Abstract
Background
Bariatric surgery produces a substantial weight loss and improves the comorbidities associated with obesity such as diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia, although inability to lose weight or weight regain has been estimated to occur in 20 % of cases. The objective of the present study was to assess the influence of weight variations on biochemical indicators during a 4-year period after bariatric surgery.
Methods
A 4-year retrospective longitudinal study was conducted on 138 patients with grade III obesity submitted to Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, with the assessment of anthropometric measurements and biochemical indicators. The patients were divided into two groups according to percent excess weight loss (%EWL): %EWL > 50 % and %EWL < 50 %, and into two groups according to weight regain: <10 % and >10 %. The Student t test for independent samples was used to assess the differences in biochemical indicators between groups (p ≤ 0.05).
Results
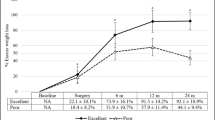
Four years after surgery, there was a weight loss of 49.4 ± 21.8 kg and %EWL of 61 ± 21.2 %, with 73.2 % (n = 101) of the patients showing %EWL of 50 % or more. Significant weight regain occurred in 24.6 % of the sample. There was a difference in weight, BMI, total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, triglycerides, and albumin between patients with different %EWL. No difference in biochemical indicators was observed between subjects with and without regain.
Conclusion
Four years after surgery, greater %EWL was associated with a better lipid profile. In addition, weight regain did not change the biochemical indicators of this patient series.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Novais PFS, Junior IR, Leite CVS, et al. Evolução e classificação do peso corporal em relação aos resultados da cirurgia bariátrica – derivação gástrica em Y de Roux. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metab. 2010;54(3):303–10.
Schouten R, Wiryasaputra DC, van Dielen FMH, et al. Long-term results of bariatric restrictive procedures: a prospective study. Obes Surg. 2010;20:1617–26.
Fobi MA. Surgical treatment of obesity: a review. J Nat Med Assoc. 2004;96(1):61–75.
Fried M. Bariatric and metabolic surgery. Minerva Endocrinol. 2013;38(3):237–44.
Mundi MS, Lorentz PA, Swain J, et al. Moderate physical activity as predictor of weight loss after bariatric surgery. Obes Surg. 2013;23(10):1645–9.
Goldman RL, Canterberry M, Borckardt JJ, Madan A, Byrne TK, George MS, O'Neil PM, Hanlon CA. Executive control circuitry differentiates degree of success in weight loss following gastric-bypass surgery. Obes (Silver Spring). 2013 [Epub ahead of print].
Pinheiro-Júnior S, Pinhel MA, Nakazone MA, et al. Effect of genetic variants related to lipid metabolism as risk factors for cholelithiasis after bariatric surgery in Brazilian population. Obes Surg. 2012;22(4):623–33.
Magro DO, Geloneze B, Delfini R, et al. Long-term weight regain after gastric bypass: a 5-year prospective study. Obes Surg. 2008;6:648–51.
Conceição E, Bastos AP, Brandão I, Vaz AR, Ramalho S, Arrojado F, da Costa JM, Machado PP. Loss of control eating and weight outcomes after bariatric surgery: a study with a Portuguese sample. Eat Weight Disord. 2013 [Epub ahead of print].
Ferraz AA, de Siqueira LT, Filho EN, de Araújo Júnior JG, Campos JM, de Barros-Correia TX, Muniz MG, Ferraz EM. Revision surgery for treatment of weight regain after Roux-En-Y gastric bypass. Obes Surg. 2013 [Epub ahead of print].
Shah M, Simha V, Garg A. Review: long term impact of bariatric surgery on body weight, comorbities, and nutritional status. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:4223–31.
Lopez PP, Patel NA, Koche LS. Outpatient complications encountered following Roux-en Y gastric by-pass. Med Clin N Am. 2007;91:471–83.
MLF. Height and weight tables: Metropolitan Life Foundation. New York: Metropolitan Life Insurance Company; 1983.
Sjöström L, Narbro K, Sjöström CD, et al. Swedish Obese Subjects Study. Effects of bariatric surgery on mortality in Swedish obese subjects. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(8):741–52.
Käkelä P, Jääskeläinen T, Torpström J, Ilves I, Venesmaa S, Pääkkönen M, Gylling H, Paajanen H, Uusitupa M, Pihlajamäki J. Genetic risk score does not predict the outcome of obesity surgery. Obes Surg. 2013.
