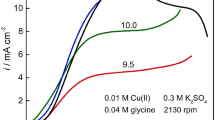
Abstract
The reduction of Cu(II) has been investigated in the presence of Alizarin Red S in two different background solutions namely KCl and acetate buffer through this study. The electroactive intermediate species have been extensively characterised by using Direct Current Polarography and Deferential Pulse Polarography techniques. It has been observed that Cu2+ was reduced to elemental copper in a two-step single-electron transfer process. However, the kinetics of charge transfer is dampened in the presence of Alizarin due to the complexation of active copper ions with ionised Alizarin, making the electrodeposition more controlled. In the first technique, the peaks of the 57 mM-Cu2+ reduction and for the 57 mM-Alizarin reduction have been observed. Using the second technique, the voltammograms exhibit the peaks at pH = 2, 3, where the first peak is for the reduction process of two carbonyl groups in Alizarin, and the second one is for Cu2+ reduction as one-step two-electron transfer. At pH = 5, the complex formation reveals that copper can be hardly reduced on the cathode, whereas Alizarin has two small peaks for two carbonyl groups after being in the investigated alkali mediums. The clear peak at pH = 11 indicates that copper is no more in the structure of a complex. The stoichiometries of the salt and complex have been also verified where both are (1:1). Coating experiments were carried out at 25 °C, 35 °C and 60 °C to investigate the relations between the current efficiency and pH, current density, molarity concentration and time and obtain the optimal operating conditions for copper electrodeposition on steel and stainless steel.





























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham SD, David ST, Bennie RB, Joel C, Kumar DS (2016) Eco-friendly and green synthesis of BiVO4 nanoparticle using microwave irradiation as photocatalayst for the degradation of Alizarin Red S. J Mol Struct 1113:174–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2016.01.053
Albadarin AB, Mangwandi C (2015) Mechanisms of Alizarin Red S and Methylene blue biosorption onto olive stone by-product: Isotherm study in single and binary systems. J Environ Manag 164:86–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.08.040
Ali N, Karam A (2015) Optimal conditions for electrodeposition of copper (II) in presence of Alizarin Red’s by physicochemical methods. Chemistry and materials research 7 (9):77. https://iiste.org/Journals/index.php/CMR/article/view/25453.
Ali NM-S, Amaniampong PN, Karam A (2016) Determination of optimal conditions for electrodeposition of Tin (II) in the presence of Alizarin Red S. Heliyon 2(12):e00212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2016.e00212
Andricacos PC (1999) Copper on-chip interconnections: A breakthrough in electrodeposition to make better chips. The Electrochemical Society Interface, vol 8. IOP Publishing, https://www.electrochem.org/dl/interface/spr/spr99/IF3-99-Pages32-37.pdf
Asenbauer J, Eisenmann T, Kuenzel M, Kazzazi A, Chen Z, Bresser D (2020) The success story of graphite as a lithium-ion anode material–fundamentals, remaining challenges, and recent developments including silicon (oxide) composites. Sustain Energy Fuels 4(11):5387–5416. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0SE00175A
Callister WD, Rethwisch DG (2018a) Phase transformations: development of microstructure and alteration of mechanical properties. In: Materials science and engineering: an introduction, 10th edn. Wiley. https://www.wiley.com/en-us/Materials+Science+and+Engineering%3A+An+Introduction%2C+10th+Edition-p-9781119405498
Callister WD, Rethwisch DG (2018b) Applications and processing of metal alloys. In: Materials science and engineering: an introduction, 10th edn. Wiley. https://www.wiley.com/en-us/Materials+Science+and+Engineering%3A+An+Introduction%2C+10th+Edition-p-9781119405498
Di Bari GA, Schlesinger M, Paunovic M (2000) Modern electroplating. New York, M Schlesinger and M Paunovic, Eds, John Wiley&Sons, Inc
Flott LW (1996) Quality control: the electroplating process. Met Finish 94(3):55–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/0026-0576(96)84173-0
Hassan SSM, Kamel AH, Hassan AA, Amr AE-GE, El-Naby HA, Elsayed EA (2020) A sno2/ceo2 nano-composite catalyst for alizarin dye removal from aqueous solutions. Nanomaterials 10(2):254. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020254
Ibsen CJS, Birkedal H (2010) Modification of bone-like apatite nanoparticle size and growth kinetics by alizarin red S. Nanoscale 2(11):2478–2486. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0nr00488j
Jannatin M, Ayu Nabila IL, Supriyanto G, Pudjiastuti P (2017) A novel spectrophotometric method for determination of histamine based on its complex reaction with Cu (II) and alizarin red S. Journal of Chemical Technology and Metallurgy 52 (6):1045–1050. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/324079386.
