Abstract
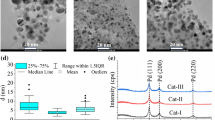
Liquid-phase hydrogenation of 4-chloronitrobenzene (4-CNB) to 4-chloroaniline (4-CAN) under mild reaction conditions (0.6 MPa, 25 °C, methanol-diethyl ether, 1:1 vol.) over palladium and platinum catalysts containing 1 mass% of metal supported on beta zeolite (M/B) or γ-alumina (M/A) was studied. The catalysts were prepared by the incipient wetness method using amino nitrate complexes and hydrogen as the reducing agent. SEM, adsorption–desorption nitrogen isotherms, XRD, TEM, and hydrogen chemisorption techniques were used for their characterization. The techniques employed revealed the presence of relatively large metal particles (approximately 15 nm; about 3% of metal dispersion). Stability of the catalysts during the hydrogenation was high; no catalyst changes were observed after two recycle runs. Hydrogenation over M/A catalysts was found to be faster than that over M/B catalysts in the methanol–diethyl ether mixture. Selectivity of only about 75% to 4-CAN was achieved over the M/A catalyst in methanol. Positive effect of the acid support (beta zeolite) and low polarity of the reaction environment (diethyl ether) are reflected in the high selectivity to 4-CAN; of about 99% at virtually 100% conversion of 4-CNB.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AC:
-
Activated carbon
- Al-PILC:
-
Al-pillared clay
- AN:
-
Aniline
- ASMA:
-
Amino poly[styrene-co-maleic anhydride]
- B:
-
Benzene
- BET:
-
Brunauer, Emmet, and Teller
- 4-CAN:
-
4-Chloroaniline
- CHAN:
-
Cyclohexane
- ClPhNO:
-
Chloronitrosobenzene
- ClPhHNOH:
-
N-chloro-phenylhydroxylamine
- CN:
-
Carbon nitride
- 4-CNB:
-
4-Chloronitrobenzene
- CNT:
-
Carbon nanotubes
- DABP:
-
4,4′-Diaminobiphenyl
- DETE:
-
Diethyl ether
- DMF:
-
Dimethylformamide
- DR:
-
Dubinin–Radushkevich
- DOX:
-
1,4-Dioxane
- EG:
-
Ethylene glycol
- EtOAc:
-
Ethyl acetate
- EtOH:
-
Ethanol
- FTIR:
-
Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy
- GO:
-
Graphite oxide
- HDC:
-
Hydrodechlorination
- HDN:
-
Hydrodenitrogenation
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- M/A:
-
1 mass% of metal supported on γ-alumina
- M/B:
-
1 mass% of metal supported on beta zeolite
- MeOH:
-
Methanol
- MC:
-
Mesoporous carbon
- MS:
-
Mesoporous silica
- NB:
-
Nitrobenzene
- NTO:
-
Nitrotoluene
- NAN:
-
Nitroaniline
- NAS:
-
Nitroanisole
- NMR:
-
Nuclear magnetic resonance
- NTs:
-
Nanotubes
- Rec.:
-
Number of repetitions with the same catalyst
- SAED:
-
Selective electron diffraction
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscopy
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscopy
- THF:
-
Tetrahydrofurane
- TMB:
-
Trimethylbenzene
- TOFH2 :
-
Turn over frequencies (molH2 mol −1metal s−1)
- TOFs,H2 :
-
Turn over frequencies with respect to the metal surface (molH2 m−2 s−1)
- Tol:
-
Toluene
- TPD:
-
Temperature-programmed desorption
- W:
-
Water
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
- XPS:
-
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
- C :
-
coefficient in the BET isotherm
- d :
-
Average size of metal particles (nm)
- d H2,CHS :
-
Average size of metal particles estimated from H2 sorption (nm)
- d TEM :
-
Average size of metal particles estimated from TEM (nm)
- d s,TEM :
-
Average size of metal particles estimated from TEM with respect to the surface (nm)
- d V,TEM :
-
Average size of metal particles estimated from TEM with respect to the volume (nm)
- d XRD :
-
Average size of metal particles estimated from XRD (nm)
- D M :
-
Dispersion of metal (%)
- D hkl :
-
Lattice parameter (nm)
- f H2,M :
-
Factor expressing number of metal atoms interacting with hydrogen molecule
- K:
-
The Scherrer’s constant (usually 0.9)
- m cat :
-
Mass of a catalyst (g)
- n CNB,0 :
-
Moles of x-CNB in the starting reaction mixture (mol)
- n CNB,t :
-
Moles of x-CNB in the reaction mixture at time t (mol)
- n H2,Chs :
-
Moles of H2 chemisorbed on catalyst sample (mol g−1)
- n H2,r :
-
Moles of H2 consumed in the hydrogenation process (mol)
- n Y :
-
Moles of component “Y” in the reaction mixture (mol)
- P :
-
Polarity of a solvent (Pwater = 100)
