Abstract
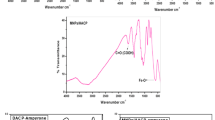
The drug loading efficiency of magnetite nanoparticles (MNPs) can be enhanced by coating with polyethylene glycol (PEG) which is a biocompatible polymer. The PEG-coated MNPs could be the potential candidates for carrying the drug molecules to the targeted sites. In this study, size-controlled MNPs were synthesized and functionalized with PEG of molecular weights 700, 2000 and 5000. The MNPs and PEGylated MNPs (PMNPs) samples were characterized through X-ray diffraction (XRD), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and surface area and pore size measurements by Brunauer, Emmett and Teller (BET) and Barrett–Joyner–Halenda (BJH) methods. The diffraction data showed that MNPs are purely crystalline with face cubic crystal structure, whereas the spherical shape of the particles was confirmed by TEM. The TGA supports thermal stability of nanoparticles which was markedly enhanced by coating with PEG. The BJH data (hysteresis loops) showed that MNPs were mesoporous in nature. After characterization, the PEGylated MNPs were loaded with gallic acid (GA). The spectroscopic evidences regarding the successful PEGylation and loading of GA onto PMNPswere acquired from FTIR spectroscopy. The in vitro sustained drug release efficacy of PMNPs was evaluated via UV–visible spectroscopy. Among all the synthesized samples, P750MNPs-10 showed the highest % drug release i.e., 98% into phosphate buffer saline (PBS) solution of pH 4.4 and 90% in PBS of pH 7.4. The highest % drug release at pH 10 may be attributed to smaller particle size with high surface area. The highest % drug release can also be associated with the weak interactions between P750MNPs-10 and GA through hydrogen bonding.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen TM, Cullis PR (2013) Liposomal drug delivery systems: from concept to clinical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65(1):36–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2012.09.037
Allen TM, Hansen CB, de Menezes DEL (1995) Pharmacokinetics of long-circulating liposomes. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 16(2):267–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/0169-409X(95)00029-7
Arruebo M, Pacheco R, Ibarra M, Santamaría J (2007) Magnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nano Today 2:22–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1748-0132(07)70084-1
Barahuie F, Dorniani D, Saifullah B, Gothai S, Hussein MZ, Pandurangan AK, Arulselvan P, Norhaizan ME (2017) Sustained release of anticancer agent phytic acid from its chitosan-coated magnetic nanoparticles for drug-delivery system. Int J Nanomed 12:2361–2372. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S126245
Bulte JWM, Kraitchman DL (2004) Iron oxide MR contrast agents for molecular and cellular imaging. NMR Biomed 17(7):484–499. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.924
Cerda-Sumbarda YD, Zapata-Gonzalez I, Licea-Claverie A, Zizumbo-Lopez A, Ramos-de Valle LF, Espinoza-Martínez A (2019) Poly(hexylacrylate)Core-poly(ethyleneglycol methacrylate)Shell nanogels as fillers for poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) nanocomposite hydrogels. Polym Eng Sci 59(1):170–181. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.24884
Cho K, Wang X, Nie S, Chen Z, Shin DM (2008) Therapeutic nanoparticles for drug delivery in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14(5):1310–1316. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-07-1441
Chomoucka J, Drbohlavova J, Huska D, Adam V, Kizek R, Hubalek J (2010) Magnetic nanoparticles and targeted drug delivering. Pharmacol Res 62(2):144–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2010.01.014
Curl RL (1963) Dispersed phase mixing: I. Theory and effects in simple reactors. AIChE J 9(2):175–181. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.690090207
D’Souza S (2014) A review of in vitro drug release test methods for nano-sized dosage forms. Adv Pharm 304757. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/304757
Darminto, Cholishoh MN, Perdana FA, Baqiya MA, Mashuri, Cahyono Y, Triwikantoro (2011) Preparing Fe3O4 nanoparticles from Fe2+ ions source by co‐precipitation process in various pH. AIP Conference Proceedings 1415:234. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3667264
