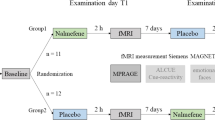
Abstract
High levels of impulsivity are a risk factor for the initiation of heroin use and a core behavioral characteristic of heroin dependence. Impulsivity also contributes to the maintenance of drug use and hinders effective therapy. Here we sought to identify neuroimaging markers of impulsivity in heroin-dependent individuals (HDI), with a focus on the nucleus accumbens (NAc), a key region implicated in impulsivity and drug addiction generally. Volume and resting-state functional connectivity (RSFC) differences of the bilateral NAc were investigated between 21 HDI and 21 age-, gender-, nicotine-, alcohol-matched healthy controls (HC). The neuroimaging results were then correlated with the Barratt Impulsivity Scales (BIS-11). Higher motor impulsivity (t = 2.347, p = 0.0253) and larger right NAc volume (F (1,38) = 4.719, p = 0.036) was observed in HDI. The right NAc volume was positively correlated with BIS total (r = 0.6196, p = 0.0239) /motor (r = 0.5921, p = 0.0330) scores in HC and BIS motor (r = 0.5145, p = 0.0170) score in HDI. A negative correlation was found between RSFC of the right NAc-bilateral superior frontal gyrus (SFG) and motor impulsivity in HDI (left: r=-0.6537, p = 0.0013; right: r=-0.6167, p = 0.0029) and HC (left: r=-0.6490,p = 0.0164; right: r=-0.6993, p = 0.0078). We aimed to reveal novel multimodality neuroimaging biomarkers of the higher impulsivity in HDI by focusing on the NAc and corresponding functional circuits. Higher motor impulsivity was observed in HDI. Furthermore, the volume of the right NAc and the RSFC strength of right NAc-SFG could be neuroimaging biomarkers for the severity of impulsivity in HDI. These potential biomarkers could be a target for novel treatments in HDI.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araujo, S. D. C., Body, S. C., Hampson, C. L., Langley, R. W., Deakin, J. F. W., Anderson, I. M., ... Szabadi, E. (2009). Effects of lesions of the nucleus accumbens core on inter-temporal choice: Further observations with an adjusting-delay procedure. Behavioural Brain Research, 202(2), 272–277.
Argyriou, E., Um, M., Carron, C. R., & Cyders, M. A. (2018). Age and impulsive behavior in drug addiction: A review of past research and future directions. Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior, 164, 106–117.
Bari, A., & Robbins, T. W. (2013). Inhibition and impulsivity: Behavioral and neural basis of response control. Progress in Neurobiology, 108, 44–79.
Basar, K., Sesia, T., Groenewegen, H. J., Steinbusch, H. W. M., Visservandewalle, V., & Temel, Y. (2010). Nucleus accumbens and impulsivity. Progress in Neurobiology, 92(4), 533–557.
Bezzina, G., Cheung, T. H. C., Asgari, K., Hampson, C. L., Body, S. C., Bradshaw, C. M., & Anderson, I. M. (2007). Effects of quinolinic acid-induced lesions of the nucleus accumbens core on inter-temporal choice: a quantitative analysis. Psychopharmacology (Berlin), 195(1), 71–84.
Burnette, E. M., Grodin, E. N., Lim, A. C., Mackillop, J., Karno, M. P., & Ray, L. A. (2019). Association between impulsivity and neural activation to alcohol cues in heavy drinkers. Psychiatry Research-Neuroimaging, 293, 110986.
Burns, J., Kroll, D. S., Feldman, D. E., Liu, C. K., Manza, P., Wiers, C. E., & Wang, G. (2019). Molecular imaging of opioid and dopamine systems: insights into the pharmacogenetics of opioid use disorders. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 10, 626.
Cai, C., Yuan, K., Yin, J., Feng, D., Bi, Y., Li, Y., ... Tian, J. (2016). Striatum morphometry is associated with cognitive control deficits and symptom severity in internet gaming disorder. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 10(1), 12–20.
