Abstract
Purpose
Myxozoans are economically important group of metazoan parasites, which can cause diseases in a large variety of commercially important fishes. Increased knowledge on molecular features has shown that traditional descriptive characters may be misleading. Combination of both descriptive and molecular features is therefore necessary for an integrated taxonomic assessment.
Methods
Cyprinid Labeo batesii, sampled in the Makombè River at Nkondjock in Cameroon were examined for myxosporeans. Identification of parasite species was based on morphological and molecular sequence analyses of myxospores. Phylogenetic analysis was performed using maximum likelihood (ML) and Bayesian inference (BI) methods.
Results
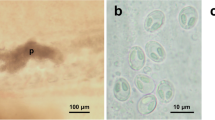
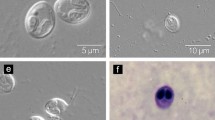
The scales of L. batesii were infected by Myxobolus nkondjockei sp. nov Their mature myxospores are ovoid in frontal view and lenticular in lateral view, with two rounded ends. These myxospores measured 10.3 (10–10.9) μm length and 8.0 (7.3–8.5) μm width. Myxospores have two ovoid and equal sizes polar capsules. They measured 4.5 (4.0–5.0) µm in length and 2.4 (2–2.9) µm in width. Polar tubules were coiled in 4–5 turns perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the polar capsules. Phylogenetic analysis of the 18S rDNA sequence show clustering of M. nkondjockei sp. n. close to an undetermined species Myxobolus sp. reported infecting gill lamellas of Labeo rohita from India.
Conclusion
The morphological, molecular and phylogenetic data provided for M. nkondjockei sp. n. are solid basis for further identification of this myxozoan of which pathogenicity probably plays an economic role at culturing the hosts.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Griffin W, Wang W, de Souza MC (2019) The sustainable development goals and the economic contribution of fisheries and aquaculture. FAO Aquac Newsl 60:51–52
Volff, (2005) Genome evolution and biodiversity in teleost fish. Heredity 94:280–294. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.hdy.6800635
Wolf K, Markiw ME (1984) Biology contravenes taxonomy in the Myxozoa: new discoveries show alternation of invertebrate and vertebrate hosts. Science 225:1449–1452. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.225.4669.1449
Fiala I, Bartošová-Sojková P, Whipps CM (2015) Classification and phylogenetics of Myxozoa. In: Okamura B, Gruhl A, Bartholomew JL (eds) Myxozoan evolution, ecology and development. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 85–110
Eiras JC, Molnár K, Lu YS (2005) Synopsis of the species of Myxobolus Bütschli, 1882 (Myxozoa: Myxosporea: Myxobolidae). Syst Parasitol 61:1–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-004-6343-9
Eiras JC, Zhang J, Molnár K (2014) Synopsis of the species of Myxobolus Bütschli, 1882 (Myxozoa: Myxosporea, Myxobolidae) described between 2005 and 2013. Syst Parasitol 88:11–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-014-9484-5
Eiras JC, Cruz CF, Saraiva A, Adriano EA (2021) Synopsis of the species of Myxobolus (Cnidaria, Myxozoa, Myxosporea) described between 2014 and 2020. Folia Parasitol. https://doi.org/10.14411/fp.2021.012
Winfield IJ, Nelson JS (2012) Cyprinid fishes: systematics, biology and exploitation. Springer Science and Business Media, Berlin
Reid GM (1985) A revision of African species of Labeo (Pisces: Cyprinidae) and a redefinition of the genus. Verlag von J, Cramer
Weyl OLF, Booth AJ (1999) On the life history of a cyprinid fish, Labeo cylindricus. Environ Biol Fishes 55:215–225. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007543319416
Olufeagba SO, Okomoda VT, Okache W (2016) Growth performance of all male tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fed commercial and on-farm compounded diet. Banats J Biotechnol 7:70–76. https://doi.org/10.7904/2068-4738-VII(13)-70
Molnár K (1994) Comments on the host organ and tissue specificity of fish myxosporeans and on the types of their intrapiscine development. Parasitol Hung 27:5–20
Okamura B, Gruhl A, Bartholomew JL (2015) Myxozoan evolution, ecology and development. Springer International Publishing, Switzerland
