Abstract
Purpose
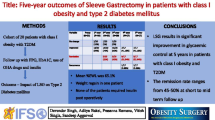
The objective of the study is to evaluate the effects of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG) on mid- to long-term regulation of blood glucose in patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM)
Materials and Methods
In this prospective and observational single-center study, a total of 234 patients with obesity and a diagnosis of T2DM who underwent LSG between 2015 and 2020 were evaluated. The demographics and laboratory data, consisting of body mass index (BMI), glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c%), and fasting plasma glucose (FPG) and total weight loss (TWL%), were compared preoperative and postoperative at 12th and 18th months and annual follow-up for seven consecutive years.
Results
The mean age of 234 patients (female(n)/male(n):191/43) included in the study was 44.69±9.72 years, while the preoperative mean BMI, FPG, and HbA1c values were 47.9±6.82, 132.09±42.84 mg/dl, and 7.02±1.35% respectively. The mean rate of weight loss (TWL%), which was 34.7 in the 18 months, decreased to 23.15 in the 7th year. While the HbA1c % value was 7.02±1.35 in the preoperative, it was found 5.71 ± 0.75 (p<0.001) and 6.30 ± 1.77 (p<0.05) at the 18th month and 7th year after the operation, respectively. While the DM remission rate was 71.1% at the postoperative 18th month, it was 45.4% at the 7th year, despite the patients regaining weight in the follow-ups.
Conclusions
Our study revealed that LSG resulted in high remission rates that continued for 7 years after the surgery, although sustained improvement or remission of diabetes despite some weight regain after the first 18 months.
Graphical Abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grundy SM. Multifactorial causation of obesity: implications for prevention. Am J Clin Nutr. 1998;67(Suppl):563S–72S.
Hill JO, Peters JC. Environmental contributions to the obesity epidemic. Science. 1998;280:1371–4.
Angrisani L, Santonicola A, Iovino P, et al. Bariatric surgery and endoluminal procedures: IFSO worldwide survey 2014. Obes Surg. 2017;27(9):2279–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-017-2666-x. Erratum in: Obes Surg. 2017
Thaler JP, Cummings DE. Hormonal and metabolic mechanisms of diabetes remission after gastrointestinal surgery. Endocrinology. 2009;150(6):2518–25.
Rubino F, Forgione A, Cummings DE, et al. The mechanism of diabetes control after gastrointestinal bypass surgery reveals a role of the proximal small intestine in the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes. Ann Surg. 2006;244(5):741.
Melissas J, Daskalakis M. Gastric emptying after sleeve gastrectomy. Obes Surg. 2011;21(11):1810–1.
Melissas J, Koukouraki S, Askoxylakis J, et al. Sleeve gastrectomy-a restrictive procedure? Obes Surg. 2007;17(1):57–62.
Karamanakos SN, Vagenas K, Kalfarentzos F, et al. Weight loss, appetite suppression, and changes in fasting and post-prandial Ghrelin and peptide-YY levels after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy: a prospective, double blind study. Ann Surg. 2008;247(3):401–7.
Bohdjalian A, Langer F, Shakeri-Leidenmühler S, et al. Sleeve gastrectomy as sole and definitive bariatric procedure: 5-year results for weight loss and Ghrelin. Obes Surg. 2010;20(5):535–40.
Seeras K, Sankararaman S, Lopez PP. Sleeve gastrectomy. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2020.
Benaiges D, Flores Le-Roux JA, Pedro-Botet J, Chillarón JJ, Renard M, Parri A, Ramón JM, Pera M, Goday A. Sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass are equally effective in correcting insulin resistance. Int J Surg. 2013;11(4):309–13.
Riddle MC, Cefalu WT, Evans PH, Gerstein HC, Nauck MA, Oh WK, Rothberg AE, le Roux CW, Rubino F, Schauer P, Taylor R, Twenefour D. Consensus report: Definition and interpretation of remission in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2021;44(10):2438–44. https://doi.org/10.2337/dci21-0034.
