatesan K, Ahmad F, Krisharaju K, Gayasuddin M, Shaik RA (2020a) Application of the box-behnken design for the production of soluble curcumin: skimmed milk powder inclusion complex for improving the treatment of colorectal cancer. Food Sci Nutri 8(10):1–17
Moideen MMJ, Karuppaiyan K, Kandhasamy R, Seetharaman S (2020b) Skimmed milk powder and pectin decorated solid lipid nanoparticle containing (SLN) soluble curcumin used for the treatment of colorectal cancer. J Food Process Eng 43(3):1–15
Pandey M, Choudhury H, Binti Abd Aziz A, Bhattamisra SK, Gorain B, Su JST, Tan CL, Chin WY, Yip KY (2021) Potential of stimuli-responsive in situ gel system for sustained ocular drug delivery: recent progress and contemporary research. Polymers (Basel) 13(8):1340
Pavoni L, Perinelli DR, Bonacucina G, Cespi M, Palmieri GF (2020) An overview of micro- and nanoemulsions as vehicles for essential oils: formulation preparation and stability. Nanomaterials 10(1):135
Prieto C, Calvo L (2013) Performance of the biocompatible surfactant tween 80, for the formation of microemulsions suitable for new pharmaceutical processing. J Appl Chem 2013:93035610
Sabale V, Vora S (2012) Formulation and evaluation of microemulsion-based hydrogel for topical delivery. Int J Pharm Investig 2(3):140–9
Saleh MA, Mohamed JMM, Ruby JJ, Kanthiah S, Alanazi YF, Majrashi KA, Alshahrani SM, Eladl MA, Alaryani FS, El-Sherbiny M, Menaa F (2023) Preparation of memantine-loaded chitosan nanocrystals in vitro and ex vivo toxicity analysis. Crystals 13(1):21
Souto EB, Cano A, Martins-Gomes C, Coutinho TE, Zielińska A, Silva AM (2022) Microemulsions and nanoemulsions in skin drug delivery. Bioengineering (Basel) 9(4):158
Viswanadhan Vasantha P, Sherafudeen SP, Rahamathulla M, Mathew ST, Murali S, Alshehri S, Shakeel F, Alam P, Sirhan AY, Narayana Iyer BA (2023) Combination of cellulose derivatives and chitosan-based polymers to investigate the effect of permeation enhancers added to in situ nasal gels for the controlled release of loratadine and chlorpheniramine. Polymers (basel) 15(5):1206
Wen H, Jung H, Li X (2015) Drug delivery approaches in addressing clinical pharmacology-related issues: opportunities and challenges. AAPS J 17(6):1327–1340
Yadav SK, Mishra MK, Tiwari A, Shukla A (2016) Emulgel: a new approach for enhanced topical drug delivery. Int J Curr Pharm Res 9(1):15–19
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University Researchers Supporting Project number (PNURSP2023R110), Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, and by the Researchers Supporting program, AlMaarefa University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Also, this study is supported via funding from Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University project number (PSAU/2023/R/1444). The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University for funding this work through large group Research Project under a grant number (R.G.P.2/66/44).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: to update acknowledgement.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mohamed, J.M.M., Nasreen, A., Al Mohaini, M.A. et al. Optimization of capsaicin microemulgel: a comprehensive in vitro evaluation and pseudo ternary diagram. Chem. Pap. 78, 2155–2164 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-023-03216-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-023-03216-1