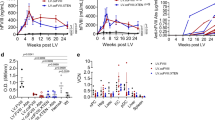
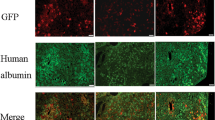
Abstract
Gene therapy provides a potential cure for hemophilia B, and significant progress has been achieved in liver-directed gene transfer mediated by adeno-associated viral vectors. Recent clinical trials involving the use of a self-complementary adeno-associated virus serotype 8-human codon-optimized factor IX (AAV8-hFIXco) vector demonstrated encouraging efficacy with hFIX expression stabilized at 1% to 6% of normal level in patients, but safety concerns related to high vector doses are still present. Thus, further improvement of AAV vectors and hFIX expression cassette may positively contribute to the ultimate success of hemophilia B gene therapy. In this study, to obtain a higher expression level of hFIX that potentiates the coagulant capacity of recipients, human FIX expression vector was optimized by upgrading the codon adaption index and adjusting the GC content, inserting a Kozak sequence (GCCACC), and introducing a gain-of-function mutation, R338L (FIX Padua). The efficiency of the published and the presently constructed cassettes was compared through in vivo screening. In addition, the regulatory elements that control the FIX gene expression in these cassettes were screened for liver-specific effectiveness. Among all the constructed cassettes, scAAV-Pre-hFIXco-SIH-R338L, which was the construct under the control of the prothrombin enhancer and prealbumin promoter, resulted in the highest level of coagulant activity, and the expression levels of two constructed cassettes (scAAV-Chi-hFIXco-SIH-R338L and scAAV-Pre-hFIXco-SIH-R338L) were also higher than that of the published cassette (scAAV-LP1-hFIXco-SJ). In summary, our strategies led to a substantial increase in hFIX expression at the protein level or a remarkably elevated coagulant activity. Thus, these reconstructs of hFIX with AAV vector may potentially contribute to the creation of an efficacious gene therapy of hemophilia B.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thrombosis and Hemostasis Group, Chinese Society of Hematology, Chinese Medical Association/Hemophilia Treatment Center Collaborative Network of China. Consensus of Chinese experts on diagnosis and treatment of hemophilia(2013). Chin J Hematol (Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi) 2013; 34(5): 461–463 (in Chinese)
Nilsson IM, Berntorp E, Löfqvist T, Pettersson H. Twenty-five years’ experience of prophylactic treatment in severe haemophilia A and B. J Intern Med 1992; 232(1): 25–32
Manco-Johnson MJ, Abshire TC, Shapiro AD, Riske B, Hacker MR, Kilcoyne R, Ingram JD, Manco-Johnson ML, Funk S, Jacobson L, Valentino LA, Hoots WK, Buchanan GR, DiMichele D, Recht M, Brown D, Leissinger C, Bleak S, Cohen A, Mathew P, Matsunaga A, Medeiros D, Nugent D, Thomas GA, Thompson AA, McRedmond K, Soucie JM, Austin H, Evatt BL. Prophylaxis versus episodic treatment to prevent joint disease in boys with severe hemophilia. N Engl J Med 2007; 357(6): 535–544
Nathwani AC, Tuddenham EG, Rangarajan S, Rosales C, McIntosh J, Linch DC, Chowdary P, Riddell A, Pie AJ, Harrington C, O’Beirne J, Smith K, Pasi J, Glader B, Rustagi P, Ng CY, Kay MA, Zhou J, Spence Y, Morton CL, Allay J, Coleman J, Sleep S, Cunningham JM, Srivastava D, Basner-Tschakarjan E, Mingozzi F, High KA, Gray JT, Reiss UM, Nienhuis AW, Davidoff AM. Adenovirus-associated virus vector-mediated gene transfer in hemophilia B. N Engl J Med 2011; 365(25): 2357–2365
Nathwani AC, Gray JT, Ng CY, Zhou J, Spence Y, Waddington SN, Tuddenham EG, Kemball-Cook G, McIntosh J, Boon-Spijker M, Mertens K, Davidoff AM. Self-complementary adeno-associated virus vectors containing a novel liver-specific human factor IX expression cassette enable highly efficient transduction of murine and nonhuman primate liver. Blood 2006; 107(7): 2653–2661
Li YM, Li DJ, Xu XJ, Cui M, Zhen HH, Wang Q. Effect of codon optimization on expression levels of human cystatin C in Pichia pastoris. Genet Mol Res 2014; 13(3): 4990–5000
Burgess-Brown NA, Sharma S, Sobott F, Loenarz C, Oppermann U, Gileadi O. Codon optimization can improve expression of human genes in Escherichia coli: a multi-gene study. Protein Expr Purif 2008; 59(1): 94–102