- s M :
-
Specific surface of metal particles (m2 g−1)
- s A,M :
-
Surface equivalent of one metal atom (m2)
- S Y :
-
Selectivity to compound “Y” (%)
- t :
-
Time (s)
- T FP :
-
Flash point temperature (°C)
- T AI :
-
Autoignition temperature (°C)
- v a :
-
Adsorbed amount expressed in the liquefied form (cm3 g−1)
- V mi :
-
Volume of micropores (cm3 g−1)
- w M :
-
Content of the metal in the dry catalyst (wt%)
- x :
-
Relative pressure (x = p/ps)
- x H2,25°C :
-
Mole fraction of H2 at 25 °C and 101.325 kPa
- X CNB :
-
Conversion of chloronitrobenzene (%)
- ε r :
-
Relative permittivity (dielectric constant)
- Δ M :
-
Loose of the metal content as a portion of the initial amount of metal (%)
- δ :
-
Solubility parameter
- \(\overline{\delta }\) :
-
Average error
- λ:
-
Wavelength of the X-ray used for the XRD (nm)
- ρ :
-
Density (kg m−3)
- η :
-
Dynamic viscosity (cP)
- μ :
-
Dipole moment (D)
References
Amorim C, Keane MA (2008) Palladium supported on structured and nonstructured carbon: a consideration of Pd particle size and the nature of reactive hydrogen. J Colloid Interface Sci 322(1):196–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2008.02.021
Antonetti C, Oubenali M, Galletti AMR, Serp P, Vannucci G (2012) Novel microwave synthesis of ruthenium nanoparticles supported on carbon nanotubes active in the selective hydrogenation of p-chloronitrobenzene to p-chloroaniline. Appl Catal A 421:99–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2012.02.003
Aramendıa MA, Borau V, Garcıa M, Jimenez C, Marinas JM, Urbano FJ (2003) Liquid-phase hydrodehalogenation of substituted chlorobenzenes over palladium supported catalysts. Appl Catal B 43(1):71–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-3373(02)00279-5
Aranovich GL (1991) New polymolecular adsorption isotherm. J Colloid Interface Sci 141(1):30–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9797(91)90299-N
Arjunan V, Raj A, Sakiladevi S, Carthigayan K, Mohan S (2012) A comparative spectroscopic, electronic structure and chemical shift investigations of o-chloronitrobenzene, p-chloronitrobenzene and m-chloronitrobenzene. J Mol Struct 1007:122–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2011.10.033
Bai Q, Li D, He L, Xiao H, Sui N, Liu M (2015) Solvent-free selective hydrogenation of o-chloronitrobenzene to o-chloroaniline over alumina supported Pt nanoparticles. Prog Nat Sci Mater Int 25(3):179–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnsc.2015.05.005
Bhatia S (1989) Zeolite catalysts: principles and applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton, p 304. ISBN 9780849356285
Blaser HU, Steiner H, Studer M (2009) Selective catalytic hydrogenation of functionalized nitroarenes: an update. ChemCatChem 1(2):210–221. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.200900129
Brunauer S, Emmett PH, Teller E (1938) Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J Am Chem Soc 60(2):309–319. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01269a023
Buttersack C, Hofmann J, Gläser R (2016) Determination of micropore volume and external surface of zeolites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 236:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2016.08.018
Campos CH, Jofré M, Torres CC, Pawelec B, Fierro JLG, Reyes P (2014) Chemoselective hydrogenation of o-, p- and m-chloronitrobenzene at ambient temperature on Au/Fe2O3 catalysts. Appl Catal A 482:127–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2014.06.001
Canton P, Menegazzo F, Polizzi S, Pinna F, Pernicone N, Riello P, Fagherazzi G (2003) Structure and size of poly-domain Pd nanoparticles supported on silica. Catal Lett 88(3–4):141–146. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1024001520260
Cárdenas-Lizana F, Keane MA (2013) The development of gold catalysts for use in hydrogenation reactions. J Mater Sci 48(2):543–556. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-012-6766-7
Cárdenas-Lizana F, Lamey D, Perret N, Gómez-Quero S, Kiwi-Minsker L, Keane MA (2012) Au/Mo2N as a new catalyst formulation for the hydrogenation of p-chloronitrobenzene in both liquid and gas phases. Catal Commun 21:46–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2012.01.027