Bray GA, Bouchard C, Church TS, et al. Is it time to change the way we report and discuss weight loss? Obesity (Silver Spring). 2009;17(4):619–21.
Misra S, Bhattacharya S, Saravana Kumar S, Nandhini BD, Saminathan SC, Praveen RP. Long-term outcomes of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy from the Indian subcontinent. Obes Surg. 2019;29(12):4043–55.
Gissey LC, Casella JR, Mariolo AG, et al. 10-year follow-up after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy: outcomes in a monocentric series. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2018;14(10):1480–7.
Mihmanli M, Isil RG, Bozkurt E, Demir U, Kaya C, Bostanci O, Isil CT, Sayin P, Oba S, Ozturk FY, Altuntas Y. Post-operative effects of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy in patients with extremeobesity with type 2 diabetes. Springerplus. 2016;22(5):497.
Mizera M, Wysocki M, Bartosiak K, Franczak P, Hady HR, Kalinowski P, Myśliwiec P, Orłowski M, Paluszkiewicz R, Piecuch J, Szeliga J, Walędziak M, Major P, Pędziwiatr M. Type 2 diabetes remission 5 years after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy: multicenter cohort study. Obes Surg. 2021;31(3):980–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-020-05088-w.
Lemanu DP, Singh PP, Rahman H, Hill AG, Babor R, MacCormick AD. Five-year results after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy: a prospective study. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2015;11(3):518–24.
Himpens J, Dobbeleir J, Peeters G. Long-term results of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy for obesity. Ann Surg. 2010;252(2):319–24.
Juodeikis Ž, Brimas G. Long-term results after sleeve gastrectomy: a systematic review. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2017;13(4):693–9.
Diamantis T, Apostolou KG, Alexandrou A, et al. Review of long-term weight loss results after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2014;10(1):177–83.
Neagoe R, Muresan M, Timofte D, Darie R, Razvan I, Voidazan S, Muresan S, Sala D. Long-term outcomes of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy - a single-center prospective observational study. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2019;14(2):242–8.
Hans PK, Guan W, Lin S, Liang H. Long-term outcome of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy from a single center in mainland China. Asian J Surg. 2018;41(3):285–90.
Abbatini F, Rizzello M, Casella G, Alessandri G, Capoccia D, Leonetti F, Basso N. Long-term effects of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy, gastric bypass, and adjustable gastric banding on type 2 diabetes. Surg Endosc. 2010;24(5):1005–10.
Yang P, Bonham AJ, Ghaferi AA, Varhan OA. Comparing diabetes outcomes: weight-independent effects of sleeve gastrectomy versus matched patients with similar weight loss. Ann Surg. 2022;275(5):924–7. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0000000000004298.
Schauer PR, Kashyap SR, Wolski K, Brethauer SA, Kirwan JP, Pothier CE, Thomas S, Abood B, Nissen SE, Bhatt DL. Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy in patients with obesity with diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(17):1567–76.
Schauer PR, Bhatt DL, Kirwan JP, et al. Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy for diabetes—3-year outcomes. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:2002–13.
Schauer PR, Bhatt DL, Kirwan JP, Wolski K, Aminian A, Brethauer SA, Navaneethan SD, Singh RP, Pothier CE, Nissen SE, Kashyap SR, Investigators STAMPEDE. Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy for diabetes - 5-year outcomes. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(7):641–51.
Acknowledgements
Seda Sancak, as principal investigator, had full access to all the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
To conduct the study, institutional review board approval was obtained. The study was carried out in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (2013) of the World Medical Association. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Consent to Participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Key Points:
• Obesity and diabetes mellitus are a global health problem.
• Metabolic surgery may be an option for non-responsive diabetic obese patients.
• Metabolic surgery in diabetic obese patients aids weight loss and metabolic control.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Çeler, Ö., Er, H.C., Sancak, S. et al. The Effects of Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy (LSG) on Obesity-Related Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: a Prospective Observational Study from a Single Center. OBES SURG 33, 2695–2701 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-023-06707-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-023-06707-y