Ward NJ, Buckley SM, Waddington SN, Vandendriessche T, Chuah MK, Nathwani AC, McIntosh J, Tuddenham EG, Kinnon C, Thrasher AJ, McVey JH. Codon optimization of human factor VIII cDNAs leads to high-level expression. Blood 2011; 117(3): 798–807
Sack BK, Merchant S, Markusic DM, Nathwani AC, Davidoff AM, Byrne BJ, Herzog RW. Transient B cell depletion or improved transgene expression by codon optimization promote tolerance to factor VIII in gene therapy. PLoS ONE 2012; 7(5): e37671
Miao CH, Thompson AR, Loeb K, Ye X. Long-term and therapeutic-level hepatic gene expression of human factor IX after naked plasmid transfer in vivo. Mol Ther 2001; 3(6): 947–957
Zhang G, Song YK, Liu D. Long-term expression of human α1-antitrypsin gene in mouse liver achieved by intravenous administration of plasmid DNA using a hydrodynamics-based procedure. Gene Ther 2000; 7(15): 1344–1349
Aliño SF, Crespo A, Dasí F. Long-term therapeutic levels of human α1-antitrypsin in plasma after hydrodynamic injection of nonviral DNA. Gene Ther 2003; 10(19): 1672–1679
Nguyen AT, Dow AC, Kupiec-Weglinski J, Busuttil RW, Lipshutz GS. Evaluation of gene promoters for liver expression by hydrodynamic gene transfer. J Surg Res 2008; 148(1): 60–66
Al-Dosari M, Zhang G, Knapp JE, Liu D. Evaluation of viral and mammalian promoters for driving transgene expression in mouse liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2006; 339(2): 673–678
Xu ZL, Mizuguchi H, Ishii-Watabe A, Uchida E, Mayumi T, Hayakawa T. Optimization of transcriptional regulatory elements for constructing plasmid vectors. Gene 2001; 272(1–2): 149–156
Simioni P, Tormene D, Tognin G, Gavasso S, Bulato C, Iacobelli NP, Finn JD, Spiezia L, Radu C, Arruda VR. X-linked thrombophilia with a mutant factor IX (factor IX Padua). N Engl J Med 2009; 361(17): 1671–1675
Minghetti PP, Ruffner DE, Kuang WJ, Dennison OE, Hawkins JW, Beattie WG, Dugaiczyk A. Molecular structure of the human albumin gene is revealed by nucleotide sequence within q11-22 of chromosome 4. J Biol Chem 1986; 261(15): 6747–6757
Frain M, Hardon E, Ciliberto G, Sala-Trepat JM. Binding of a liverspecific factor to the human albumin gene promoter and enhancer. Mol Cell Biol 1990; 10(3): 991–999
Hayashi Y, Chan J, Nakabayashi H, Hashimoto T, Tamaoki T. Identification and characterization of two enhancers of the human albumin gene. J Biol Chem 1992; 267(21): 14580–14585
Costa RH, Grayson DR, Darnell JE Jr. Multiple hepatocyte-enriched nuclear factors function in the regulation of transthyretin and α 1-antitrypsin genes. Mol Cell Biol 1989; 9(4): 1415–1425
Costa RH, Lai E, Darnell JE Jr. Transcriptional control of the mouse prealbumin (transthyretin) gene: both promoter sequences and a distinct enhancer are cell specific. Mol Cell Biol 1986; 6(12): 4697–4708
Tsuzuki T, Mita S, Maeda S, Araki S, Shimada K. Structure of the human prealbumin gene. J Biol Chem 1985; 260(22): 12224–12227
Monaci P, Nicosia A, Cortese R. Two different liver-specific factors stimulate in vitro transcription from the human α1-antitrypsin promoter. EMBO J 1988; 7(7): 2075–2087
De Simone V, Ciliberto G, Hardon E, Paonessa G, Palla F, Lundberg L, Cortese R. Cis- and trans-acting elements responsible for the cell-specific expression of the human α1-antitrypsin gene. EMBO J 1987; 6(9): 2759–2766
Bancroft JD, McDowell SA, Degen SJ. The human prothrombin gene: transcriptional regulation in HepG2 cells. Biochemistry 1992; 31(49): 12469–12476
Chen Y, Schroeder JA, Kuether EL, Zhang G, Shi Q. Platelet gene therapy by lentiviral gene delivery to hematopoietic stem cells restores hemostasis and induces humoral immune tolerance in FIX (null) mice. Mol Ther 2014; 22(1): 169–177
Song YK, Liu F, Zhang G, Liu D. Hydrodynamics-based transfection: simple and efficient method for introducing and expressing transgenes in animals by intravenous injection of DNA. Methods Enzymol 2002; 346: 92–105
Liu F, Song Y, Liu D. Hydrodynamics-based transfection in animals by systemic administration of plasmid DNA. Gene Ther 1999; 6(7): 1258–1266
Nathwani AC, Davidoff AM, Hanawa H, Hu Y, Hoffer FA, Nikanorov A, Slaughter C, Ng CY, Zhou J, Lozier JN, Mandrell TD, Vanin EF, Nienhuis AW. Sustained high-level expression of human factor IX (hFIX) after liver-targeted delivery of recombinant adeno-associated virus encoding the hFIX gene in rhesus macaques. Blood 2002; 100(5): 1662–1669
