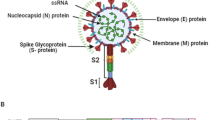
Abstract
RNA interference is an upcoming methodology being designed to specifically target viral infections. The current study suggests a strategy to design probable small interfering RNAs (siRNA) for targeting the viral genome of SARS-CoV-2, as a case study. siRNAs were designed against the targets from a highly conserved region of the spike gene of SARS-CoV-2 having no significant matches within the human genome. Four targets/viral RNAs (vRNA) with high predicted inhibition values were selected for further evaluation. The predicted siRNAs were examined for their properties and stability using molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. Further, to understand the RNA-Induced Silencing Complex (RISC) mechanism of the predicted siRNA targets of SARS-CoV-2, the human argonaute (Ago2) protein in complex with the four siRNA-vRNA duplexes was built. MD simulations of apo-Ago2, four selected siRNA-vRNA duplexes and four Ago2 bound to these siRNA-vRNA duplexes were carried out for 1 μs each. Amongst the four duplex-bound Ago2 simulation systems, the siRNA-vRNA3 duplex showed stable base pairing in the seed region, favourable and strong interactions with functionally important residues of Ago2 protein through the simulation length. Therefore, the designed siRNA3 molecule may act as an effective therapeutic agent against the SARS-CoV-2. The reported in-silico strategy may be beneficial for the identification and designing of probable siRNAs against any viral genome in RNAi therapeutics. However, the experimental validation of these molecules would be required for proving their use as therapeutics.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amadei A, Linssen ABM, Berendsen HJC (1993) Essential dynamics of proteins. Proteins 17(4):412–425. https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.340170408
Amarzguioui M, Prydz H (2004) An algorithm for selection of functional siRNA sequences. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 316:1050–1058. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.02.157
Apparailly F, Jorgensen C (2012) siRNA-based therapeutic approaches for rheumatic diseases. Nature reviews Rheumatology.
Bantounas I, Phylactou LA, Uney JB (2004) RNA interference and the use of small interfering RNA to study gene function in mammalian systems. J Mol Endocrinol 33:545–557
Bellaousov S, Reuter JS, Seetin MG, Mathews DH (2013) RNAstructure: web servers for RNA secondary structure prediction and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 41(W1):W471–W474
Berkhout B (2009) Toward a Durable Anti-HIV Gene Therapy Based on RNA Interference. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1175:3–14
Bernstein E, Caudy AA, Hammond SM, Hannon GJ (2001) Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature 409:363–366. https://doi.org/10.1038/35053110
Bhandare V, Ramaswamy A (2016) Structural dynamics of human argonaute2 and its interaction with siRNAs designed to target mutant tdp43. Advances in bioinformatics, 2016.
Birmingham A, Anderson E, Sullivan K, Reynolds A, Boese Q, Leake D et al (2007) A protocol for designing sirnas with high functionality and specificity. Nat Protoc 2(9):2068–2078. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.278
Boden D, Pusch O, Lee F, Tucker L, Ramratnam B (2003) Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Escape from RNA Interference. J Virol 77:11531–11535
Boehr DD, Nussinov R, Wright PE (2009) The role of dynamic conformational ensembles in biomolecular recognition. Nat Chem Biol 5:789–796. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.232
