Abstract
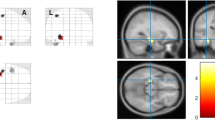
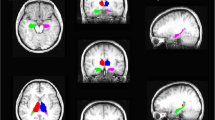
We aimed to perform a meta-analysis to systematically determine the most consistent regions of gray matter volume (GMV) abnormality in patients of unilateral mesial temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis (MTLE-HS), and to reveal the difference of GMV abnormality between the patients with left-sided and right-sided MTLE-HS. A comprehensive and systematic search was performed in PubMed for voxel-based morphometry (VBM) studies of MTLE-HS. A total of 12 MTLE-HS studies, including 9 left-sided MTLE-HS (LMTLE-HS) and 8 right-sided MTLE-HS (RMTLE-HS) studies were included. The activation likelihood estimation (ALE) method was applied in our meta-analysis. Compared to the healthy controls, MTLE-HS patients showed significant GMV decrease in the parahippocampal gyrus, left pulvinar and right pyramis. For LMTLE-HS, the most consistent GMV decrease was detected in the left parahippocampal gyrus. For RMTLE-HS, the most consistent GMV decrease was found in the right parahippocampal gyrus. No shared regions of significant GMV reduction were found between LMTLE-HS and RMTLE-HS either. This meta-analysis revealed that MTLE-HS patients had significant GMV reduction even beyond the hippocampus, and the subtypes showed distinct reduction patterns. Our findings, if were further verified with larger samples, would have implications for the clinical diagnosis of MTLE-HS.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alessio, A., et al. (2006). Memory and language impairments and their relationships to hippocampal and perirhinal cortex damage in patients with medial temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy & Behavior, 8(3), 593–600.
Allegri, R. F., Drake, M., & Thomson, A. (1999). [Neuropsychological findings in patients with middle temporal lobe epilepsy]. Revista De Neurologia, 29(12), 1160.
Benarroch, E. E. (2015). Pulvinar: associative role in cortical function and clinical correlations. Neurology, 84(7), 738–747.
Bernasconi, N., et al. (2004) Whole-brain voxel-based statistical analysis of gray matter and white matter in temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroimage, 23(2), 717–723.
Bonilha, L., et al. (2004). Voxel-based morphometry reveals gray matter network atrophy in refractory medial temporal lobe epilepsy. Archives of Neurology, 61(9), 1379–1384.
Bonilha, L., et al. (2006). Gray matter atrophy associated with duration of temporal lobe epilepsy. NeuroImage, 32(3), 1070–1079.
Bonilha, L., et al. (2007). Extrahippocampal gray matter atrophy and memory impairment in patients with medial temporal lobe epilepsy. Human Brain Mapping, 28(12), 1376–1390.
Brázdil, M., et al. (2008). Correlation study of optimized voxel-based morphometry and 1H MRS in patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy and hippocampal sclerosis (MTLE/HS). Human Brain Mapping, 30(4), 1226–1235.
Brockwell, S. E., & Gordon, I. R. (2001). A comparison of statistical methods for meta-analysis. Statistics in Medicine, 20(6), 825–840.
Eichenbaum, H., Otto, T., & Cohen, N. J. (1992). The hippocampus–what does it do? Behavioral & Neural Biology, 57(1), 2–36.
Eickhoff, S. B., et al. (2011). Activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis revisited. NeuroImage, 59(3), 2349–2361.
Golby, A. J., et al. (2002). Memory lateralization in medial temporal lobe epilepsy assessed by functional MRI. Epilepsia, 43(8), 855–863.
Han, M. W., et al. (2011). Central auditory processing impairment in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy & Behavior, 20(2), 370–374.
Hermann, B. P., et al. (1997). Neuropsychological characteristics of the syndrome of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Jama Neurology, 54(4), 369–376.
Kapur, N., & Prevett, M. (2003). Unexpected amnesia: are there lessons to be learned from cases of amnesia following unilateral temporal lobe surgery? Brain, 126(12), 2573–2585.
Keller, S. S., et al. (2002). Voxel-based morphometric comparison of hippocampal and extrahippocampal abnormalities in patients with left and right hippocampal atrophy. Neuroimage, 16(1), 23–31.
Keller, S. S., et al. (2004). Comparison of standard and optimized voxel-based morphometry for analysis of brain changes associated with temporal lobe epilepsy. NeuroImage, 23(3), 860–868.
Köhler, S., et al. (1998). Memory impairments associated with hippocampal versus parahippocampal-gyrus atrophy: an MR volumetry study in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychologia, 36(9), 901–914.
