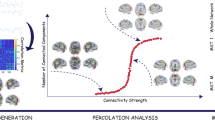
Abstract
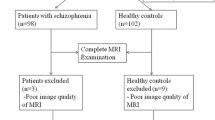
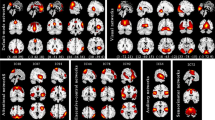
Schizophrenia is often regarded as a psychiatric disorder caused by disrupted connections in the brain. Evidence suggests that the gray matter of schizophrenia patients is damaged in a modular pattern. Recently, abnormal topological organization was observed in the gray matter networks of patients with schizophrenia. However, the modular-level alteration of gray matter networks in schizophrenia remains unclear. In this study, single-subject gray matter networks were constructed for a total of 217 subjects (116 patients with schizophrenia and 101 controls). We analyzed the topological characteristics of the brain network and the strengths of connections between and within modules. Compared with the outcomes in the control group, the global efficiency and participation coefficient values of the single-subject gray matter networks in schizophrenic patients were significantly reduced. The nodal participation coefficient of the regions involving the frontoparietal attention network, default mode network and subcortical network were significantly decreased in subjects with schizophrenia. The intermodule connections between the frontoparietal attention network and visual network and between the default mode network and subcortical network, in the frontoparietal attention network were significantly reduced in the patient group. In the frontoparietal attention network, the intramodule nodal connection strength of the left orbital inferior frontal gyrus and right inferior parietal gyrus was significantly decreased in schizophrenia patients. Reduced intermodule nodal connection strength between the frontoparietal attention network and visual network was associated with the severity of schizophrenia symptoms. These findings suggest that abnormal intramodule and intermodule connections in the structural brain network may a biomarker of schizophrenia symptoms.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Achard, S., & Bullmore, E. (2007). Efficiency and cost of economical brain functional networks. PLoS Computational Biology, 3(2), e17. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.0030017
Alexander-Bloch, A., Giedd, J. N., & Bullmore, E. (2013). Imaging structural co-variance between human brain regions. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience, 14(5), 322–336. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3465
Avena-Koenigsberger, A., Misic, B., & Sporns, O. (2017). Communication dynamics in complex brain networks. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience, 19(1), 17–33. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn.2017.149
Backes, V., Kellermann, T., Voss, B., Kramer, J., Depner, C., Schneider, F., & Habel, U. (2011). Neural correlates of the attention network test in schizophrenia. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, 261(Suppl 2), S155-160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-011-0264-9
Barnett, K. J., Foxe, J. J., Molholm, S., Kelly, S. P., Shalgi, S., Mitchell, K. J., & Newell, F. N. (2008). Differences in early sensory-perceptual processing in synesthesia: A visual evoked potential study. NeuroImage, 43(3), 605–613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.07.028
Baum, G. L., Ciric, R., Roalf, D. R., Betzel, R. F., Moore, T. M., Shinohara, R. T., & Satterthwaite, T. D. (2017). Modular segregation of structural brain networks supports the development of executive function in youth. Current Biology, 27(11), 1561–15721568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2017.04.051
Berge, D., Carmona, S., Salgado, P., Rovira, M., Bulbena, A., & Vilarroya, O. (2014). Limbic activity in antipsychotic naive first-episode psychotic subjects during facial emotion discrimination. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, 264(4), 271–283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-013-0465-5
Bramon, E., Rabe-Hesketh, S., Sham, P., Murray, R. M., & Frangou, S. (2004). Meta-analysis of the P300 and P50 waveforms in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 70(2–3), 315–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2004.01.004
Burke, L., Androutsos, C., Jogia, J., Byrne, P., & Frangou, S. (2008). The Maudsley Early Onset Schizophrenia Study: the effect of age of onset and illness duration on fronto-parietal gray matter. European Psychiatry, 23(4), 233–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpsy.2008.03.007