Stiassny MLG, Teugels GG, Hopkins CD (2007) Freshwater and brackish fish from lower Guinea. Western Central Africa Institute of Research for Development, Paris
Vivien J (2012) Guide des Mammifères et poissons du Cameroun. Nguila Kerou, Saint berthevin
Lom J, Arthur JR (1989) A guideline for the preparation of species descriptions in Myxosporea. J Fish Dis 12:151–156. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2761.1989.tb00287.x
Lekeufack-Folefack GB, Feudjio-Dongmo B, Fomena A, Tene-Fossog B, Wondji MJ (2020) An optimized protocol for Myxosporidia (Cnidaria: Myxosporea) DNA extraction for molecular studies. Open J Anim Sci 10:378. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojas.2020.103023
Molnár K, Eszterbauer E, Székely C, Dán Á, Harrach B (2002) Morphological and molecular biological studies on intramuscular Myxobolus spp. of cyprinid fish. J Fish Dis 25:643–652. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2761.2002.00409.x
Adriano EA, Carriero MM, Maia AAM, Silva MRM, Naldoni J, Ceccarelli PS, Arana S (2012) Phylogenetic and host–parasite relationship analysis of Henneguya multiplasmodialis n. sp. infecting Pseudoplatystoma spp. in Brazilian Pantanal wetland. Vet Parasitol 185:110–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2011.10.008
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl Acids Symp 41:95–98
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.17.3389
Ronquist F, Teslenko M, van der Mark P, Ayres DL, Darling A, Höhna S, Larget B, Liu SMA, Huelsenbeck JP (2012) MrBayes 3.2: efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst Biol 61:539–542. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/sys029
Kozlov AM, Darriba D, Flouri T, Morel B, Stamatakis A (2019) RAxML-NG: a fast, scalable and user-friendly tool for maximum likelihood phylogenetic inference. Bioinformatics 35:4453–4455. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btz305
Darriba D, Taboada GL, Doallo R, Posada D (2012) jModelTest 2: more models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat Methods 9:772–772. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2109
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rate of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01731581
Rambaut A (2016) FigTree v1. 4.3 software Institute of Evolutionary Biology. University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh
Lekeufack-Folefack GB, Abdel-Baki AAS, Onana ANO, Fomena A, Mansour L (2019) Morphological and molecular characterization of Myxobolus dibombensis sp. n. (Myxozoa: Myxobolidae), a parasite of the African carp Labeobarbus batesii (Teleostei: Cyprinidae) from Dibombe River. Cameroon Parasitol Res 118:763–771
Lekeufack-Folefack GB, Tchoutezo-Tiwa AE, Al-Tamimi J, Fomena A, Al-Omar SY, Mansour L (2021) Myxobolus opsaridiumi sp. nov. (Cnidaria: Myxosporea) infecting different tissues of an ornamental fish, Opsaridium ubangiensis (Pellegrin, 1901), in Cameroon: morphological and molecular characterization. Eur J Taxon 733:56–71
Bertin L (1958) Ecailles et sclérifications dermiques. In: Grasse P-P (ed) Traité de zoologie. Masson, Paris, pp 482–504
Whitear M (1970) The skin surface of bony fishes. J Zoology 160:437–454
Egusa S, Maeno Y, Sorimachi M (1990) A new species of Myxozoa, Myxobolus episquamalis sp. nov. infecting the scales of the mullet. Mugil cephalus L Fish pathology 25:87–91. https://doi.org/10.3147/jsfp.25.87
Moshu A, Molnár K (1997) Thelohanellus (Myxozoa: Myxosporea) infection of the scales in the European wild carp Cyprinus carpio carpio. Dis Aquat Organ 28(2):115–123. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao028115
Iversen ES (1954) A new myxosporidian, Myxosoma squamalis, parasite of some salmonid fishes. J Parasitol 40:397–404. https://doi.org/10.2307/3273884
Wainwright DK, Lauder GV (2017) Mucus matters: The slippery and complex surfaces of fish. Funct Surf Biol III:223–246. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-74144-4_10