Case DA, Betz RM, Cerutti DS, Cheatham TE III, Darden TA, Duke RE et al (2016) AMBER 2016. University of California, San Francisco
Case DA, Aktulga HM, Belfon B-S, Brozell SR, Cerutti DS, Cheatham TE III, Cisneros GA, Cruzeiro VWD, Darden TA, Duke RE, Giambasu G, Gilson MK, Gohlke H, Goetz AW, Harris R, Izadi S, Izmailov SA, Jin C, Kasavajhala K, Kaymak MC, King E, Kovalenko A, Kurtzman T, Lee TS, LeGrand S, Li P, Lin C, Liu J, Luchko T, Luo R, Machado M, Man V, Manathunga M, Merz KM, Miao Y, Mikhailovskii O, Monard G, Nguyen H, O’Hearn KA, Onufriev A, Pan F, Pantano S, Qi R, Rahnamoun A, Roe DR, Roitberg A, Sagui C, Schott-Verdugo S, Shen J, Simmerling CL, Skrynnikov NR, Smith J, Swails J, Walker RC, Wang J, Wei JH, Wolf RM, Wu X, Xue Y, York DM, Zhao S, Kollman PA (2021) Amber 2021. University of California, San Francisco
Chakraborty C, Sharma AR, Sharma G, Doss CGP, Lee SS (2017) Therapeutic miRNA and siRNA: moving from bench to clinic as next generation medicine. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 8:132–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2017.06.005
Chan JFW, Kok KH, Zhu Z, Chu H, To KKW, Yuan S, Yuen KY (2020) Genomic characterization of the 2019 novel human-pathogenic coronavirus isolated from a patient with atypical pneumonia after visiting Wuhan. Emerg Microbes Infect 9:221–236
Chan CY, Carmack CS, Long DD, Maliyekkel A, Shao Y, Roninson IB, Ding Y (2009) A structural interpretation of the effect of GC-content on efficiency of RNA interference. BMC Bioinformatics (10 Suppl 1), S33. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-10-s1-s33
Chandra PK, Kundu AK, Hazari S, Chandra S, Bao L, Ooms T, Morris GF, Wu T, Mandal T, Dash S (2012) Inhibition of Hepatitis C Virus Replication by Intracellular Delivery of Multiple siRNAs by Nanosomes. Mol Ther 20:1724–1736
Chang Z, Babiuk LA, Hu J (2007) Therapeutic and prophylactic potential of small interfering RNAs against severe acute respiratory syndrome: Progress to date. BioDrugs 21:9–15
Chen Y, Cheng G, Mahato RI (2008) RNAi for Treating Hepatitis B Viral Infection. Pharm Res 25:72–86
Chen W, Feng P, Liu K, Wu M, Lin H (2020) Computational identification of small interfering RNA targets in SARS-CoV-2. Virologica Sinica 35(3):359–361
Cherian SS, Agrawal M, Basu A, Abraham P, Gangakhedkar RR, Bhargava B (2020) Perspectives for repurposing drugs for the coronavirus disease 2019. Indian J Med Res 151(2–3):160. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_585_20. (PMID: 32317408)
Chowdhury UF, Shohan MUS, Hoque KI, Beg MA, Siam MKS, Moni MA (2021) A computational approach to design potential siRNA molecules as a prospective tool for silencing nucleocapsid phosphoprotein and surface glycoprotein gene of SARS-CoV-2. Genomics 113(1):331–343
Dal-Ré R, Banzi R, Georgin-Lavialle S, Porcher R, Sofat R, Zeitlinger M, Rosendaal FR (2021) Remdesivir for COVID-19 in Europe: Will it provide value for money? Lancet Respir. Med 9:127–128
Dana H et al (2017) Molecular mechanisms and biological functions of siRNA. Int J Biomed Sci 13:48–57
Das AT, Brummelkamp TR, Westerhout EM, Vink M, Madiredjo M, Bernards R, Berkhout B (2004) Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Escapes from RNA Interference-Mediated Inhibition. J Virol 78:2601–2605
Deerberg A, Willkomm S, Restle T (2013) Minimal mechanistic model of siRNA-dependent target RNA slicing by recombinant human Argonaute 2 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110(44):17850–17855
Elbashir SM, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T (2001) RNA interference is mediated by 21- and 22-nucleotide RNAs. Genes Dev 15:188–200. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.862301