Butler, P. D., & Javitt, D. C. (2005). Early-stage visual processing deficits in schizophrenia. Current Opinion in Psychiatry, 18(2), 151–157. https://doi.org/10.1097/00001504-200503000-00008
Campbell, I. M., & Gregson, R. A. M. (1972). Olfactory short term memory in normal, schizophrenic and brain-damaged cases. Australian Journal of Psychology, 24(2), 179–185. https://doi.org/10.1080/00049537208255802
Chatterjee, I., Kumar, V., Rana, B., Agarwal, M., & Kumar, N. (2020). Identification of changes in grey matter volume using an evolutionary approach: an MRI study of schizophrenia. Multimedia Systems, 26(4), 383–396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-020-00649-6
Csermely, P., Xia, M., Wang, J., & He, Y. (2013). BrainNet viewer: a network visualization tool for human brain connectomics. PLoS One, 8(7). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0068910
Dosenbach, N. U., Fair, D. A., Cohen, A. L., Schlaggar, B. L., & Petersen, S. E. (2008). A dual-networks architecture of top-down control. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 12(3), 99–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2008.01.001
Dosenbach, N. U., Fair, D. A., Miezin, F. M., Cohen, A. L., Wenger, K. K., Dosenbach, R. A., & Petersen, S. E. (2007). Distinct brain networks for adaptive and stable task control in humans. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104(26), 11073–11078. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0704320104
Fair, D. A., Cohen, A. L., Power, J. D., Dosenbach, N. U., Church, J. A., Miezin, F. M., & Petersen, S. E. (2009). Functional brain networks develop from a “local to distributed” organization. PLoS Computational Biology, 5(5), e1000381. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000381
Fornito, A., Yücel, M., Patti, J., Wood, S. J., & Pantelis, C. (2009). Mapping grey matter reductions in schizophrenia: An anatomical likelihood estimation analysis of voxel-based morphometry studies. Schizophrenia Research, 108(1–3), 104–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2008.12.011
Frascarelli, M., Tognin, S., Mirigliani, A., Parente, F., Buzzanca, A., Torti, M. C., & Fusar-Poli, P. (2015). Medial frontal gyrus alterations in schizophrenia: relationship with duration of illness and executive dysfunction. Psychiatry Research, 231(2), 103–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2014.10.017
Guimera, R., & Amaral, L. A. (2005). Cartography of complex networks: modules and universal roles. Journal of Statistical Mechanics, 2005(P02001), nihpa35573. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-5468/2005/02/P02001
Gusnard, D. A., Akbudak, E., Shulman, G. L., & Raichle, M. E. (2001). Medial prefrontal cortex and self-referential mental activity: relation to a default mode of brain function. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 98(7), 4259–4264. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.071043098
Haberly, L. B. (1998). Olfactory cortex. In The synaptic organization of the brain (4th ed., pp. 377–416). Oxford University Press.
He, Y., Chen, Z. J., & Evans, A. C. (2007). Small-world anatomical networks in the human brain revealed by cortical thickness from MRI. Cerebral Cortex, 17(10), 2407–2419. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhl149
Kikinis, Z., Fallon, J. H., Niznikiewicz, M., Nestor, P., Davidson, C., Bobrow, L., & Shenton, M. E. (2010). Gray matter volume reduction in rostral middle frontal gyrus in patients with chronic schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 123(2–3), 153–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2010.07.027
Li, M., Becker, B., Zheng, J., Zhang, Y., Chen, H., Liao, W., & Chen, H. (2019). Dysregulated maturation of the functional connectome in antipsychotic-naive, first-episode patients with adolescent-onset schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 45(3), 689–697. https://doi.org/10.1093/schbul/sby063
Li, X., Wu, K., Zhang, Y., Kong, L., Bertisch, H., & DeLisi, L. E. (2019). Altered topological characteristics of morphological brain network relate to language impairment in high genetic risk subjects and schizophrenia patients. Schizophrenia Research, 208, 338–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2019.01.025
Li, Y., Li, W. X., Xie, D. J., Wang, Y., Cheung, E. F. C., & Chan, R. C. K. (2018). Grey matter reduction in the caudate nucleus in patients with persistent negative symptoms: An ALE meta-analysis. Schizophrenia Research, 192, 9–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2017.04.005