Cangemi, S., Giorgi, I., Bonfiglio, N. S., Renati, R., & Vittadini, G. (2010). Impulsiveness and time perception in alcohol dependent patients in alcoholic rehabilitation treatment. Giornale Italiano di Medicina del Lavoro Ed Ergonomia, 32(3 Suppl B), B23.
Cardinal, R. N., Pennicott, D. R., Sugathapala, C. L., Robbins, T. W., & Everitt, B. J. (2001). Impulsive choice induced in rats by lesions of the nucleus accumbens core. Science, 292(5526), 2499–2501.
Chambers, R. A., & Potenza, M. N. (2003). Neurodevelopment, impulsivity, and adolescent gambling. Journal of Gambling Studies, 19(1), 53–84.
Chang, L., Yakupov, R., Cloak, C., & Ernst, T. (2006). Marijuana use is associated with a reorganized visual-attention network and cerebellar hypoactivation. Brain, 129(5), 1096–1112.
Chen, C., Huang, M., Yen, J., Chen, C., Liu, G., Yen, C., & Ko, C. (2015). Brain correlates of response inhibition in Internet gaming disorder. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 69(4), 201–209.
Christakou, A., Robbins, T. W., & Everitt, B. J. (2004). Prefrontal cortical–ventral striatal interactions involved in affective modulation of attentional performance: implications for corticostriatal circuit function. The Journal of Neuroscience, 24(4), 773–780.
Clark, L., Robbins, T. W., Ersche, K. D., & Sahakian, B. J. (2006). Reflection impulsivity in current and former substance users. Biological Psychiatry, 60(5), 515–522.
Crews, F. T., & Boettiger, C. A. (2009). Impulsivity, frontal lobes and risk for addiction. Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior, 93(3), 237–247.
Dalley, J. W., Everitt, B. J., & Robbins, T. W. (2011). Impulsivity, compulsivity, and top-down cognitive control. Neuron, 69(4), 680–694.
Dalley, J. W., Fryer, T. D., Brichard, L., Robinson, E. S. J., Theobald, D. E. H., Laane, K., ... Probst, K. C. (2007). Nucleus accumbens D2/3 receptors predict trait impulsivity and cocaine reinforcement. Science, 315(5816), 1267–1270.
Dalley, J. W., Mar, A. C., Economidou, D., & Robbins, T. W. (2008). Neurobehavioral mechanisms of impulsivity: Fronto-striatal systems and functional neurochemistry. Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior, 90(2), 250–260.
Dardenne, K., Eshel, N., Luka, J., Lenartowicz, A., Nystrom, L. E., & Cohen, J. D. (2012). Role of prefrontal cortex and the midbrain dopamine system in working memory updating. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109(49), 19900–19909.
de Wit, H. (2009). Impulsivity as a determinant and consequence of drug use: a review of underlying processes. Addiction Biology, 14(1), 22–31.
Eagle, D. M., & Robbins, T. W. (2003). Inhibitory control in rats performing a stop-signal reaction-time task: effects of lesions of the medial striatum and d-amphetamine. Behavioral Neuroscience, 117(6), 1302–1317.
Eklund, A., Nichols, T. E., & Knutsson, H. (2016). Cluster failure: Why fMRI inferences for spatial extent have inflated false-positive rates. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 113(28), 7900–7905.
Feja, M., & Koch, M. (2015). Frontostriatal systems comprising connections between ventral medial prefrontal cortex and nucleus accumbens subregions differentially regulate motor impulse control in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berlin), 232(7), 1291–1302.
Field, M., & Cox, W. M. (2008). Attentional bias in addictive behaviors: A review of its development, causes, and consequences. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 97(1), 1–20.
Haber, S. N. (2003). The primate basal ganglia: parallel and integrative networks. Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy, 26(4), 317–330.
Heatherton, T. F., Kozlowski, L. T., Frecker, R. C., & Fagerstrom, K. O. (1991). The Fagerström test for nicotine dependence: a revision of the Fagerstrom tolerance questionnaire. Addiction, 86(9), 1119–1127.
