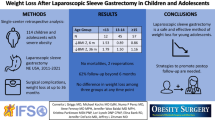
Abstract
Introduction
Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG) is a widely accepted stand-alone bariatric operation. Data on adolescent patients undergoing LSG are limited. The aim of this study was to demonstrate that LSG is safe and effective for patients strictly under 18 years old with severe obesity.
Methods
Prospectively collected data from consecutive patients undergoing LSG were retrospectively analyzed. Patients with more than 1-year follow-up were included in the analysis for weight loss and comorbidity evaluation. Quality of life (QoL) was evaluated using the Short-Form 36 questionnaire.
Results
Eighty-four patients under 18 years old (range: 15–17 years) underwent LSG. Median weight was 128 kg and median body mass index (BMI) 43.7 kg/m2. Median duration of surgery was 68.5 min. One major complication was recorded: a patient developed severe pneumonia that necessitated ventilatory support in intensive care unit and intravenous antibiotic treatment. Mortality was null. Median length of hospital stay was 4 days. Six, 12, and 24 months after LSG, median BMI decreased significantly to 34.3, 29.8, and 28.8 kg/m2, respectively (p < 0.001), with a mean percentage of total body weight loss of 29.1% at 2 years. Obesity-related comorbidities improved at 1 year, while all SF-36 scale scores of QoL assessment improved significantly.
Conclusion
This study suggests that LSG is safe and effective for patients under 18 years old, resulting in significant weight loss, comorbidity remission, and QoL improvement. Careful patient selection after adequate risk versus benefit evaluation by an expert multidisciplinary team is essential.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cunningham SA, Kramer MR, Narayan KM. Incidence of childhood obesity in the United States. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:403–11.
Baker JL, Olsen LW, Sorensen TI. Childhood body-mass index and the risk of coronary heart disease in adulthood. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:2329–37.
Must A, Jacques PF, Dallal GE, et al. Long-term morbidity and mortality of overweight adolescents. A follow-up of the Harvard growth study of 1922 to 1935. N Engl J Med. 1992;327:1350–5.
Schwimmer JB, Burwinkle TM, Varni JW. Health-related quality of life of severely obese children and adolescents. JAMA. 2003;289:1813–9.
Matson KL, Fallon RM. Treatment of obesity in children and adolescents. J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther. 2012;17:45–57.
Danielsson P, Kowalski J, Ekblom O, et al. Response of severely obese children and adolescents to behavioral treatment. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2012;166:1103–8.
Kalarchian MA, Levine MD, Arslanian SA, et al. Family-based treatment of severe pediatric obesity: randomized, controlled trial. Pediatrics. 2009;124:1060–8.
Deitel M, Crosby RD, Gagner M. The first international consensus summit for sleeve gastrectomy (SG), new York City, October 25-27, 2007. Obes Surg. 2008;18:487–96.
O'Brien PE, MacDonald L, Anderson M, et al. Long-term outcomes after bariatric surgery: fifteen-year follow-up of adjustable gastric banding and a systematic review of the bariatric surgical literature. Ann Surg. 2013;257:87–94.
Treadwell JR, Sun F, Schoelles K. Systematic review and meta-analysis of bariatric surgery for pediatric obesity. Ann Surg. 2008;248:763–76.
Almogy G, Crookes PF, Anthone GJ. Longitudinal gastrectomy as a treatment for the high-risk super-obese patient. Obes Surg. 2004;14:492–7.
Weller WE, Rosati C. Comparing outcomes of laparoscopic versus open bariatric surgery. Ann Surg. 2008;248:10–5.
Risstad H, Sovik TT, Engstrom M, et al. Five-year outcomes after laparoscopic gastric bypass and laparoscopic duodenal switch in patients with body mass index of 50 to 60: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Surg. 2015;150:352–61.
van Rutte PW, Smulders JF, de Zoete JP, et al. Outcome of sleeve gastrectomy as a primary bariatric procedure. Br J Surg. 2014;101:661–8.