De Jong WH, Borm PJA (2008) Drug delivery and nanoparticles:applications and hazards. Int J Nanomed 3(2):133–149. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijn.s596
Dong L, Yan L, Hou WG, Liu SJ (2010) Synthesis and release behavior of composites of camptothecin and layered double hydroxide. J Solid State Chem 183:1811–1816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2010.05.035
Dorniani D, Hussein MZB, Kura AU, Fakurazi S, Shaari AH, Ahmad Z (2012) Preparation of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles coated with gallic acid for drug delivery. Int J Nanomed 7:5745
Dorniani D, Hussein M, Kura A, Fakurazi S, Shaari A, Ahmad Z (2013) Sustained release of prindopril erbumine from its chitosan-coated magnetic nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Int J Mol Sci 14:23639–23653. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141223639
Dorniani D, Kura AU, Hussein-Al-Ali SH, Hussein MZB, Fakurazi S, Shaari AH, Ahmad Z (2014) In vitro sustained release study of gallic acid coated with magnetite-PEG and magnetite-PVA for drug delivery system. Sci World J 416354. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/416354
Faraji M, Yamini Y, Rezaee M (2010) Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, stabilization, functionalization, characterization, and applications. J Iran Chem Soc 7(1):1–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03245856
Guerra D, Viana R, Airoldi C (2009) Adsorption of mercury cation on chemically modified clay. Mater Res Bull 44:485–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2008.08.002
Gunasundari E, Senthil Kumar P, Christopher FC, Arumugam T, Saravanan A (2017) Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles loaded ultrasonic-assisted Spirulina platensis using algal extract and their antimicrobial activity. IET Nanobiotechnol 11(6):754–758. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-nbt.2016.0223
Javid A, Ahmadian S, Saboury AA, Kalantar SM, Rezaei-Zarchi S, Shahzad S (2014) Biocompatible APTES–PEG modified magnetite nanoparticles: effective carriers of antineoplastic agents to ovarian cancer. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 173(1):36–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0740-6
Kayal S, Ramanujan R (2010) Doxorubicin loaded PVA coated iron oxide nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery. Mater Sci Eng C 30:484–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2010.01.006
Khan B, Nawaz M, Waseem M, Hussain R, Arif S, Price G, Haq S, Rehman W (2019) Adsorption of methylene blue onto size controlled magnetite nanoparticles. Mater Res Exp. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab2ef9
LaMer VK, Dinegar RH (1950) Theory, production and mechanism of formation of monodispersed hydrosols. J Am Chem Soc 72(11):4847–4854. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01167a001
Mahmoudi M, Simchi A, Imani M, Milani AS, Stroeve P (2008) Optimal design and characterization of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles coated with polyvinyl alcohol for targeted delivery and imaging. J Phys Chem B 112(46):14470–14481. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp803016n
Mahmoudi M, Simchi A, Imani M (2009) Cytotoxicity of uncoated and polyvinyl alcohol coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 113(22):9573–9580. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp9001516
Na K, Lee ES, Bae YH (2003) Adriamycin loaded pullulan acetate/sulfonamide conjugate nanoparticles responding to tumor pH: pH-dependent cell interaction, internalization and cytotoxicity in vitro. J Control Rel 87(1–3):3–13
Na K, Lee ES, Bae YH (2007) Self-organized nanogels responding to tumor extracellular pH: pH-dependent drug release and in vitro cytotoxicity against MCF-7 cells. Bioconj Chem 18(5):1568–1574
Niemann B, Sundmacher K (2010) Nanoparticle precipitation in microemulsions: population balance model and identification of bivariate droplet exchange kernel. J Coll Interf Sci 342(2):361–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2009.10.066