Cárdenas-Lizana F, Gómez-Quero S, Amorim C, Keane MA (2014a) Gas phase hydrogenation of p-chloronitrobenzene over Pd–Ni/Al2O3. Appl Catal A 473:41–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2014.01.001
Cárdenas-Lizana F, Wang X, Lamey D, Li M, Keane MA, Kiwi-Minsker L (2014b) An examination of catalyst deactivation in p-chloronitrobenzene hydrogenation over supported gold. Chem Eng J 255:695–704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.04.116
Červený L, Bartoň J, Růžička V (1977) The effect of solvents on the catalytic hydrogenation of p-substituted nitrobenzenes. Collect Czechoslov Chem Commun 42(12):3402–3409. https://doi.org/10.1135/cccc19773402
Chen YZ, Chen YC (1994) Hydrogenation of para-chloronitrobenzene over nickel borides. Appl Catal A 115(1):45–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/0926-860X(94)80377-3
Chen YW, Lee DS (2013a) Selective hydrogenation of p-chloronitrobenzene on nanosized PdNiB catalysts. J Nanoparticles 2013:132180. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/132180
Chen YW, Lee DS (2013b) Liquid phase hydrogenation of p-chloronitrobenzene on Au-Pd/TiO2 catalysts: effects of reduction methods. Mod Res Catal 2(2):25–34. https://doi.org/10.4236/mrc.2013.22004
Chen YW, Sasirekha N, Liu YC (2009) Hydrogenation of p-chloronitrobenzene over NiPtB nanoalloy catalysts. J Non Cryst Solids 355(22):1193–1201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.noncrysol.2009.05.007
Chen C, Wu Q, Chen F, Zhang L, Pan S, Bian C, Zheng X, Meng X, Xiao FS (2015a) Aluminium-rich beta zeolite-supported platinum nanoparticles for the low-temperature catalytic removal of toluene. J Mater Chem A 3(10):5556–5562. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TA06407K
Chen T, Li D, Jiang H, Xiong C (2015b) High-performance Pd nanoalloy on functionalized activated carbon for the hydrogenation of nitroaromatic compounds. Chem Eng J 259:61–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.07.054
Chen H, He D, He Q, Jiang P, Zhou G, Fu W (2017) Selective hydrogenation of p-chloronitrobenzene over an Fe promoted Pt/AC catalyst. RSC Adv 7(46):29143–29148. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA04700B
Corma A, Serna P, Concepción P, Calvino JJ (2008) Transforming nonselective into chemoselective metal catalysts for the hydrogenation of substituted nitroaromatics. JACS 130(27):8748–8753. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja800959g
de Lucas A, Ramos MJ, Dorado F, Sánchez P, Valverde JL (2005) Influence of the Si/Al ratio in the hydroisomerization of n-octane over platinum and palladium beta zeolite-based catalysts with or without binder. Appl Catal A 289(2):205–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2005.05.001
Dongil AB, Rivera-Cárcamo C, Pastor-Pérez L, Sepúlveda-Escribano A, Reyes P (2015) Ir supported over carbon materials for the selective hydrogenation of chloronitrobenzenes. Catal Today 249:72–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2014.10.034
Dongil AB, Pastor-Pérez L, Fierro JL, Escalona N, Sepúlveda-Escribano A (2016) Synthesis of palladium nanoparticles over graphite oxide and carbon nanotubes by reduction in ethylene glycol and their catalytic performance on the chemoselective hydrogenation of para-chloronitrobenzene. Appl Catal A 513:89–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2015.11.048
Dorokhov VG, Savchenko VI (2014) Kinetics of the liquid-phase catalytic hydrogenation of chlorine-containing aromatic nitro compounds in the presence of pyridine. Kinet Catal 55(4):446–455. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0023158414040028
Dutta D, Dutta DK (2014) Selective and efficient hydrogenation of halonitrobenzene catalyzed by clay supported Nio-nanoparticles. Appl Catal A 487:158–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2014.09.004
Dyson PJ, Jessop PG (2016) Solvent effects in catalysis: rational improvements of catalysts via manipulation of solvent interactions. Catal Sci Technol 6(10):3302–3316. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CY02197A
