Abstract
Background
Gastric bypass (GBP) is one of the most effective surgical procedures to treat morbid obesity and the related comorbidities. This study aimed at identifying preoperative predictors of successful weight loss and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) remission 1 year after GBP.
Methods
Prospective longitudinal study of 771 patients who underwent GBP was performed at four Italian centres between November 2011 and May 2013 with 1-year follow-up. Preoperative anthropometric, metabolic and social parameters, the surgical technique and the previous failed bariatric procedures were analyzed. Weight, the body mass index (BMI), the percentage of excess weight lost (% EWL), the percentage of excess BMI lost (% BMIL) and glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) were recorded at follow-up.
Results
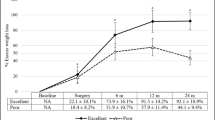
Univariate and multivariate analysis showed that BMI <50 kg/m2 (p = 0.006) and dyslipidaemia (p = 0.05) were predictive factors of successful weight loss. Multivariate analysis of surgical technique showed significant weight loss in patients with a small gastric pouch (p < 0.001); the lengths of alimentary and biliary loops showed no statistical significance. All diabetic patients had a significant reduction of HbA1c (p < 0.001) after surgery. BMI ≥ 50 kg/m2 (p = 0.02) and low level of preoperative HbA1c (p < 0.01) were independent risk factors of T2DM remission after surgery.
Conclusions
This study provides a useful tool for making more accurate predictions of best results in terms of weight loss and metabolic improvement.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Residori L, García-Lorda P, Flancbaum L, et al. Prevalence of co-morbidities in obese patients before bariatric surgery: effect of race. Obes Surg. 2003;13(3):333–40.
Allison DB, Fontaine KR, Manson JE, et al. Annual deaths attributable to obesity in the United States. JAMA. 1999;282(16):1530–8.
Buchwald H, Avidor Y, Braunwald E, et al. Bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2004;292(14):1724–37.
Livhits M, Mercado C, Yermilov I, et al. Preoperative predictors of weight loss following bariatric surgery: systematic review. Obes Surg. 2012;22(1):70–89.
Magro DO, Geloneze B, Delfini R, et al. Long-term weight regain after gastric bypass: a 5-year prospective study. Obes Surg. 2008;18:648–51.
Schauer PR, Kashyap SR, Wolski K, et al. Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy in obese patients with diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(17):1567–76.
Alger-Mayer S, Polimeni JM, Malone M. Preoperative weight loss as a predictor of long-term success following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Obes Surg. 2008;18(7):772–5.
Barazzoni R, Zanetti M, Nagliati C, et al. Gastric bypass does not normalize obesity-related changes in ghrelin profile and leads to higher acylated ghrelin fraction. Obesity. 2013;21(4):718–22.
Gastrointestinal Surgery for Severe Obesity. NIH Consensus Statement. 1991 Mar 25-27; 9:1-20.
O'Brien PE, McPhail T, Chaston TB, et al. Systematic review of medium-term weight loss after bariatric operations. Obes Surg. 2006;16:1032–40.
Nguyen NT, Goldman C, Rosenquist CJ, et al. Laparoscopic versus open gastric bypass: a randomized study of outcomes, quality of life, and costs. Ann Surg. 2001;23:279–89.
Suter M, Giusti V, Héraief E, et al. Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: initial 2-year experience. Surg Endosc. 2003;17:603–9.
Coleman KJ, Toussi R, Fujioka K. Do gastric bypass patient characteristics, behavior, and health differ depending upon how successful weight loss is defined? Obes Surg. 2010;20(10):1385–92.
Contreras JE, Santander C, Court I, et al. Correlation between age and weight loss after bariatric surgery. Obes Surg. 2013;23(8):1286–9.
Ortega E, Morínigo R, Flores L, et al. Predictive factors of excess body weight loss 1 year after laparoscopic bariatric surgery. Surg Endosc. 2012;26(6):1744–50.
Robert M, Pelascini E, Disse E, et al. Preoperative fat-free mass: a predictive factor of weight loss after gastric bypass. Obes Surg. 2013;23(4):446–55.
Roberts K, Duffy A, Kaufman J, et al. Size matters: gastric pouch size correlates with weight loss after laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Surg Endosc. 2007;21(8):1397–402.
Müller MK, Wildi S, Scholz T, et al. Laparoscopic pouch resizing and redo of gastro-jejunal anastomosis for pouch dilatation following gastric bypass. Obes Surg. 2005;15(8):1089–95.