Lambrecq, V., et al. (2013). Evolution of brain gray matter loss in Huntington’s disease: a meta-analysis. European Journal of Neurology, 20(2), 315–321.
Li, J., Zhang, Z., & Shang, H. (2012). A meta-analysis of voxel-based morphometry studies on unilateral refractory temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Research, 98(2), 97–103.
Lu, J., et al. (2012). Altered hemispheric symmetry found in left-sided mesial temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis (MTLE/HS) but not found in right-sided MTLE/HS. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 31(1), 53–59.
McMillan, A. B., et al. (2004). Voxel-based morphometry of unilateral temporal lobe epilepsy reveals abnormalities in cerebral white matter. NeuroImage, 23(1), 167–174.
Mueller, S. G., et al. (2006). Voxel-based optimized morphometry (VBM) of gray and white matter in temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) with and without mesial temporal sclerosis. Epilepsia, 47(5), 900–907.
Pail, M., et al. (2010). An optimized voxel-based morphometric study of gray matter changes in patients with left-sided and right-sided mesial temporal lobe epilepsy and hippocampal sclerosis (MTLE/HS). Epilepsia, 51(4), 511–518.
Pandya, D. N. (1995). Anatomy of the auditory cortex. Revue Neurologique, 151(8–9), 486.
Pell, G. S., et al. (2008). Composite voxel-based analysis of volume and T2 relaxometry in temporal lobe epilepsy. NeuroImage, 39(3), 1151–1161.
Phillips, D. P. (2002). Central auditory system and central auditory processing disorders: some conceptual issues. Seminars in Hearing, 23(4), 251–262.
Portas, C. M., et al. (1998). A specific role for the thalamus in mediating the interaction of attention and arousal in humans. Journal of Neuroscience the Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 18(21), 8979–8989.
Raine, A., et al. (2000). Reduced prefrontal gray matter volume and reduced autonomic activity in antisocial personality disorder. Archives of General Psychiatry, 57(2), 119–127.
Riederer, F., et al. (2008). Network atrophy in temporal lobe epilepsy A voxel-based morphometry study. Neurology, 71(6), 419–425.
Santana, M. T., et al. (2010). Auras and clinical features in temporal lobe epilepsy: a new approach on the basis of voxel-based morphometry. Epilepsy Research, 89(2), 327–338.
Squire, L. R., & Squire, L. R. (1992). Memory and the hippocampus: a synthesis from findings with rats, monkeys, and humans. Psychological Review, 99(2), 195–231.
Tae, W. S., et al. (2010). Gray, white matter concentration changes and their correlation with heterotopic neurons in temporal lobe epilepsy. Korean Journal of Radiology Official Journal of the Korean Radiological Society, 11(1), 25–36.
Treiman, D. M. (2001). GABAergic mechanisms in epilepsy. Epilepsia, 42(3), 8–12.
Wei, W., et al. (2016). More severe extratemporal damages in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis than that with other lesions: a multimodality MRI study. Medicine, 95(10), e3020.
Wheeler, S. M., et al. (2012). Visuospatial associative memory and hippocampal functioning in congenital hypothyroidism. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 18(1), 49–56.
Yu, F., et al. (2015). Patterns of gray matter atrophy in atypical parkinsonism syndromes: a VBM meta-analysis. Brain and Behavior, 5(6), e00329.
Zhang, Z., et al. (2009a). Impaired perceptual networks in temporal lobe epilepsy revealed by resting fMRI. Journal of Neurology, 256(10), 1705–1713.
Zhang, Z., et al. (2009b). Impaired attention network in temporal lobe epilepsy: a resting FMRI study. Neuroscience Letters, 458(3), 97–101.
Zolamorgan, S., et al. (1989). Lesions of perirhinal and parahippocampal cortex that spare the amygdala and hippocampal formation produce severe memory impairment. Journal of Neuroscience the Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 9(12), 4355–4370.
Funding
This work was supported by The Seed Funding from Scientific and Technical Innovation Council of Shenzhen Government (No. 000048), Special Funding Scheme for Supporting the Innovation and Research of Shenzhen High-caliber Overseas Intelligent (No. KQCX20140519103243534), and Shenzhen Municipal Scheme for Basic Research (No. JCYJ20170303160116960).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, L., Bin, G., Zeng, H. et al. Meta-analysis of voxel-based morphometry studies of gray matter abnormalities in patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy and unilateral hippocampal sclerosis. Brain Imaging and Behavior 12, 1497–1503 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-017-9797-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-017-9797-5