Hu, Y., Salmeron, B. J., Gu, H., Stein, E. A., & Yang, Y. (2015). Impaired functional connectivity within and between frontostriatal circuits and its association with compulsive drug use and trait impulsivity in cocaine addiction. JAMA Psychiatry, 72(6), 584–592.
Jin, C., Zhang, T., Cai, C., Bi, Y., Li, Y., Yu, D., ... Yuan, K. (2016). Abnormal prefrontal cortex resting state functional connectivity and severity of internet gaming disorder. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 10(3), 719–729.
Johnson, M. W., Bickel, W. K., Baker, F., Moore, B. A., Badger, G. J., & Budney, A. J. (2010). Delay discounting in current and former marijuana-dependent individuals. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology, 18(1), 99–107.
Kim, J., Chun, J., Park, C., Cho, H. M., Choi, J., Yang, S., & Kim, D. (2019). The correlation between the Frontostriatal network and impulsivity in internet gaming disorder. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 1191.
Ko, C., Hsieh, T., Chen, C., Yen, C., Chen, C., Yen, J., ... Liu, G. (2014). Altered brain activation during response inhibition and error processing in subjects with Internet gaming disorder: a functional magnetic imaging study. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, 264(8), 661–672.
Koehler, S., Hasselmann, E., Wustenberg, T., Heinz, A., & Romanczukseiferth, N. (2015). Higher volume of ventral striatum and right prefrontal cortex in pathological gambling. Brain Structure & Function, 220(1), 469–477.
Kozak, K., Lucatch, A. M., Lowe, D. J. E., Balodis, I. M., Mackillop, J., & George, T. P. (2019). The neurobiology of impulsivity and substance use disorders: implications for treatment. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1451(1), 71–91.
Kreek, M. J., Nielsen, D. A., Butelman, E. R., & Laforge, K. S. (2005). Genetic influences on impulsivity, risk taking, stress responsivity and vulnerability to drug abuse and addiction. Nature Neuroscience, 8(11), 1450–1457.
Li, M., Tian, J., Zhang, R., Qiu, Y., Wen, X., Ma, X., ... Huang, R. (2014). Abnormal cortical thickness in heroin-dependent individuals. NeuroImage, 88, 295–307.
Li, X., Zhang, F., Zhou, Y., & Shen. (2013). Decision-making deficits are still present in heroin abusers after short- to long-term abstinence. Drug & Alcohol Dependence, 130(1–3), 61–67.
Liston, C., Watts, R., Tottenham, N., Davidson, M. C., Niogi, S. N., Ulug, A. M., & Casey, B. J. (2006). Frontostriatal microstructure modulates efficient recruitment of cognitive control. Cerebral Cortex, 16(4), 553–560.
Ma, N., Liu, Y., Li, N., Wang, C., Zhang, H., Jiang, X., ... Zhang, D. (2010). Addiction related alteration in resting-state brain connectivity. NeuroImage, 49(1), 738–744.
McHugh, M. J., Demers, C. H., Braud, J., Briggs, R., Adinoff, B., & Stein, E. A. (2013). Striatal-insula circuits in cocaine addiction: implications for impulsivity and relapse risk. The American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse, 39(6), 424–432.
Moeller, F. G., Barratt, E. S., Dougherty, D. M., Schmitz, J. M., & Swann, A. C. (2001). Psychiatric aspects of impulsivity. American Journal of Psychiatry, 158(11), 1783–1793.
Mogenson, G. J., Jones, D. L., & Yim, C. Y. (1980). From motivation to action: functional interface between the limbic system and the motor system. Progress in Neurobiology, 14(2), 69–97.
Nestler, E. J., & Carlezon, W. A. (2006). The mesolimbic dopamine reward circuit in depression. Biological Psychiatry, 59(12), 1151–1159.
Niaz, K., Carpentier, C., Pietschmann, T., & Davis, P. (2019). World Drug Report 2019.