Ertl G, Weitkamp J, Knozinger H (eds) (2008) Preparation of solid catalysts. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken
Fadoni M, Lucarelli L (1999) Temperature programmed desorption, reduction, oxidation and flow chemisorption for the characterisation of heterogeneous catalysts. Theoretical aspects, instrumentation and applications. In: Dabrowski A (ed) Studies in surface science and catalysis, vol 120A. Elsevier Science B.V, Amsterdam, pp 177–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-2991(99)80553-9
Fu T, Hu P, Wang T, Dong Z, Xue N, Peng L, Guo X, Ding W (2015) High selectivity to p-chloroaniline in the hydrogenation of p-chloronitrobenzene on Ni modified carbon nitride catalyst. Chin J Catal 36(11):2030–2035. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(15)60904-4
Fu H, Zhang L, Wang Y, Chen S, Wan Y (2016) Thermally reduced gold nanocatalysts prepared by the carbonization of ordered mesoporous carbon as a heterogeneous catalyst for the selective reduction of aromatic nitro compounds. J Catal 344:313–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2016.09.021
Gómez-Quero S, Cárdenas-Lizana F, Keane MA (2010) Solvent effects in the hydrodechlorination of 2, 4-dichlorophenol over Pd/Al2O3. AIChE J 56(3):756–767. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.12012
Han XX, Chen Q, Zhou RX (2007) Study on the hydrogenation of p-chloronitrobenzene over carbon nanotubes supported platinum catalysts modified by Mn, Fe Co, Ni and Cu. J Mol Catal A Chem 277(1–2):210–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2007.07.052
Harkins WD, Jura G (1943) An adsorption method for the determination of the area of a solid without the assumption of a molecular area, and the area occupied by nitrogen molecules on the surfaces of solids. J Chem Phys 11(9):431–432. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1723871
Horáček J, Šťávová G, Kelbichová V, Kubička D (2013) Zeolite-beta-supported platinum catalysts for hydrogenation/hydrodeoxygenation of pyrolysis oil model compounds. Catal Today 204:38–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2012.08.015
Horniaková J, Králik M, Kaszonyi A, Mravec D (2001) A practical approach to the treatment of adsorption–desorption isotherms, acidity and catalytic behaviour of zeolite catalysts. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 46:287–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1387-1811(01)00309-2
Hudec P, Smiešková A, Židek Z, Schneider P, Šolcová O (2002) Determination of microporous structure of zeolites by t-plot method—state-of-the-art. In: Aiello R, Giordanio G, Testa P (eds) Studies in surface science and catalysis, vol 142. Elsevier Science B.V, Amsterdam, pp 1587–1594. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-2991(02)80328-7
Indra A, Rajamohanan PR, Gopinath CS, Bhaduri S, Lahiri GK (2011) Selective hydrogenation of chloronitrobenzenes with an MCM-41 supported platinum allyl complex derived catalyst. Appl Catal A 399:117–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2011.03.044
Jiménez C, Romero FJ, Roldán R, Marinas JM, Gómez JP (2003) Hydroisomerization of a hydrocarbon feed containing n-hexane, n-heptane and cyclohexane on zeolite-supported platinum catalysts. Appl Catal A 249(1):175–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-860X(03)00177-7
Johansson M, Skulason E, Nielsen G, Murphy S, Nielsen RM, Chorkendorff I (2010) Hydrogen adsorption on palladium and palladium hydride at 1bar. Surf Sci 604(7):718–729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susc.2010.01.023
Karge HG (2008) Concepts and analysis of surface acidity and basicity. In Ertl G, Knözinger H, Schüth F, Weitkamp J (eds) Handbook of heterogeneous catalysis, 2nd edn, vol 8. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, pp 1096–1122. ISBN: 9783527312412
Králik M (2014) Adsorption, chemisorption, and catalysis. Chem Pap 68(12):1625–1638. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-014-0624-9
