Abstract
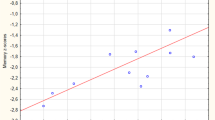
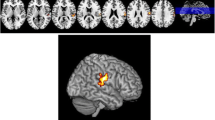
Early-onset Parkinson’s disease (EOPD) has a clinical course and characteristics distinct from middle-late-onset Parkinson’s disease (M-LOPD). Although many studies have investigated these differences, the neural mechanisms of these characteristics remain unclear. This study aimed to investigate the morphological differences, and their related clinical significance, between EOPD and M-LOPD patients. We recruited two groups of patients, 28 EOPD patients and 37 M-LOPD patients, and two age- and sex-matched control groups (23 controls in each group). The voxel-based morphometry (VBM) technique was used to examine changes in gray matter (GM) density between patients and their corresponding controls. Compared with controls, EOPD patients had lower GM density in the left putamen, inferior frontal gyrus and insula, and higher GM density in the right occipital lobe and bilateral cerebellum posterior lobes. M-LOPD patients had lower GM density in the left cerebellum posterior lobe, occipital lobe and right supplementary motor area (SMA), and higher GM density in the left middle temporal gyrus. Correlation analyses showed that GM density values in the right cerebellum posterior lobe positively correlated with the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) motor scores and the Hoehn–Yahr stages in EOPD patients. Our results reveal different patterns of structural changes in EOPD and M-LOPD patients. A probable compensatory effect of the cerebellum was observed and may partly explain the slower decline of motor function in EOPD patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alves, G., Wentzel-Larsen, T., Aarsland, D., & Larsen, J. P. (2005). Progression of motor impairment and disability in Parkinson disease: A population-based study. Neurology, 65(9), 1436–1441. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000183359.50822.f2.
Ashburner, J. (2007). A fast diffeomorphic image registration algorithm. NeuroImage, 38(1), 95–113. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.07.007.
Bartzokis, G., Cummings, J. L., Markham, C. H., Marmarelis, P. Z., Treciokas, L. J., Tishler, T. A., Marder, S. R., & Mintz, J. (1999). MRI evaluation of brain iron in earlier- and later-onset Parkinson’s disease and normal subjects. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 17(2), 213–222.
Benninger, D. H., Thees, S., Kollias, S. S., Bassetti, C. L., & Waldvogel, D. (2009). Morphological differences in Parkinson's disease with and without rest tremor. Journal of Neurology, 256(2), 256–263. doi:10.1007/s00415-009-0092-2.
Biundo, R., Formento-Dojot, P., Facchini, S., Vallelunga, A., Ghezzo, L., Foscolo, L., Meneghello, F., & Antonini, A. (2011). Brain volume changes in Parkinson's disease and their relationship with cognitive and behavioural abnormalities. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 310(1–2), 64–69. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2011.08.001.
Borghammer, P., Ostergaard, K., Cumming, P., Gjedde, A., Rodell, A., Hall, N., & Chakravarty, M. M. (2010). A deformation-based morphometry study of patients with early-stage Parkinson's disease. European Journal of Neurology, 17(2), 314–320. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2009.02807.x.
Camicioli, R., Gee, M., Bouchard, T. P., Fisher, N. J., Hanstock, C. C., Emery, D. J., & Martin, W. R. (2009). Voxel-based morphometry reveals extra-nigral atrophy patterns associated with dopamine refractory cognitive and motor impairment in parkinsonism. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders, 15(3), 187–195. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2008.05.002.
Catalan, M. J., Ishii, K., Honda, M., Samii, A., & Hallett, M. (1999). A PET study of sequential finger movements of varying length in patients with Parkinson's disease. Brain : A Journal of Neurology, 122(Pt 3), 483–495.
DeYoe, E. A., Carman, G. J., Bandettini, P., Glickman, S., Wieser, J., Cox, R., Miller, D., & Neitz, J. (1996). Mapping striate and extrastriate visual areas in human cerebral cortex. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 93(6), 2382–2386.
Eggers, C., Gunther, M., Rothwell, J., Timmermann, L., & Ruge, D. (2015). Theta burst stimulation over the supplementary motor area in Parkinson's disease. Journal of Neurology, 262(2), 357–364. doi:10.1007/s00415-014-7572-8.
de la Fuente-Fernandez, R., Schulzer, M., Kuramoto, L., Cragg, J., Ramachandiran, N., Au, W. L., Mak, E., McKenzie, J., McCormick, S., Sossi, V., Ruth, T. J., Lee, C. S., Calne, D. B., & Stoessl, A. J. (2011). Age-specific progression of nigrostriatal dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Annals of Neurology, 69(5), 803–810. doi:10.1002/ana.22284.
Garcia-Diaz, A. I., Segura, B., Baggio, H. C., Marti, M. J., Valldeoriola, F., Compta, Y., Vendrell, P., Bargallo, N., Tolosa, E., & Junque, C. (2014). Structural MRI correlates of the MMSE and pentagon copying test in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders, 20(12), 1405–1410. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2014.10.014.
Gibb, W. R., & Lees, A. J. (1988). A comparison of clinical and pathological features of young- and old-onset Parkinson's disease. Neurology, 38(9), 1402–1406.