Gumbs AA, Gagner M, Dakin G, et al. Sleeve gastrectomy for morbid obesity. Obes Surg. 2007;17:962–9.
Himpens J, Dobbeleir J, Peeters G. Long-term results of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy for obesity. Ann Surg. 2010;252:319–24.
Deitel M, Gagner M, Erickson AL, et al. Third international summit: current status of sleeve gastrectomy. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2011;7:749–59.
Eid GM, Brethauer S, Mattar SG, et al. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy for super obese patients: forty-eight percent excess weight loss after 6 to 8 years with 93% follow-up. Ann Surg. 2012;256:262–5.
O'Brien PE, Sawyer SM, Laurie C, et al. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding in severely obese adolescents: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2010;303:519–26.
Nadler EP, Reddy S, Isenalumhe A, et al. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding for morbidly obese adolescents affects android fat loss, resolution of comorbidities, and improved metabolic status. J Am Coll Surg. 2009;209:638–44.
de la Cruz-Munoz N, Messiah SE, Cabrera JC, et al. Four-year weight outcomes of laparoscopic gastric bypass surgery and adjustable gastric banding among multiethnic adolescents. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2010;6:542–7.
Inge TH, Courcoulas AP, Jenkins TM, et al. Weight loss and health status 3 years after bariatric surgery in adolescents. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:113–23.
Boza C, Viscido G, Salinas J, et al. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy in obese adolescents: results in 51 patients. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2012;8:133–7. discussion 7-9
Till H, Bluher S, Hirsch W, et al. Efficacy of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG) as a stand-alone technique for children with morbid obesity. Obes Surg. 2008;18:1047–9.
Nocca D, Nedelcu M, Nedelcu A, et al. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy for late adolescent population. Obes Surg. 2014;24:861–5.
Alqahtani AR, Antonisamy B, Alamri H, et al. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy in 108 obese children and adolescents aged 5 to 21 years. Ann Surg. 2012;256:266–73.
Ejaz A, Patel P, Gonzalez-Heredia R, et al. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy as first-line surgical treatment for morbid obesity among adolescents. J Pediatr Surg. 2017;52:544–8.
Inge TH, Coley RY, Bazzano LA, et al. Comparative effectiveness of bariatric procedures among adolescents: the PCORnet bariatric study. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2018;14:1374–86.
El-Matbouly MA, Khidir N, Touny HA, et al. A 5-year follow-up study of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy among morbidly obese adolescents: does it improve body image and prevent and treat diabetes? Obes Surg. 2018;28:513–9.
Haute Autorité de Santé (2016) Définition des critères de réalisation des interventions de chirurgie bariatrique chez les moins de 18 ans. https://www.has-sante.fr/portail/jcms/c_2010309/fr/definition-des-criteres-de-realisation-des-interventions-de-chirurgie-bariatrique-chez-les-moins-de-18-ans. Accessed 30 Mar 2016.
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, et al. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985;28:412–9.
Gaillard M, Tranchart H, Lainas P, et al. Single-port laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy as a routine procedure in 1000 patients. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2016;12:1270–7.
Leplege A, Ecosse E, Verdier A, et al. The French SF-36 health survey: translation, cultural adaptation and preliminary psychometric evaluation. J Clin Epidemiol. 1998;51:1013–23.
Ruiz-Cota P, Bacardi-Gascon M, Jimenez-Cruz A. Long-term outcomes of metabolic and bariatric surgery in adolescents with severe obesity with a follow-up of at least 5 years: a systematic review. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2019;15:133–44.
Parikh M, Issa R, McCrillis A, et al. Surgical strategies that may decrease leak after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 9991 cases. Ann Surg. 2013;257:231–7.
Khen-Dunlop N, Dabbas M, De Filippo G, et al. Primordial influence of post-operative compliance on weight loss after adolescent laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. Obes Surg. 2016;26:98–104.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lainas, P., De Filippo, G., Di Giuro, G. et al. Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy for Adolescents Under 18 Years Old with Severe Obesity. OBES SURG 30, 267–273 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-019-04150-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-019-04150-6