Kralik M, Vallusova Z, Laluch J, Mikulec J, Macho V (2008) Comparison of ruthenium catalysts supported on beta and mordenite in the hydrocycloalkylkation of benzene. Pet Coal 50(1):44–51
Králik M, Vallušová Z, Major P, Takáčová A, Hronec M, Gašparovičová D (2014) Hydrogenation of chloronitrobenzenes over Pd and Pt catalysts supported on cationic resins. Chem Pap 68(12):1690–1700. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-014-0565-3
Kratky V, Kralik M, Mecarova M, Stolcova M, Zalibera L, Hronec M (2002) Effect of catalyst and substituents on the hydrogenation of chloronitrobenzenes. Appl Catal A 235:225–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-860X(02)00274-0
Krátky V, Králik M, Kaszonyi A, Štolcová M, Zalibera L, Mečárová M, Hronec M (2003) Reaction pathways and the role of solvent in the hydrogenation of chloronitrobenzenes. Collect Czechoslov Chem Commun 68:1819–1832. https://doi.org/10.1135/cccc20031819
Lecloux AJ (1981) Texture of catalysts. In: Anderson JR, Boudart M (eds) Catalysis: science and technology, vol 2. Springer, Berlin, pp 171–230. ISBN 354010593X
Lee DS, Chen YW (2013) Hydrogenation of p-chloronitrobenzene on La-doped NiMoB nanocluster catalysts. Chin J Catal 34(11):2018–2028. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(12)60687-1
Li H, Lin H, Hu Y, Li H, Li P, Zhou X (2011) Hollow Pt-Ni alloy nanospheres with tunable chamber structure and enhanced activity. J Mater Chem 21(45):18447–18453. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1jm11461a
Li HB, Liu L, Ma XY (2016) Effective hydrogenation of haloaromatic nitro compounds catalysed by iridium nanoparticles deposited on multiwall carbon nanotubes. Synth React Inorg Metal Org Nano Metal Chem 46(10):1499–1505. https://doi.org/10.1080/15533174.2015.1137013
Liu X, Mäki-Arvela P, Aho A, Vajglova Z, Gun’ko VM, Heinma I, Kumar N, Eränen K, Salmi T, Murzin DY (2018) Zeta Potential of beta zeolites: influence of structure, acidity, pH, temperature and concentration. Molecules 23(4):946. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23040946
Lyu J, Wang J, Lu C, Ma L, Zhang Q, He X, Li X (2014) Size-dependent halogenated nitrobenzene hydrogenation selectivity of Pd nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 118(5):2594–2601. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp411442f
Lyubimenko EN, Goltsova MV (2014) The form changing of palladium plate induced by small one-side hydrogen impacts. Metallofiz Noveishie Tekhnol 36(2):247–258. https://doi.org/10.15407/mfint.36.02.0247 (in Russian)
Ma L, Wang J, Wang H, Zhang Q, Lu C, He X, Li X (2017) High halogenated nitrobenzene hydrogenation selectivity over nano Ir particles. Chin J Chem Eng 25(3):306–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2016.08.005
Mo M, Zhou M, Xie M, Han L, Guo X, Ding W (2015) Tri-component noncrystalline Ni–Cu–B nanotubes with enhanced stability and catalytic performance for hydrogenation of p-chloronitrobenzene. Catal Commun 64:66–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2015.02.005
Murzin DY (2016) Solvent effects in catalysis: implementation for modelling of kinetics. Catal Sci Technol 6(14):5700–5713. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CY00495D
Ning JB, Xu J, Liu J, Miao H, Ma H, Chen C, Li XQ, Zhou L, Yu W (2007) A remarkable promoting effect of water addition on selective hydrogenation of p-chloronitrobenzene in ethanol. Catal Commun 8:1763–1766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2007.01.032
Nuzhdin AL, Moroz BL, Bukhtiyarova GA, Reshetnikov SI, Pyrjaev PA, Aleksandrov PV, Bukhtiyarov VI (2015) Selective liquid-phase hydrogenation of a nitro group in substituted nitrobenzenes over Au/Al2O3 catalyst in a packed-bed flow reactor. ChemPlusChem 80(12):1741–1749. https://doi.org/10.1002/cplu.201500310
Phung TK, Busca G (2015) Diethyl ether cracking and ethanol dehydration: acid catalysis and reaction paths. Chem Eng J 272:92–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.03.008
Pietrowski M (2012) Recent developments in heterogeneous selective hydrogenation of halogenated nitroaromatic compounds to halogenated anilines. Curr Org Synth 9(4):470–487. https://doi.org/10.2174/157017912802651456