McGuire, P. K., Paulesu, E., Frackowiak, R. S., & Frith, C. D. (1996). Brain activity during stimulus independent thought. NeuroReport, 7(13), 2095–2099
Moberg, P. J., Agrin, R., Gur, R. E., Gur, R. C., Turetsky, B. I., & Doty, R. L. (1999). Olfactory dysfunction in schizophrenia: a qualitative and quantitative review. Neuropsychopharmacology, 21(3), 325–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(99)00019-6
Packard, M. G., & Knowlton, B. J. (2002). Learning and memory functions of the Basal Ganglia. Annual Review of Neuroscience (Palo Alto, CA), 25, 563–593. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.25.112701.142937
Quinn, M., McHugo, M., Armstrong, K., Woodward, N., Blackford, J., & Heckers, S. (2018). Impact of substance use disorder on gray matter volume in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Research-Neuroimaging, 280, 9–14
Raichle, M. E., & Snyder, A. Z. (2007). A default mode of brain function: a brief history of an evolving idea. NeuroImage, 37(4), 1083–1090. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.02.041 discussion 1097 – 1089
Rapoport, J. L., Giedd, J. N., & Gogtay, N. (2012). Neurodevelopmental model of schizophrenia: update 2012. Molecular Psychiatry, 17(12), 1228–1238. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2012.23
Roiser, J. P., Wigton, R., Kilner, J. M., Mendez, M. A., Hon, N., Friston, K. J., & Joyce, E. M. (2013). Dysconnectivity in the frontoparietal attention network in schizophrenia. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 4, 176. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2013.00176
Salgado-Pineda, P., Fakra, E., Delaveau, P., McKenna, P. J., Pomarol-Clotet, E., & Blin, O. (2011). Correlated structural and functional brain abnormalities in the default mode network in schizophrenia patients. Schizophrenia Research, 125(2–3), 101–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2010.10.027
Seidlitz, J., Vasa, F., Shinn, M., Romero-Garcia, R., Whitaker, K. J., Vertes, P. E., & Consortium, N. (2018). Morphometric similarity networks detect microscale cortical organization and predict inter-individual cognitive variation. Neuron, 97(1), 231–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2017.11.039
Son, S., Miyata, J., Mori, Y., Isobe, M., Urayama, S. I., Aso, T., & Takahashi, H. (2017). Lateralization of intrinsic frontoparietal network connectivity and symptoms in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging, 260, 23–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2016.12.007
Sporns, O., & Betzel, R. F. (2016). Modular brain networks. Annual Review of Psychology, 67, 613–640. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-122414-033634
Stegmayer, K., Horn, H., Federspiel, A., Razavi, N., Bracht, T., Laimbock, K., & Walther, S. (2014). Supplementary motor area (SMA) volume is associated with psychotic aberrant motor behaviour of patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Research-Neuroimaging, 223(1), 49–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2014.05.002
Stegmayer, K., Horn, H., Federspiel, A., Razavi, N., Bracht, T., Laimbock, K., & Walther, S. (2014). Ventral striatum gray matter density reduction in patients with schizophrenia and psychotic emotional dysregulation. Neuroimage Clin, 4, 232–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2013.12.007
Sutherling, W. W., & Levesque, M. F. (1996). Electrical stimulation of the supplementary sensorimotor area. Advances in Neurology, 70, 211–215
Tijms, B. M., Sprooten, E., Job, D., Johnstone, E. C., Owens, D. G., Willshaw, D., & Lawrie, S. M. (2015). Grey matter networks in people at increased familial risk for schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 168(1–2), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2015.08.025
Tu, P. C., Lee, Y. C., Chen, Y. S., Li, C. T., & Su, T. P. (2013). Schizophrenia and the brain’s control network: Aberrant within- and between-network connectivity of the frontoparietal network in schizophreniae. Schizophrenia Research, 147(2–3), 339–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2013.04.011
Turetsky, B. I., Hahn, C. G., Borgmann-Winter, K., & Moberg, P. J. (2009). Scents and nonsense: olfactory dysfunction in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 35(6), 1117–1131. https://doi.org/10.1093/schbul/sbp111