Gobble RM, Parikh MS, Greives MR, et al. Gastric banding as a salvage procedure for patients with weight loss failure after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Surg Endosc. 2008;22(4):1019–22.
Zingg U, McQuinn A, DiValentino D, et al. Revisional vs. primary Roux-en-Y gastric bypass–a case-matched analysis: less weight loss in revisions. Obes Surg. 2010;20(12):1627–32.
Slegtenhorst BR, van der Harst E, Demirkiran A, et al. Effect of primary versus revisional Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: inferior weight loss of revisional surgery after gastric banding. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2013;9(2):253–8.
Goldstein DJ. Beneficial health effects of modest weight loss. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1992;16(6):397–415.
Reinhold RB. Critical analysis of long term weight loss following gastric bypass. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1982;155(3):385–94.
American Diabetes Association. Executive summary: standard of medical care in diabetes- 2011. Diabetes Care. 2011;34 Suppl 1:S4–S10.
Dixon JB, Zimmet P, Alberti KG, et al. International Diabetes Federation Taskforce on Epidemiology and Prevention. Bariatric surgery: an IDF statement for obese Type 2 diabetes. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2011;7(4):433–47.
Buchwald H, Estok R, Fahrbach K, et al. Weight and type 2 diabetes after bariatric surgery: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Med. 2009;122(3):248–56.
Buchwald H, Oien DM. Metabolic/bariatric surgery worldwide 2011. Obes Surg. 2013;23(4):427–36.
Yan YX, Wang GF, Xu N, et al. Correlation between postoperative weight loss and diabetes mellitus remission: a meta-analysis. Obes Surg. 2014;24(11):1862–9.
Dixon JB, Chuang LM, Chong K, et al. Predicting the glycemic response to gastric bypass surgery in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(1):20–6.
Dogan K, Betzel B, Homan J, et al. Long-term effects of laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass on diabetes mellitus, hypertension and dyslipidaemia in morbidly obese patients. Obes Surg. 2014;24(11):1835–42.
Robert M, Ferrand-Gaillard C, Disse E, et al. Predictive factors of type 2 diabetes remission 1 year after bariatric surgery: impact of surgical techniques. Obes Surg. 2013;23(6):770–5.
Dixon JB, Hur KY, Lee WJ, et al. Gastric bypass in Type 2 diabetes with BMI < 30: weight and weight loss have a major influence on outcomes. Diabet Med. 2013;30(4):e127–34.
Yamaguchi CM, Faintuch J, Hayashi SY, et al. Refractory and new-onset diabetes more than 5 years after gastric bypass for morbid obesity. Surg Endosc. 2012;26(10):2843–7.
Hamza N, Abbas MH, Darwish A, et al. Predictors of remission of type 2 diabetes mellitus after laparoscopic gastric banding and bypass. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2011;7(6):691–6.
Chikunguwo SM, Wolfe LG, Dodson P, et al. Analysis of factors associated with durable remission of diabetes after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2010;6(3):254–9.
Hall TC, Pellen MG, Sedman PC, et al. Preoperative factors predicting remission of type 2 diabetes mellitus after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery for obesity. Obes Surg. 2010;20(9):1245–50.
Kinzl JF, Schrattenecker M, Traweger C, et al. Psychosocial predictors of weight loss after bariatric surgery. Obes Surg. 2006;16(12):1609–14.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Dr. Eugenia Dal Fovo for translating this article and Dr Fabiola Giudici for statistical analysis.
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Conflict of Interest
Silvia Palmisano: no conflict of interest.
Marta Silvestri: no conflict of interest.
Michela Giuricin: no conflict of interest.
Nicolò de Manzini: no conflict of interest.
Edoardo Baldini: no conflict of interest.
Simone Albertario: no conflict of interest.
Patrizio Capelli: no conflict of interest.
Bernardo Marzano: no conflict of interest.
Giovanni Fanti: no conflict of interest.
Aron Zompichiatti: no conflict of interest.
Paolo Millo: no conflict of interest.
Massimiliano Fabozzi: no conflict of interest.
Riccardo Brachet Contul: no conflict of interest.
Elisa Ponte: no conflict of interest.
Rosaldo Allieta: no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Palmisano, S., Silvestri, M., Giuricin, M. et al. Preoperative Predictive Factors of Successful Weight Loss and Glycaemic Control 1 Year After Gastric Bypass for Morbid Obesity. OBES SURG 25, 2040–2046 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-015-1662-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-015-1662-2