Pizarro AH, Molina CB, Casas JA, Rodriguez JJ (2014) Catalytic HDC/HDN of 4-chloronitrobenzene in water under ambient-like conditions with Pd supported on pillared clay. Appl Catal B 158:175–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.04.011
Plößer J, Dedeaga F, Lucas M, Claus P (2016a) The effect of catalyst preparation conditions on the synthesis of menthol from citronellal on Ru/H-BEA. Appl Catal A 516:100–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2016.02.014
Plößer J, Lucas M, Warna J, Salmi T, Murzin DY, Claus P (2016b) Kinetics of the one-pot transformation of citronellal to menthols on Ru/H-BEA catalysts. Org Process Res Dev 20(9):1647–1653. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.oprd.6b00214
Ragaini V, Giannantonio R, Magni P, Lucarelli L, Leofanti G (1994) Dispersion measurement by the single introduction method coupled with the back-sorption procedure: a chemisorption and TPD study of the different chemisorbed hydrogen species: II. Pd on alumina. J Catal 146(1):116–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9517(94)90014-0
Regalbuto JR, Antos GJ (2004) Preparation of reforming catalysts. In: Antos GJ, Aitani AM (eds) Catalytic naphtha reforming, revised and expanded. Chemical industries. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 133–186 ISBN: 0824750586, 97808203913505
Samant MG, Boudart M (1991) Support effects on electronic structure of platinum clusters in Y zeolite. J Phys Chem 95(10):4070–4074. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100163a034
Satterfield CN (1980) Heterogeneous catalysis in practice. McGraw-Hill chemical engineering series. McGraw-Hill, New York
Scherrer P (1918) Bestimmung der Grösse und der inneren Struktur von Kolloidteilchen mittels Röntgenstrahlen. Nachrichten von der Königlichen Gesellschaft der Wissenschafen zu Göttingen 26(2):98–100 (in German)
Schneider P (1995) Adsorption isotherms of microporous-mesoporous solids revisited. Appl Catal A 129:157–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/0926-860X(95)00110-7
Serna P, Corma A (2015) Transforming nano metal nonselective particulates into chemoselective catalysts for hydrogenation of substituted nitrobenzenes. ACS Catal 5(12):7114–7121. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.5b01846
Skripov NI, Belykh LB, Sterenchuk TP, Schmidt FK (2015) Effect of the nature of a solvent on properties of Pd–P catalysts in hydrogenation of ortho-chloronitrobenzene. Russ J Appl Chem 88(8):1255–1260. https://doi.org/10.1134/S107042721508054
Smallwood I (2012) Handbook of organic solvent properties. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford
Song J, Huang ZF, Pan L, Li K, Zhang X, Wang L, Zou JJ (2018) Review on selective hydrogenation of nitroarene by catalytic, photocatalytic and electrocatalytic reactions. Appl Catal B 227:386–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.01.052
Sundaraganesan N, Karpagam J, Sebastian S, Cornard JP (2009) The spectroscopic (FTIR, FT-IR gas phase and FT-Raman), first order hyperpolarizabilities, NMR analysis of 2,4-dichloroaniline by ab initio HF and density functional methods. Spectrochim Acta Part A 73:11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2009.01.007
Thommes M, Kaneko K, Neimark AV, Olivier JP, Rodriguez-Reinoso F, Rouquerol J, Sing KSW (2015) Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl Chem 87(9–10):1051–1069. https://doi.org/10.1515/pac-2014-1117
Tkachenko OP, Kustov LM, Tarasov AL, Klementiev KV, Kumar N, Murzin DY (2009) Pd/H-Beta catalysts: characterization and reactivity in piperonyl alcohol selective oxidation. Appl Catal A 359(1–2):144–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2009.02.049
Treacy MM, Higgins JB (2007) Collection of simulated XRD powder patterns for zeolites fifth (5th) revised edition. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Trueba M, Trasatti SP (2005) γ-Alumina as a support for catalysts: a review of fundamental aspects. Eur J Inorg Chem 17:3393–3403. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejic.200500348