Frank F, Sonenberg N, Nagar B (2010) Structural basis for 5′-nucleotide base-specific recognition of guide RNA by human AGO2. Nature 465:818–822
GetContacts: https://getcontacts.github.io/
Haasnoot J, Berkhout B (2009) Nucleic acids-based therapeutics in the battle against pathogenic viruses. Cytochrome P450(189):243–263
Hammond SM, Bernstein E, Beach D, Hannon GJ (2000) An RNA-directed nuclease mediates post-transcriptional gene silencing in Drosophila Cells. Nature 404:293–296. https://doi.org/10.1038/35005107
Harikrishna S, Pradeepkumar PI (2017) Probing the binding interactions between chemically modified siRNAs and human argonaute 2 using microsecond molecular dynamics simulations. J Chem Inf Model 57(4):883–896
Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S, Krüger N, Herrler T, Erichsen S, Schiergens TS, Herrler G, Wu NH, Nitsche A et al (2020) SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell 181:271-280.e8
Hu B, Weng Y, Xia XH, Liang XJ, Huang Y (2019) Clinical advances of siRNA therapeutics. J Gene Med 21:e3097. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgm.3097
Hu B, Zhong L, Weng Y, Peng L, Huang Y, Zhao Y, Liang XJ (2020) Therapeutic siRNA: state of the art. Signal Transduct Target Ther 5:1–25
Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K (1996) VMD: visual molecular dynamics. J Mol Graph 14(1):33–38
Iwakawa HO, Tomari Y (2022) Life of RISC: formation, action, and degradation of RNA-induced silencing complex. Mol Cell 82(1):30–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2021.11.026
Jaskiewicz L, Filipowicz W (2008) Role of Dicer in posttranscriptional RNA silencing. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 320:77–97
Jo WK, Drosten C, Drexler JF (2021) The evolutionary dynamics of endemic human coronaviruses. Virus Evol. 7:veab020
Johnson M, Zaretskaya I, Raytselis Y, Merezhuk Y, McGinnis S, Madden TL (2008) NCBI BLAST: a better web interface. Nucl Acids Res 36(suppl_2):W5–W9
Kibbe WA (2007) OligoCalc: an online oligonucleotide properties calculator. Nucl Acids Res 35(2):43–46
Kitade Y, Akao Y (2010) MicroRNAs and their therapeutic potential for human diseases: microRNAs, miR-143 and -145, function as anti-oncomirs and the application of chemically modified miR-143 as an anti-cancer drug. J Pharmacol Sci 114:276–280
Kobayashi Y, Fukuhara D, Akase D, Aida M, Ui-Tei K (2022) siRNA seed region is divided into two functionally different domains in RNA interference in response to 2’-OMe modifications. ACS Omega 7(2):2398–2410. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c06455
Konstantinidou SK, Papanastasiou IP (2020) Repurposing current therapeutic regimens against SARS-CoV-2 (Review). Exp Ther Med 20:1845–1855
Koscianska E, Starega-Roslan J, Krzyzosiak WJ (2011) The role of Dicer protein partners in the processing of microRNA precursors. PLoS ONE 6:e28548
Koulgi S, Jani V, Uppuladinne MVN, Sonavane U, Joshi R (2020) Remdesivir-bound and ligand-free simulations reveal the probable mechanism of inhibiting the RNA dependent RNA polymerase of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. RSC Adv 10(45):26792–26803. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra04743k
Koulgi S, Jani V, Mallikarjunachari Uppuladinne VN, Sonavane U, Joshi R (2022) Structural insight into the binding interactions of NTPs and nucleotide analogues to RNA dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2. J Biomol Struct Dyn 40(16):7230–7244. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2021.1894985
Kumar M, Lata S, Raghava GPS (2009) siRNApred: SVM based method for predicting efficacy value of siRNA. Proceedings of the OSCADD-2009: International conference on open source for computer aided drug discovery: IMTECH, Chandigarh.