Patkar, A. A., Murray, H. W., Mannelli, P., Gottheil, E., Weinstein, S. P., & Vergare, M. J. (2004). Pre-treatment measures of impulsivity, aggression and sensation seeking are associated with treatment outcome for African-American cocaine-dependent patients. Journal of Addictive Diseases, 23(2), 109–122.
Patton, J. H., Stanford, M. S., & Barratt, E. S. (1995). Factor structure of the barratt impulsiveness scale. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 51(6), 768–774.
Perry, J. L., & Carroll, M. E. (2008). The role of impulsive behavior in drug abuse. Psychopharmacology (Berlin), 200(1), 1–26.
Pothuizen, H. H. J., Jongenrelo, A. L., Feldon, J., & Yee, B. K. (2005). Double dissociation of the effects of selective nucleus accumbens core and shell lesions on impulsive-choice behaviour and salience learning in rats. European Journal of Neuroscience, 22(10), 2605–2616.
Qiu, Y., Jiang, G., Ma, X., Su, H., Lv, X., & Zhuo, F. (2017). Aberrant interhemispheric functional and structural connectivity in heroin-dependent individuals. Addiction Biology, 22(4), 1057–1067.
Saunders, J. B., Aasland, O. G., Babor, T. F., Fuente, L., & Grant, M. (1993). Development of the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT): WHO collaborative project on early detection of persons with harmful alcohol consumption-II. Addiction, 88(6), 791–804.
Schippers, M. C., Binnekade, R., Schoffelmeer, A. N., Pattij, T., & De Vries, T. J. (2012). Unidirectional relationship between heroin self-administration and impulsive decision-making in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berlin), 219(2), 443–452.
Schmaal, L., Joos, L., Koeleman, M., Veltman, D. J., Brink, D., & Goudriaan, A. E. (2013). Effects of modafinil on neural correlates of response inhibition in alcohol-dependent patients. Biological Psychiatry, 73(3), 211–218.
Sun, Y., Wang, Y., Han, X., Jiang, W., Ding, W., Cao, M., ... Zhou, Y. (2019). Sex differences in resting-state cerebral activity alterations in internet gaming disorder. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 13(5), 1406–1417.
Tomasi, D., & Volkow, N. D. (2013). Striatocortical pathway dysfunction in addiction and obesity: differences and similarities. Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 48(1), 1–19.
Verdejo-García, A., Lawrence, A. J., & Clark, L. (2008). Impulsivity as a vulnerability marker for substance-use disorders: Review of findings from high-risk research, problem gamblers and genetic association studies. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 32(4), 777–810.
Vink, M., Zandbelt, B. B., Gladwin, T. E., Hillegers, M. H. J., Hoogendam, J. M., Wildenberg, D., M. V., W. P., ... Kahn, R. S. (2014). Frontostriatal activity and connectivity increase during proactive inhibition across adolescence and early adulthood. Human Brain Mapping, 35(9), 4415–4427.
Volkow, N. D., Fowler, J. S., & Wang, G. (2003). The addicted human brain: insights from imaging studies. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 111(10), 1444–1451.
Volkow, N. D., Wang, G., Fowler, J. S., Tomasi, D., & Telang, F. (2011). Addiction: Beyond dopamine reward circuitry. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108(37), 15037–15042.
Wang, S., Chen, Y., Lee, C., & Cheng, C. (2019). Opioid addiction, genetic susceptibility, and medical treatments: a review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(17), 4294.
Wang, Y., Zhu, J., Li, Q., Li, W., Wu, N., Zheng, Y., ... Wang, W. (2013). Altered fronto-striatal and fronto-cerebellar circuits in heroin-dependent individuals: a resting-state FMRI study. PLoS One, 8(3), e58098.
Xie, C., Li, S. J., Shao, Y., Fu, L., Goveas, J., Ye, E., ... Zhang, Z. (2011). Identification of hyperactive intrinsic amygdala network connectivity associated with impulsivity in abstinent heroin addicts. Behavioural Brain Research, 216(2), 0–646.