Tungler A, Tarnai T, Hegedus L, Fodor K, Máthé T (1998) Palladium-mediated heterogeneous catalytic hydrogenations. Selectivity of liquid-phase reactions for the fine chemicals industry. Platin Met Rev 42(3):108–115
Villegas JI, Kumar N, Heikkilä T, Lehto VP, Salmi T, Murzin DY (2007) A study on the dimerization of 1-butene over beta zeolite. Top Catal 45(1–4):187–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-007-0263-2
Wang J, Fan G, Wang H, Li F (2011) Synthesis, characterization, and catalytic performance of highly dispersed supported nickel catalysts from Ni–Al layered double hydroxides. Ind Eng Chem Res 50(24):13717–13726. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie2015087
Wang Y, Rong Z, Wang Y, Zhang P, Wang Y, Qu J (2015) Ruthenium nanoparticles loaded on multiwalled carbon nanotubes for liquid-phase hydrogenation of fine chemicals: an exploration of confinement effect. J Catal 329:95–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2015.04.034
Wang W, Xu W, Thapa KB, Yang X, Liang J, Zhu L, Zhu J (2017) Morpholine-modified Pd/γ-Al2O3@ASMA pellet catalyst with excellent catalytic selectivity in the hydrogenation of p-chloronitrobenzene to p-chloroaniline. Catalysts 7(10):292. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7100292
Xiao C, Wang X, Lian C, Liu H, Liang M, Wang Y (2012) Selective hydrogenation of halonitrobenzenes. Curr Org Chem 16(2):280–296. https://doi.org/10.2174/138527212798993077
Xu Q, Wang L, Chen J, Li X, Li R (2007) Selective hydrogenation of p-chloronitrobenzene over Ru–Ir/γ-Al2O3 catalyst modified by organic amines. Chin J Catal 28(7):579–581. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(07)60047-3
Yang J, Xiong C, Han X, Zhou L (2009) Liquid phase hydrogenation of chloronitrobenzene to chloroaniline with PtM/CNTs (M=La, Ce, Pr, Nd and Sm) catalysts. Ind J Chem 48A:1358–1363
Yang B, Zhang Q, Ma X, Kang J, Shi J, Tang B (2016) Preparation of a magnetically recoverable nanocatalyst via cobalt-doped Fe3O4 nanoparticles and its application in the hydrogenation of nitroarenes. Nano Res 9(7):1879–1890. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1080-3
Young CL (1981) Hydrogen and deuterium. In: IUPAC solubility data series, vol 5/6. Pergamon press, Oxford
Yu K, Kumar N, Aho A, Roine J, Heinmaa I, Murzin DY, Ivaska A (2016) Determination of acid sites in porous aluminosilicate solid catalysts for aqueous phase reactions using potentiometric titration method. J Catal 335:117–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2015.12.010
Yu W, Lin HW, Tan CS (2017) Direct synthesis of Pd incorporated in mesoporous silica for solvent-free selective hydrogenation of chloronitrobenzenes. Chem Eng J 325:124–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.05.051
Zhang X, Zhang P, Yu H, Ma Z, Zhou S (2015) Mesoporous KIT-6 supported Pd–MxOy (M=Ni Co, Fe) catalysts with enhanced selectivity for p-chloronitrobenzene hydrogenation. Catal Lett 145(3):784–793. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-015-1480-0
Zhao B, Chen YW (2010) Hydrogenation of p-chloronitrobenzene on Mo, La, Fe, and W-modified NiCoB nanoalloy catalysts. J Non Cryst Solids 356:839–847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2010.01.009
Zhao Z, Yang H, Li Y (2014) Synergistic effect from Lewis acid and the Ni–W2C/AC catalyst for highly active and selective hydrogenation of aryl nitro to aryl amine. RSC Adv 4(43):22669–22677. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA01808G
Acknowledgements
This publication is a result of the project implementation: Hydrogenation in the Liquid Phase, ITMS: 26,220,220,144, supported by the Research & Development Operational Programme funded by the ERDF.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Králik, M., Gašparovičová, D., Turáková, M. et al. Hydrogenation of 4-chloronitrobenzenes over palladium and platinum catalysts supported on beta zeolite and γ-alumina. Chem. Pap. 73, 397–414 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-018-0589-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-018-0589-1