Maggard MA, Shugarman LR, Suttorp M, et al. Meta-analysis: surgical treatment of obesity. Ann Intern Med. 2005;142(7):547–59.
Buchwald H, Estok R, Fahrbach K, et al. Weight and type 2 diabetes after bariatric surgery: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Med. 2009;122:248–56.
Pories WJ, Swanson MS, MacDonald KG, et al. Who would have thought it? An operation proves to be the most effective therapy for adult-onset diabetes mellitus. Ann Surg. 1995;222(3):339–52.
Pedrosa IV, Burgos MG, Souza NC, et al. Nutrition aspects in obese before and after bariatric surgery. Ver Col Bras Cir. 2009;4:316–22.
Valezi AC, Mali Júnior J, de Brito EM, et al. Gastroplastia vertical com bandagem em Y-de-Roux: Análise de resultados. Rev Col Bras Cir. 2004;31(1):49–56.
Quadros MRR, Savaris AL, Ferreira MV, et al. Intolerância alimentar no pós-operatório de pacientes submetidos à cirurgia bariátrica. Rev Bras Nutr Clin. 2007;22(1):15–9.
Sjostrom CD, Lissner L, Wedel H, et al. Reduction in incidence of diabetes, hypertension and lipid disturbances after intentional weight loss induced by bariatric surgery: the SOS Intervention Study. Obes Res. 1999;7:477–84.
Karmali S, Brar B, Shi X, et al. Weight recidivism post-bariatric surgery: a systematic review. Obes Surg. 2013;23(11):1922–33.
Freire RH, Borges MC, Alvarez-Leite JI, et al. Food quality, physical activity, and nutritional follow-up as determinant of weight regain after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Nutrition. 2012;28(1):53–8.
Kofman MD, Lent MR, Swencionis C. Maladaptive eating patterns, quality of life, and weight outcomes following gastric bypass: results of an Internet survey. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2010;18(10):1938–43.
Junior WS. do Amaral JL, Nonino-Borges CB. Factors related to weight loss up to 4 years after bariatric surgery. Obes Surg. 2011;21(11):1724–30.
Higa K, Ho T, Tercero F, et al. Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: 10-year follow-up. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2011;7(4):516–25.
Christou NV, Look D, Maclean LD. Weight gain after short- and long-limb gastric bypass in patients followed for longer than 10 years. Ann Surg. 2006;244(5):734–40.
Benaiges D, Flores-Le-Roux JA, Pedro-Botet J, et al. Obemar Group. Impact of restrictive (sleeve gastrectomy) vs hybrid bariatric surgery (Roux-en-Y gastric bypass) on lipid profile. Obes Surg. 2012;22(8):1268–75.
Ruiz-Tovar J, Zubiaga L, Llavero C, Diez M, Arroyo A, Calpena R. Serum cholesterol by morbidly obese patients after Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy and additional physical activity. Obes Surg. 2013.
Carvalho PS, Moreira CLCB, Barelli MC, et al. Cirurgia bariátrica cura síndrome metabólica? Arq Bras Endocrinol Metab. 2007;51(1):79–85.
Poirier P, Cornier MA, Mazzone T, et al. Bariatric surgery and cardiovascular risk factors: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2011;123:1683–701.21.
Beleli CAV, Filho AC, Silva RM, et al. Los predictores de pérdida de peso en los pacientes sometidos a la derivación gástrica en Y de Roux. Bariatrica e Metabolica Ibero Americana. 2011;1:17–23.
Brethauer SA, Aminian A, Romero-Talamás H, et al. Can diabetes be surgically cured? Long-term metabolic effects of bariatric surgery in obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann Surg. 2013;258(4):628–36. discussion 636–7.
Gasteyger C, Suter M, Calmes JM, et al. Changes in body composition, metabolic profile and nutritional status 24 months after gastric banding. Obes Surg. 2006;16(3):243–50.
Andrews NC. Understanding heme transport. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(23):2508–9.
Acknowledgments
None.
Conflict of Interest
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nicoletti, C.F., de Oliveira, B.A.P., de Pinhel, M.A.S. et al. Influence of Excess Weight Loss and Weight Regain on Biochemical Indicators During a 4-Year Follow-up After Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass. OBES SURG 25, 279–284 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-014-1349-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-014-1349-0