Yuan, K., Jin, C., Cheng, P., Yang, X., Dong, T., Bi, Y., ... Liu, J. (2013). Amplitude of low frequency fluctuation abnormalities in adolescents with online gaming addiction. PLoS One, 8(11), e78708.
Yuan, K., Wen, X., Wang, S., Liu, S., Shao, Z., Zhang, M., & Yu, D. (2020). Potential neural mechanism of single session transcranial magnetic stimulation on smoking craving. Information Sciences, 63(170105), 1–170105.
Yuan, K., Yu, D., Bi, Y., Li, Y., Guan, Y., Liu, J., ... Tian, J. (2016). The implication of frontostriatal circuits in young smokers: A resting-state study. Human Brain Mapping, 37(6), 2013–2026.
Yuan, K., Yu, D., Bi, Y., Wang, R., Li, M., Zhang, Y., ... Lu, X. (2017). The left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and caudate pathway: New evidence for cue-induced craving of smokers. Human Brain Mapping, 38(9), 4644–4656.
Yuan, K., Yu, D., Cai, C., Feng, D., Li, Y., Bi, Y., ... Li, L. (2017). Frontostriatal circuits, resting state functional connectivity and cognitive control in internet gaming disorder. Addiction Biology, 22(3), 813–822.
Yuan, K., Zhao, M., Yu, D., Manza, P., Volkow, N. D., Wang, G.-J., & Tian, J. (2018). Striato-cortical tracts predict 12-h abstinence-induced lapse in smokers. Neuropsychopharmacology : official publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology, 43(12), 2452–2458.
Yuan, K., Yu, D., Zhao, M., Li, M., Wang, R., Li, Y., ... Wang, G. (2018). Abnormal frontostriatal tracts in young male tobacco smokers. NeuroImage, 183, 346–355.
Zandbelt, B. B., & Vink, M. (2010). On the role of the striatum in response inhibition. PLoS One, 5(11), e13848.
Zeng, H., Lee, T. M. C., Waters, J. H., So, K., Sham, P. C., Schottenfeld, R. S., & Chawarski, M. C. (2013). Impulsivity, cognitive function, and their relationship in heroin-dependent individuals. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 35(9), 897–905.
Zhai, T., Shao, Y., Chen, G., Ye, E., Ma, L., Wang, L., ... Zou, F. (2015). Nature of functional links in valuation networks differentiates impulsive behaviors between abstinent heroin-dependent subjects and nondrug-using subjects. NeuroImage, 115, 76–84.
Zhang, Y., Gong, J., Xie, C., Ye, E., Jin, X., Song, H., ... Shao, Y. (2015). Alterations in brain connectivity in three sub-regions of the anterior cingulate cortex in heroin-dependent individuals: evidence from resting state fMRI. Neuroscience, 284, 998–1010.
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 81871426, 81871430, 61971451, the program for Young Talents of Science and Technology in Universities of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region NJYT-17-B11, the Key R & D projects in Hunan Province (2019SK2131), the Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia under Grant No. 2019JQ07, the science and technology planning project of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region 2019GG109, Chunhui Program of the Ministry of Education of the People’s Republic of China 2018-45.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Only the authors listed are responsible for the content and preparation of this manuscript. SW, KY, JuL conceptualized and designed the study. SW, MZ, SL, YX conducted the behavioral and imaging analyses. ZS, LC, JL, WY conducted the assessments. KY and JuL modified the manuscript and supervised the study. SW wrote the first draft and all authors provided input on the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
All human studies were approved by the local Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the Second Xiang-Ya Hospital of Central South University. All subjects provided signed written consent forms before participating in any experiments.
Conflict of interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Zhang, M., Liu, S. et al. Impulsivity in heroin‐dependent individuals: structural and functional abnormalities within frontostriatal circuits. Brain Imaging and Behavior 15, 2454–2463 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-020-00445-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-020-00445-w