Kurreck J (2009) RNA interference: from basic research to therapeutic applications. Angew Chem Int Ed 48:1378–1398
Levanova A, Poranen M (2018) RNA interference as a prospective tool for the control of human viral infections. Front Microbiol 9:2151
Li G, De Clercq E (2020) Therapeutic options for the 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Nat Rev Drug Discov 19:149–150. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41573-020-00016-0
Lima WF, Wu H, Nichols JG, Sun H, Murray HM, Crooke ST (2009) Binding and cleavage specificities of human Argonaute2. J Biol Chem 284(38):26017–26028
Lingel A, Simon B, Izaurralde E, Sattler M (2004) Nucleic acid 3′-end recognition by the Argonaute2 PAZ domain. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11:576–577
Liu J, Carmell MA, Rivas FV, Marsden CG, Thomson JM, Song JJ, Hammond SM, Joshua-Tor L, Hannon GJ (2004) Argonaute2 is the catalytic engine of mammalian RNAi. Science 305(5689):1437–1441
Lu XJ, Olson WK (2008) 3DNA: a versatile, integrated software system for the analysis, rebuilding and visualization of three-dimensional nucleic-acid structures. Nat Protoc 3(7):1213–1227
Lu ZJ, Gloor JW, Mathews DH (2009) Improved RNA secondary structure prediction by maximizing expected pair accuracy. RNA 15(10):1805–1813
Machhi J, Herskovitz J, Senan AM, Dutta D, Nath B, Oleynikov MD et al (2020) The natural history, pathobiology, and clinical manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 infections. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 15:359–386
Maier JA, Martinez C, Kasavajhala K, Wickstrom L, Hauser KE, Simmerling C (2015) ff14SB: improving the accuracy of protein side chain and backbone parameters from ff99SB. J Chem Theory Comput 11(8):3696–3713
Markham NR, Zuker M (2005) DINAMelt web server for nucleic acid melting prediction. Nucleic Acids Res 33:W577–W581. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gki591
Miller BR III, McGee TD Jr, Swails JM, Homeyer N, Gohlke H, Roitberg AE (2012) MMPBSA py: an efficient program for end-state free energy calculations. J Chem Theory Comput 8(9):3314–3321
Naqvi AA, Fatima K, Mohammad T, Fatima U, Singh IK, Singh A, Atif SM, Hariprasad G, Hasan GM (1866) Hassan MI (2020) Insights into SARS-CoV-2 genome, structure, evolution, pathogenesis and therapies: structural genomics approach. Mole Basis Disease 1866(10):165878
Neumeier J, Meister G (2021) siRNA specificity: RNAi mechanisms and strategies to reduce off-target effects. Front Plant Sci 11:526455
Noguchi S, Mori T, Hoshino Y, Maruo K, Yamada N et al (2011) MicroRNA-143 functions as a tumor suppressor in human bladder cancer T24 cells. Cancer Lett 307:211–220
Pal M, Berhanu G, Desalegn C, Kandi V (2020) Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2): an update. Cureus 12(3)
Park MS, Araya-Secchi R, Brackbill JA, Phan HD, Kehling AC, Abd El-Wahab EW, Dayeh DM, Sotomayor M, Nakanishi K (2019) Multidomain convergence of Argonaute during RISC assembly correlates with the formation of internal water clusters. Mol Cell 75(4):725–740
Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE (2004) UCSF Chimera—a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 25(13):1605–1612
Piekna-Przybylska D, DiChiacchio L, Mathews DH, Bambara RA (2010) A sequence similar to tRNA3Lys gene is embedded in HIV-1 U3–R and promotes minus-strand transfer. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17:83–90. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1687
Pradhan P, Pandey AK, Mishra A, Gupta P, Tripathi PK, Menon MB, Gomes J, Vivekanandan P, Kundu B (2020) Uncanny similarity of unique inserts in the 2019-nCoV spike protein to HIV-1 gp120 and Gag
Pratt AJ, MacRae IJ (2009) The RNA-induced silencing complex: a versatile gene-silencing machine. J Biol Chem 284(27):17897–17901