Gutman GA, Hatfield GW. Nonrandom utilization of codon pairs in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1989; 86(10): 3699–3703
Papadakis ED, Nicklin SA, Baker AH, White SJ. Promoters and control elements: designing expression cassettes for gene therapy. Curr Gene Ther 2004; 4(1): 89–113
Crooks GE, Hon G, Chandonia JM, Brenner SE. WebLogo: a sequence logo generator. Genome Res 2004; 14(6): 1188–1190
Tokuoka M, Tanaka M, Ono K, Takagi S, Shintani T, Gomi K. Codon optimization increases steady-state mRNA levels in Aspergillus oryzae heterologous gene expression. Appl Environ Microbiol 2008; 74(21): 6538–6546
Hu S, Li L, Qiao J, Guo Y, Cheng L, Liu J. Codon optimization, expression, and characterization of an internalizing anti-ErbB2 single-chain antibody in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif 2006; 47(1): 249–257
Xia X. How optimized is the translational machinery in Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium and Saccharomyces cerevisiae? Genetics 1998; 149(1): 37–44
Gvritishvili AG, Leung KW, Tombran-Tink J. Codon preference optimization increases heterologous PEDF expression. PLoS One 2010; 5(11): e15056
Wang L, Morizono H, Lin J, Bell P, Jones D, McMenamin D, Yu H, Batshaw ML, Wilson JM. Preclinical evaluation of a clinical candidate AAV8 vector for ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC) deficiency reveals functional enzyme from each persisting vector genome. Mol Genet Metab 2012; 105(2): 203–211
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M. MEGA3: integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform 2004; 5(2): 150–163
Xia X, Xie Z. DAMBE: software package for data analysis in molecular biology and evolution. J Hered 2001; 92(4): 371–373
Xiao W, Berta SC, Lu MM, Moscioni AD, Tazelaar J, Wilson JM. Adeno-associated virus as a vector for liver-directed gene therapy. J Virol 1998; 72(12): 10222–10226
Kay MA, Baley P, Rothenberg S, Leland F, Fleming L, Ponder KP, Liu T, Finegold M, Darlington G, Pokorny W. Expression of human α1-antitrypsin in dogs after autologous transplantation of retroviral transduced hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1992; 89(1): 89–93
Kay MA, Li Q, Liu TJ, Leland F, Toman C, Finegold M, Woo SL. Hepatic gene therapy: persistent expression of human α1-antitrypsin in mice after direct gene delivery in vivo. Hum Gene Ther 1992; 3(6): 641–647
Gehrke S, Jérôme V, Müller R. Chimeric transcriptional control units for improved liver-specific transgene expression. Gene 2003; 322: 137–143
Wu KJ, Wilson DR, Shih C, Darlington GJ. The transcription factor HNF1 acts with C/EBPα to synergistically activate the human albumin promoter through a novel domain. J Biol Chem 1994; 269(2): 1177–1182
Godbout R, Ingram R, Tilghman SM. Multiple regulatory elements in the intergenic region between the α-fetoprotein and albumin genes. Mol Cell Biol 1986; 6(2): 477–487
Costa RH, Lai E, Grayson DR, Darnell JE Jr. The cell-specific enhancer of the mouse transthyretin (prealbumin) gene binds a common factor at one site and a liver-specific factor(s) at two other sites. Mol Cell Biol 1988; 8(1): 81–90
Costa RH, Grayson DR, Xanthopoulos KG, Darnell JE Jr. A liverspecific DNA-binding protein recognizes multiple nucleotide sites in regulatory regions of transthyretin, α1-antitrypsin, albumin, and simian virus 40 genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1988; 85(11): 3840–3844
Grayson DR, Costa RH, Xanthopoulos KG, Darnell JE Jr. A cellspecific enhancer of the mouse α1-antitrypsin gene has multiple functional regions and corresponding protein-binding sites. Mol Cell Biol 1988; 8(3): 1055–1066
Lemken ML, Wybranietz WA, Schmidt U, Graepler F, Armeanu S, Bitzer M, Lauer UM. Expression liver-directed genes by employing synthetic transcriptional control units. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(34): 5295–5302
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, R., Wang, Q., Zhang, L. et al. Optimized human factor IX expression cassettes for hepatic-directed gene therapy of hemophilia B. Front. Med. 9, 90–99 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-015-0390-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-015-0390-2