Wang, H., Jin, X., Zhang, Y., & Wang, J. (2016). Single-subject morphological brain networks: connectivity mapping, topological characterization and test-retest reliability. Brain and Behavior: A Cognitive Neuroscience Perspective, 6(4), e00448. https://doi.org/10.1002/brb3.448
Wang, J., Wang, X., Xia, M., Liao, X., Evans, A., & He, Y. (2015). GRETNA: a graph theoretical network analysis toolbox for imaging connectomics. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2015.00386
Wang, K., Fan, J., Dong, Y., Wang, C. Q., Lee, T. M., & Posner, M. I. (2005). Selective impairment of attentional networks of orienting and executive control in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 78(2–3), 235–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2005.01.019
Weiss, A. P., Ellis, C. B., Roffman, J. L., Stufflebeam, S., Hamalainen, M. S., Duff, M., & Schacter, D. L. (2009). Aberrant frontoparietal function during recognition memory in schizophrenia: a multimodal neuroimaging investigation. The Journal of Neuroscience, 29(36), 11347–11359. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0617-09.2009
Xia, M., He, Y., Mechelli, A., Wei, S., Jiang, X., Liao, X., & Ma, Q. (2020). Transdiagnostic dysfunctions in brain modules across patients with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder: a connectome-based study. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 46(3), 699–712. https://doi.org/10.1093/schbul/sbz111
Yan, H., Tian, L., Wang, Q. F., Zhao, Q., Yue, W. H., Yan, J., & Zhang, D. (2015). Compromised small-world efficiency of structural brain networks in schizophrenic patients and their unaffected parents. Neuroscience Bulletin, 31(3), 275–287. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-014-1518-0
Yu, R., Hsieh, M. H., Wang, H. L., Liu, C. M., Liu, C. C., Hwang, T. J., & Tseng, W. Y. (2013). Frequency dependent alterations in regional homogeneity of baseline brain activity in schizophrenia. PLoS One1, 8(3), e57516. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0057516
Yu, T., Li, Y. L., Fan, F. M., Cao, H. B., Luo, X. G., Tan, S. P., & Tan, Y. L. (2018). Decreased gray matter volume of cuneus and lingual gyrus in schizophrenia patients with tardive dyskinesia is associated with abnormal involuntary movement. Scientific Reports, 8, ARTN 12884. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-31186-y
Zarei, M. (2018). Precentral gyrus abnormal connectivity in male and female patients with schizophrenia. Neuroimmunology and Neuroinflammation, 5(4). https://doi.org/10.20517/2347-8659.2018.02
Zhang, J., Wang, J., Wu, Q., Kuang, W., Huang, X., He, Y., & Gong, Q. (2011). Disrupted brain connectivity networks in drug-naive, first-episode major depressive disorder. Biological Psychiatry, 70(4), 334–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.05.018
Zhang, Y., Lin, L., Lin, C. P., Zhou, Y., Chou, K. H., Lo, C. Y., & Jiang, T. (2012). Abnormal topological organization of structural brain networks in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 141(2–3), 109–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2012.08.021
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62176177, 61873178, 61906130), the National Key R & D Program of China (2018AAA0102601), and the Key Research and Development Project in Shanxi (201903D121151, 2019JG020153).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Bin Wang and Yunxiao Ma conceived the idea, performed the data analysis, and wrote the draft. Miaomiao Liu, Yuxiang Guo and Ting Li have made great contributions to the subsequent revision of the paper. All authors discussed the results, and contributed to the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
We use data from the NU Schizophrenia Data Software Tool (NUSDAST) of the public schizophrenia neuroimaging database. All participants gave informed consent.
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest reported by any of the authors.
Consent to publish
This manuscript has not been previously published and is not currently in press, under review, or being considered for publication by another journal. All authors have read and approved the manuscript being submitted, and agree to its publish to this journal.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 24.6 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Y., Ma, Y., Wang, G. et al. Modular-level alterations of single-subject gray matter networks in schizophrenia. Brain Imaging and Behavior 16, 855–867 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-021-00571-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-021-00571-z