Abstract
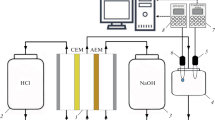
A counter-current two-compartment dialyzer equipped with an anion-exchange membrane Neosepta-AFN was used to study dialysis of a hydrochloric acid and lithium chloride mixture. To quantify this process, several characteristics were calculated from the data obtained at steady state. First, the dialysis process was characterized by the acid recovery yield and rejection coefficient of salt, which were in the range of 61–98% and 62–94%, respectively (for HCl and LiCl concentrations from 0.1 to 1.0 kmol m−3 and volumetric liquid flow rates from 8 × 10−9 to 24 × 10−9 m3 s−1). Furthermore, this study proved that dialysis of an HCl + LiCl mixture can be quantified by a single characteristic, i.e., the permeability coefficient of the membrane to chloride ions, which is a function of the concentration of both the components in the feed.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Membrane area m2
- C :
-
Constant in Eq. (7)
- c :
-
Molar concentration kmol m−3
- D :
-
Diffusivity m2 s−1
- d :
-
Width of compartment m
- d e :
-
Equivalent diameter m
- F :
-
Objective function kmol2 m−6
- J :
-
Molar flux kmol m−2 s−1
- k L :
-
Liquid mass transfer coefficient m s−1
- P :
-
Permeability coefficient of membrane m s−1
- R :
-
Rejection coefficient %
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- Sc :
-
Schmidt number
- Sh :
-
Sherwood number
- \(\dot{V}\) :
-
Volumetric liquid flow rate m3 s−1
- z :
-
Length coordinate m
- z T :
-
Height of compartment m
- v :
-
Recovery %
- calc :
-
Calculated value
- exp :
-
Experimental value
- I :
-
Referred to compartment I
- II :
-
Referred to compartment II
- A :
-
Referred to component A (HCl)
- B:
-
Referred to component B (LiCl)
- Cl− :
-
Referred to Cl− ions
- i :
-
Referred to solution/membrane interface
- in :
-
Inlet
- M :
-
Referred to membrane
- out :
-
Outlet
References
Bendová H, Palatý Z (2011) Modeling of continuous diffusion dialysis of aqueous solutions of sulphuric acid and nickel sulphate. Membr Water Treat 2(4):267–279
Bendová H, Šnejdrla P, Palatý Z (2010) Continuous dialysis of selected salts of sulphuric acid. Membr Water Treat 1(3):171–179. https://doi.org/10.12989/mwt.2010.1.3.171
Coulson JM, Richardson JF (2000) Coulson & Richardson chemical engineering, vol 1, 6th edn. Butterwoth-Heinemann, Oxford
Luo JY, Wu CM, Wu YH, Xu TW (2010) Diffusion dialysis of hydrochloride acid at different temperatures using PPO-SiO2 hybrid anion-exchange membranes. J Membr Sci 347:240–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2009.10.029
Luo JY, Wu CM, Wu YH, Xu TW (2011) Diffusion dialysis process of inorganic acids and their salts: the permeability of different acidic anions. Sep Purif Technol 78:97–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2011.01.028
Luo JY, Wu CM, Wu YH, Xu TW (2013) Diffusion dialysis of hydrochloric acid with their salts: effect of co-existence metal ions. Sep Purif Technol 118:716–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2013.08.014
Mao FL, Zhang GC, Tong JJ, Xu TW, Wu YH (2014) Anion exchange membranes used in diffusion dialysis for acid recovery from erosive and organic solutions. Sep Purif Technol 122:376–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2013.11.031
Palatý Z, Bendová H (2009) Separation of HCl + FeCl2 mixture by anion-exchange membrane. Sep Purif Technol 66(1):45–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2008.11.026
Palatý Z, Bendová H (2011) Continuous dialysis of sulphuric acid in the presence of zinc sulphate. Chem Pap 65:400–406. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-011-0007-4
Palatý Z, Bendová H (2016) Continuous dialysis of sulphuric acid and sodium sulphate mixture. J Membr Sci 497:36–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2015.07.017
Palatý Z, Bendová H (2017) Continuous dialysis of hydrochloric acid and sodium chloride mixture. Sep Sci Technol 52(16):2611–2621. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2017.1363230
Palatý Z, Žáková A (2006) Competitive transport of hydrochloric acid and zinc chloride through polymeric anion-exchange membrane. J Appl Polym Sci 101:1391–1397. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.22748
Palatý Z, Žáková A (2007) Separation of HCl + NiCl2 mixture by diffusion dialysis. Sep Sci Technol 42(9):1965–1983. https://doi.org/10.1080/15363830701313362
Palatý Z, Žáková A, Prchal P (2007) Continuous dialysis of carboxylic acids. Permeability of Neosepta-AME membrane. Desalination 216:345–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2006.09.029
Pan JF, He YB, Wu L, Jiang CX, Wu B, Mondal AN, Cheng CL, Xu TW (2015) Anion-exchange membranes from hot-pressed electrospun QPPO-SiO2 hybrid nanofibers for acid recovery. J Membr Sci 480:115–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2015.01.040
Wang C, Wu CM, Wu YH, Xu TW (2013) Polyelectrolyte complex/PVA membranes for diffusion dialysis. J Hazard Mater 261:114–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.07.018
Xu J, Lu SG, Fu D (2009) Recovery of hydrochloric acid from the waste acid solution by diffusion dialysis. J Hazard Mater 165(1–3):832–837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.10.064
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the Faculty of Chemical Technology, University of Pardubice for the institutional support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bendová, H., Palatý, Z. Continuous dialysis of hydrochloric acid and lithium chloride: permeability of anion-exchange membrane to chloride ions. Chem. Pap. 72, 1151–1157 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-017-0379-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-017-0379-1