Sitja-Bobadilla A, Schmidt-Posthaus H, Wahli T, Holland JW, Secombes CJ (2015) Fish Immune Responses to Myxozoa. In: Okamura B, Gruhl A, Bartholomew JL (eds) Myxozoan evolution, ecology and development. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 253–280. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-14753-6_14
Rothwell JT, Virgona JL, Callinan RB, Nicholls PJ, Langdon JS (1997) Occurrence of cutaneous infections of Myxobolus episquamalis (Myxozoa: Myxobolidae) in sea mullet, Mugil cephalus L. in Australia. Aust Vet J 75:349–352. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-0813.1997.tb15709.x
Deli A, Lekeufack Folefack GB, Fomena A (2017) Description of Myxidium tetraodoni sp. nov. Myxidium anisocapsularis sp. nov. and Myxobolus magai sp. nov. (Myxosporea: Bivalvulida) infecting some freshwater fishes in Cameroon (central Africa). Fish Aqua J 8:235. https://doi.org/10.4172/2150-3508.1000235
Kaur H, Singh R (2011) Two new species of Myxobolus (Myxozoa: Myxosporea: Bivalvulida) infecting an Indian major carp in Ropar and Kanjali wetlands (Punjab). J Parasitic Dis 35:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-011-0061-4
Haldar DP, Das MK, Sharma BK (1983) Studies on protozoan parasites from fishes : four new species of the genera Henneguya Thelohan, 1892, Thelohanellus Kudo, 1933 and Myxobolus Butschli, 1892. Arch Protistenkd 127:283–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-9365(83)80023-2
Landsberg JH, Lom J (1991) Taxonomy of the genera of the Myxobolus/Myxosoma group (Myxobolidae: Myxosporea), current listing of species and revision of synonyms. Syst Parasitol 18:165–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00009358
Li P, Xi BW, Zhao X, Xie J (2017) Myxobolus linzhiensis n. sp. (Myxozoa: Myxobolidae) from the gill filament of Schizothorax oconnori Lloyd (Cyprinidae: Schizothoracinae) in Tibet, China: morphological and molecular characterization. Parasitol Res 116:3097–3103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-017-5621-9
Zhang JY, Wang JG, Li AH, Gong XN (2010) Infection of Myxobolus turpisrotundus sp. n. in allogynogenetic gibel carp, Carassius auratus gibelio (Bloch), with revision of Myxobolus rotundus (s. l.) Nemeczek reported from C. auratus auratus (L.). J Fish Dis 33:625–638. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2761.2010.01161.x
Liu XH, Hua CJ, Zhang QQ, Zhao YL, Zhang D, Zhang JY (2017) Myxobolus taibaiensis sp. n. (Myxozoa: Myxosporea) infecting the intestial wall of common carp Cyprinus carpio Linnaeus in China. Folia Parasitol 64:1–7. https://doi.org/10.14411/fp.2017.001
Chen QL, Ma CL (1998) Fauna Sinica, Myxozoa: Myxosporea. Science Press, Beijing
Li P, Xi BW, Chen K, Xie J (2017) Morphological and molecular characteristic of Myxobolus yueyangensis sp. nov. (Myxozoa: Myxobolidae) from the intestine of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) in China. Acta Hydrobiol Sin 41:1251–1256
Liu XH, Batueva MD, Zhao YL, Zhang JY, Zhang QQ, Li TT, Li AH (2016) Morphological and molecular characterisation of Myxobolus pronini n. sp. (Myxozoa: Myxobolidae) from the abdominal cavity and visceral serous membranes of the gibel carp Carassius auratus gibelio (Bloch) in Russia and China. Parasites Vectors. 9:562. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-016-1836-3
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Research Supporting Project (RSP- 2021/75), King Saud University (Riyadh, Saudi Arabia). Part of this work was supported by budget funding of RAS (project 121030100028-0“Regularities of formation and anthropogenic transformation of biodiversity and biological resources of the Azov-Black Sea basin and other areas of the World Ocean” (Russian Federation).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest related to this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lekeufack-Folefack, G.B., Feudjio-Dongmo, B., Tene-Fossog, B. et al. Morphological and Molecular Characterization of Myxobolus nkondjockei sp. nov. (Myxozoa: Myxobolidae), A Parasite of Labeo batesii Boulenger, 1911 (Teleostei: Cyprinidae) from Makombè River in Cameroon. Acta Parasit. 67, 1573–1583 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11686-022-00609-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11686-022-00609-2