Khalifa ME (1998) Selective separation of uranium using alizarin red S (ARS)-modified anion-exchange resin or by flotation of U-ARS chelate. Sep Sci Technol 33(14):2123–2141. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496399808545719
Khamis MI, Ibrahim TH, Jumean FH, Sara ZA, Atallah BA (2020) Cyclic sequential removal of Alizarin Red S dye and Cr(VI) ions using wool as a low-cost adsorbent. Processes. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8050556
Lai B, Zhou Y, Wang J, Yang Z, Chen Z (2013) Application of excitation and emission matrix fluorescence (EEM) and UV–vis absorption to monitor the characteristics of Alizarin Red S (ARS) during electro-Fenton degradation process. Chemosphere 93(11):2805–2813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.09.056
Lee SH, Lee SH (2018) Conductive copper paste for crystalline silicon solar cells. In: Recent developments in photovoltaic materials and devices. IntechOpen, pp 23–41
Lemlikchi W, Sharrock P, Fiallo M, Nzihou A, Mecherri MO (2014) Hydroxyapatite and Alizarin sulfonate ARS modeling interactions for textile dyes removal from wastewaters. Procedia Eng 83:378–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2014.09.032
Li X, Li P, Wu Z, Luo D, Yu H-Y, Lu Z-H (2021) Review and perspective of materials for flexible solar cells. Mater Rep Energy 1(1):100001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matre.2020.09.001
Machado FM, Carmalin SA, Lima EC, Dias SLP, Prola LDT, Saucier C, Jauris IM, Zanella I, Fagan SB (2016) Adsorption of alizarin red S dye by carbon nanotubes: an experimental and theoretical investigation. J Phys Chem C 120(32):18296–18306. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b03884
Nuengmatcha P, Mahachai R, Chanthai S (2016) Adsorption capacity of the as-synthetic graphene oxide for the removal of alizarin red S dye from aqueous solution. Orient J Chem 32(3):1399. https://doi.org/10.13005/ojc/320314
Panahi HA, Karimi M, Moniri E, Soudi H (2008) Development of a sensitive spectrophotometeric method for determination of copper. Afr J Pure Appl Chem 2(10):096–099. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJPAC.9000057
Puchtler H, Meloan SN, Terry MS (1969) On the history and mechanism of alizarin and alizarin red S stains for calcium. J Histochem Cytochem 17(2):110–124. https://doi.org/10.1177/17.2.110
Samantaray MR, Rana NK, Kumar A, Ghosh DS, Chander N (2021) Stability study of large-area perovskite solar cells fabricated with copper as low-cost metal contact. Int J Energy Res. https://doi.org/10.1002/er.7243
Samusolomon J, Devaprasath PM (2011) Removal of Alizarin Red S (Dye) from aqueous media by using Cynodon dactylon as an adsorbent. J Chem Pharm Res 3 (5):478–490. http//:www.jocpr.com
Sangsefedi SA, Sharifi S, Rezaion HRM, Azarpour A (2018) Fluorescence and nonlinear optical properties of alizarin red S in solvents and droplet. J Fluoresc 28(3):815–825. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-018-2245-0
Skowrońska J, Zaczyński J, Kosucki A, Stawiński Ł (2020) Modern materials and surface modification methods used in the manufacture of hydraulic actuators. In: International scientific-technical conference on hydraulic and pneumatic drives and control-NSHP 2020: advances in hydraulic and pneumatic drives and control. Lecture notes in mechanical engineering - hydraulic and pneumatic drives and Control 2020. Springer, Cham, pp 427–439. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59509-8_39
Skowrońska J, Kosucki A, Stawiński Ł (2021) Overview of materials used for the basic elements of hydraulic actuators and sealing systems and their surfaces modification methods. Materials. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14061422
Takahashi S, Suzuki I, Sugawara T, Seno M, Minaki D, Anzai J-I (2017) Alizarin red S-confined layer-by-layer films as redox-active coatings on electrodes for the voltammetric determination of L-dopa. Materials 10(6):581. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10060581
Turcanu A, Bechtold T (2011) pH Dependent redox behaviour of Alizarin Red S (1,2-dihydroxy-9,10-anthraquinone-3-sulfonate) – Cyclic voltammetry in presence of dispersed vat dye. Dyes Pigm 91(3):324–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2011.04.011
Yang J-Y, Jiang X-Y, Jiao F-P, Yu J-G (2018) The oxygen-rich pentaerythritol modified multi-walled carbon nanotube as an efficient adsorbent for aqueous removal of alizarin yellow R and alizarin red S. Appl Surf Sci 436:198–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.12.029
Zhou S, Zhang X, Li W, Li L, Cai X (2017) Experimental evaluation of fluorescent (alizarin red S and calcein) and clip-tag markers for stock assessment of ark shell, Anadara broughtonii. Chin J Oceanol Limnol 35(2):265–274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-016-5137-7
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to thank Pandit Deendayal Energy University (PDEU) and Solar Research and Development Centre (SRDC) for providing the necessary facilities to carry out this investigation and their support is sincerely acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NM-SA: performing the experiments, interpreting the data, writing the original draft & editing, corresponding person. SV: reviewing & editing. DB: reviewing & editing. Dr. AK: advancing the interpretation of the data, reviewing & editing. Dr. RP: reviewing & editing. Dr. AR: reviewing & editing. Prof. IM: advancing the interpretation of the data, reviewing & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, N.MS., Vemuri, S., Bhagat, D. et al. DC and DP polarographic studies to explore the intermediate species form and operating conditions effects on electrodeposition of Cu from Cu(II) in the presence of alizarin red S. Chem. Pap. 76, 1745–1766 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-01988-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-01988-y