Niemann B, Rauscher F, Adityawarman D, Voigt A, Sundmacher K (2006) Microemulsion-assisted precipitation of particles: experimental and model-based process analysis. Chem Eng Process Process Intensif 45(10):917–935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2005.10.012
Niemann B, Veit P, Sundmacher K (2008) Nanoparticle precipitation in reverse microemulsions: particle formation dynamics and tailoring of particle size distributions. Langmuir 24(8):4320–4328. https://doi.org/10.1021/la703566v
Pang Y, Zeng G, Tang L, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Lei X, Li Z, Zhang J, Liu Z, Xiong Y (2011) Preparation and application of stability enhanced magnetic nanoparticles for rapid removal of Cr (VI). Chem Eng J 175:222–227
Paul KG, Frigo TB, Groman JY, Groman EV (2004) Synthesis of ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxides using reduced polysaccharides. Bioconj Chem 15(2):394–401. https://doi.org/10.1021/bc034194u
Plank C, Schillinger U, Scherer F, Bergemann C, Remy JS, Krötz F, Anton M, Lausier J, Rosenecker J (2003) The magnetofection method: using magnetic force to enhance gene delivery. Biol Chem 384:737–747. https://doi.org/10.1515/BC.2003.082
Prijic S, Sersa G (2011) Magnetic nanoparticles as targeted delivery systems in oncology. Radiol Oncol 45(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10019-011-0001-z
Saifuddin N, Wong CW, Nur Yasumira AA (2009) Rapid biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using culture supernatant of bacteria with microwave irradiation. J Chem 6(1):61–70
Sun C, Sze R, Zhang M (2006a) Folic acid-PEG conjugated superparamagnetic nanoparticles for targeted cellular uptake and detection by MRI. J Biomed Mater Res A 78A(3):550–557. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.30781
Sun C, Sze R, Zhang M (2006b) Folic acid-PEG conjugated superparamagnetic nanoparticles for targeted cellular uptake and detection by MRI. J Biomed Mater Res A off J Soc Biomater Jpn Soc Biomater Aust Soc Biomater Korean Soc Biomater 78(3):550–557
Tan S, Wu T, Zhang D, Zhang Z (2015) Cell or cell membrane-based drug delivery systems. Theranostics 5(8):863–881. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.11852
Tang M, Dou H, Sun K (2006) One-step synthesis of dextran-based stable nanoparticles assisted by self-assembly. Polymer 47:728–734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2005.11.091
Tao X, Jin S, Wu D, Ling K, Yuan L, Lin P, Xie Y, Yang X (2016) Effects of particle hydrophobicity, surface charge, media pH value and complexation with human serum albumin on drug release behavior of mitoxantrone-loaded pullulan nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 6(1):2
Thanh NTK, Maclean N, Mahiddine S (2014) Mechanisms of nucleation and growth of nanoparticles in solution. Chem Rev 114(15):7610–7630
Ulbrich K, Hola K, Subr V, Bakandritsos A, Tucek J, Zboril R (2016) Targeted drug delivery with polymers and magnetic nanoparticles: covalent and noncovalent approaches, release control, and clinical studies. Chem Rev 116(9):5338–5431
Vuković G, Marinković A, Obradović M, Radmilović V, Čolić M, Aleksić R, Uskoković PS (2009) Synthesis, characterization and cytotoxicity of surface amino-functionalized water-dispersible multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Appl Surf Sci 255(18):8067–8075. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.05.016
Zbigniew S, Budzyński M, Durak K, Czernel G (2017) Synthesis and characterization of iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles. Nukleonika 62(2):73–77
Zhang Y, Zhang L, Ban Q, Li J, Li C-H, Guan Y-Q (2018) Preparation and characterization of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles carrying insulin and gallic acid for insulin oral delivery. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med 14(2):353–364
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. G. Kociok-Köhn for the XRD and to Dr. Rami for TG/DTA analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, B., Nawaz, M., Price, G.J. et al. In vitro sustained release of gallic acid from the size-controlled PEGylated magnetite nanoparticles. Chem. Pap. 75, 5339–5352 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-01724-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-01724-6