Pruijssers AJ, George AS, Schäfer A, Leist SR, Gralinksi LE, Dinnon KH, Yount BL, Agostini ML, Stevens LJ, Chappell JD, Lu X (2020) Remdesivir inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in human lung cells and chimeric SARS-CoV expressing the SARS-CoV-2 RNA polymerase in mice. Cell Rep 32(3):107940
Qureshi A, Thakur N, Kumar M (2013) VIRsiRNApred: a web server for predicting inhibition efficacy of siRNAs targeting human viruses. J Transl Med 11(1):305. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5876-11-305
Rand TA, Petersen S, Du F, Wang X (2005) Argonaute2 cleaves the anti-guide strand of siRNA during RISC activation. Cell 123(4):621–629
Reuter JS, Mathews DH (2010) RNAstructure: software for RNA secondary structure prediction and analysis. BMC Bioinform 11:129. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-11-129
Ritchie H, Mathieu E, Rodés-Guirao L, Appel C, Giattino C, Ortiz-Ospina E, Hasell J, Macdonald B, Beltekian D, Roser M (2020) Coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19). OurWorldInData.org. https://ourworldindata.org/coronavirus
Roe DR, Cheatham TE 3rd (2018) Parallelization of CPPTRAJ enables large scale analysis of molecular dynamics trajectory data. J Comput Chem 39(25):2110–2117
Saadat KA (2022) RNAi-mediated siRNA sequences to combat the COVID-19 pandemic with the inhibition of SARS-CoV2. Gene Reports 101512
Saha A, Sharma AR, Bhattacharya M, Sharma G, Lee SS, Chakraborty C (2020a) Probable molecular mechanism of remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19: need to know more. Arch Med Res 51(6):585–586
Saha A, Sharma AR, Bhattacharya M, Sharma G, Lee SS, Chakraborty C (2020b) Tocilizumab: a therapeutic option for the treatment of cytokine storm syndrome in COVID-19. Arch Med Res 51(6):595–597
Saha RP, Sharma AR, Singh MK, Samanta S, Bhakta S, Mandal S, Bhattacharya M, Lee SS, Chakraborty C (2020c) Repurposing drugs, ongoing vaccine, and new therapeutic development initiatives against COVID-19. Front Pharmacol 11:1258
Schaar K, Geisler A, Kraus M, Pinkert S, Pryshliak M, Spencer JF, Tollefson AE, Ying B, Kurreck J, Wold WS, Klopfleisch R (2017) Anti-adenoviral artificial microRNAs expressed from AAV9 vectors inhibit human adenovirus infection in immunosuppressed Syrian hamsters. Mole Therapy-Nucleic Acids 8:300–316
Schirle NT, MacRae IJ (2012) The crystal structure of human Argonaute2. Science 336(6084):1037–1040
Schubert S, Grünweller A, Erdmann VA, Kurreck J (2005) Local RNA target structure influences siRNA efficacy: systematic analysis of intentionally designed binding regions. J Mol Biol 348:883–893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2005.03.011
Setten RL, Rossi JJ, Han SP (2019) The current state and future directions of RNAi-based therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 18:421–446. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-019-0017-4
Shawan MM, Sharma AR, Bhattacharya M, Mallik B, Akhter F, Shakil MS, Hossain MM, Banik S, Lee SS, Hasan MA, Chakraborty C (2021) Designing an effective therapeutic siRNA to silence RdRp gene of SARS-CoV-2. Infect Genet Evol 93:104951
Sheu-Gruttadauria J, MacRae IJ (2017) Structural foundations of RNA silencing by Argonaute. J Mol Biol 429(17):2619–2639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2017.07.018
Singh S, Gupta SK, Nischal A, Khattri S, Nath R, Pant KK, Seth PK (2012) Design of potential siRNA molecules for hepatitis delta virus gene silencing. Bioinformation 8:749–757. https://doi.org/10.6026/97320630008749
Song JJ, Smith SK, Hannon GJ, Joshua-Tor L (2004) Crystal structure of Argonaute and its implications for RISC slicer activity. Science 305(5689):1434–1437
Stein EA, Pinkert S, Becher PM, Geisler A, Zeichhardt H, Klopfleisch R, Poller W, Tschöpe C, Lassner D, Fechner H, Kurreck J (2015) Combination of RNA interference and virus receptor trap exerts additive antiviral activity in coxsackievirus B3-induced myocarditis in mice. J Infect Dis 211(4):613–622
Suzuki H, Saitoh H, Suzuki T, Takaku H (2009) Baculovirus-mediated bispecific short-hairpin small-interfering RNAs have remarkable ability to cope with both influenza viruses A and B. Oligonucleotides 19(4):307–316
Tolksdorf B, Nie C, Niemeyer D, Röhrs V, Berg J, Lauster D, Adler JM, Haag R, Trimpert J, Kaufer B, Drosten C (2021) Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 replication by a small interfering RNA targeting the leader sequence. Viruses 13(10):2030
Walls AC, Park YJ, Tortorici MA, Wall A, McGuire AT, Veesler D (2020) Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein. Cell 181(2):281–292
Wan J, Xing S, Ding L, Wang Y, Gu C, Wu Y, Rong B, Li C, Wang S, Chen K (2020) He C (2020) Human-IgG-neutralizing monoclonal antibodies block the SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cell Rep 32(3):107918
Wang J, Li LC (2012) Small RNA and its application in andrology and urology. Trans Androl Urol 1:33–43
Wang Y, Sheng G, Juranek S, Tuschl T, Patel DJ (2008) Structure of the guide-strand-containing argonaute silencing complex. Nature 456(7219):209–213
Wang Y, Juranek S, Li H, Sheng G, Wardle GS, Tuschl T, Patel DJ (2009) Nucleation, propagation and cleavage of target RNAs in Ago silencing complexes. Nature 461(7265):754–761
Wang L, Shi J, Zhang H, Li H, Gao Y et al (2013) Synergistic anticancer effect of RNAi and photothermal therapy mediated by functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes. Biomaterials 34:262–274
Werk D, Schubert S, Lindig V, Grunert HP, Zeichhardt H, Erdmann VA, Kurreck J (2005) Developing an effective RNA interference strategy against a plus-strand RNA virus: silencing of coxsackievirus B3 and its cognate coxsackievirus-adenovirus receptor. Biol Chem 386(9):857–863
Wilson JA, Richardson CD (2005) Hepatitis C virus replicons escape RNA interference induced by a short interfering RNA directed against the NS5b coding region. J Virol 79:7050–7058
Wu R, Luo KQ (2021) Developing effective siRNAs to reduce the expression of key viral genes of COVID-19. Int J Biol Sci 17(6):1521
Wu CJ, Huang HW, Liu CY, Hong CF, Chan YL (2005) Inhibition of SARS-CoV replication by siRNA. Antivir Res 65:45–48
Wu C, Liu Y, Yang Y, Zhang P, Zhong W, Wang Y et al (2020) Analysis of therapeutic targets for SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of potential drugs by computational methods. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B 10(5):766–788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2020.02.008
Yan KS, Yan S, Farooq A, Han A, Zeng L et al (2003) Structure and conserved RNA binding of the PAZ domain. Nature 426:468–474
Zamore PD, Tuschl T, Sharp PA, Bartel DP (2000) RNAi: double-stranded RNA directs the ATP-dependent cleavage of mRNA at 21 to 23 nucleotide intervals. Cell 101(1):25–33
Zgarbová M, Otyepka M, Šponer J, Mládek A, Banáš P, Cheatham TE III, Jurecka P (2011) Refinement of the Cornell et al. nucleic acids force field based on reference quantum chemical calculations of glycosidic torsion profiles. J Chem Theory Comput 7(9):2886–2902
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the Bioinformatics Resources and Applications Facility (BRAF), of C-DAC, for providing a supercomputing facility to carry out molecular dynamics simulations. The authors also acknowledge National Supercomputing Mission (NSM), India & Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), and Department of Science and Technology (DST) for the support to perform R&D work at C-DAC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Uppuladinne, M.V.N., Koulgi, S., Jani, V. et al. Unlocking the potential of RNAi as a therapeutic strategy against infectious viruses: an in-silico study. Chem. Pap. 78, 1537–1552 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-023-03180-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-023-03180-w