Hamada, M., Ugawa, Y., & Tsuji, S. (2009). High-frequency rTMS over the supplementary motor area improves bradykinesia in Parkinson's disease: Subanalysis of double-blind sham-controlled study. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 287(1–2), 143–146. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2009.08.007.
Hou, Y., Yang, J., Luo, C., Ou, R., Song, W., Liu, W., Gong, Q., & Shang, H. (2016). Patterns of striatal functional connectivity differ in early and late onset Parkinson's disease. Journal of Neurology. doi:10.1007/s00415-016-8211-3.
Hufner, K., Stephan, T., Flanagin, V. L., Deutschlander, A., Dera, T., Karch, C., Linn, J., Glasauer, S., Dieterich, M., Strupp, M., & Brandt, T. (2011). Cerebellar and visual gray matter brain volume increases in congenital nystagmus. Frontiers in Neurology, 2, 60. doi:10.3389/fneur.2011.00060.
Hwang, K. S., Beyer, M. K., Green, A. E., Chung, C., Thompson, P. M., Janvin, C., Larsen, J. P., Aarsland, D., & Apostolova, L. G. (2013). Mapping cortical atrophy in Parkinson's disease patients with dementia. Journal of Parkinson’s disease, 3(1), 69–76. doi:10.3233/JPD-120151.
Knipe, M. D., Wickremaratchi, M. M., Wyatt-Haines, E., Morris, H. R., & Ben-Shlomo, Y. (2011). Quality of life in young- compared with late-onset Parkinson's disease. Movement disorders : official journal of the Movement Disorder Society, 26(11), 2011–2018. doi:10.1002/mds.23763.
Kostic, V. S., Agosta, F., Petrovic, I., Galantucci, S., Spica, V., Jecmenica-Lukic, M., & Filippi, M. (2010). Regional patterns of brain tissue loss associated with depression in Parkinson disease. Neurology, 75(10), 857–863. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181f11c1d.
Lee, E. Y., Sen, S., Eslinger, P. J., Wagner, D., Shaffer, M. L., Kong, L., Lewis, M. M., Du, G., & Huang, X. (2013). Early cortical gray matter loss and cognitive correlates in non-demented Parkinson's patients. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders, 19(12), 1088–1093. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2013.07.018.
Lee, H. M., Kwon, K. Y., Kim, M. J., Jang, J. W., Suh, S. I., Koh, S. B., & Kim, J. H. (2014). Subcortical grey matter changes in untreated, early stage Parkinson's disease without dementia. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders, 20(6), 622–626.
Lewis, M. M., Slagle, C. G., Smith, A. B., Truong, Y., Bai, P., McKeown, M. J., Mailman, R. B., Belger, A., & Huang, X. (2007). Task specific influences of Parkinson's disease on the striato-thalamo-cortical and cerebello-thalamo-cortical motor circuitries. Neuroscience, 147(1), 224–235. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.04.006.
Liu, S. Y., Wu, J. J., Zhao, J., Huang, S. F., Wang, Y. X., Ge, J. J., Wu, P., Zuo, C. T., Ding, Z. T., & Wang, J. (2015). Onset-related subtypes of Parkinson's disease differ in the patterns of striatal dopaminergic dysfunction: A positron emission tomography study. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders, 21(12), 1448–1453. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2015.10.017.
Mehanna, R., Moore, S., Hou, J. G., Sarwar, A. I., & Lai, E. C. (2014). Comparing clinical features of young onset, middle onset and late onset Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders, 20(5), 530–534. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2014.02.013.
Mentis, M. J., Dhawan, V., Nakamura, T., Ghilardi, M. F., Feigin, A., Edwards, C., Ghez, C., & Eidelberg, D. (2003). Enhancement of brain activation during trial-and-error sequence learning in early PD. Neurology, 60(4), 612–619.
Nachev, P., Kennard, C., & Husain, M. (2008). Functional role of the supplementary and pre-supplementary motor areas. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 9(11), 856–869. doi:10.1038/nrn2478.
Owen, A. M., Doyon, J., Dagher, A., Sadikot, A., & Evans, A. C. (1998). Abnormal basal ganglia outflow in Parkinson's disease identified with PET. Implications for higher cortical functions. Brain, 121(Pt 5), 949–965.
Quinn, N., Critchley, P., & Marsden, C. D. (1987). Young onset Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders : Official Journal of the Movement Disorder Society, 2(2), 73–91. doi:10.1002/mds.870020201.
Ramirez-Ruiz, B., Marti, M. J., Tolosa, E., Gimenez, M., Bargallo, N., Valldeoriola, F., & Junque, C. (2007). Cerebral atrophy in Parkinson's disease patients with visual hallucinations. European Journal of Neurology, 14(7), 750–756. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2007.01768.x.
Reijnders, J. S., Scholtissen, B., Weber, W. E., Aalten, P., Verhey, F. R., & Leentjens, A. F. (2010). Neuroanatomical correlates of apathy in Parkinson's disease: A magnetic resonance imaging study using voxel-based morphometry. Movement Disorders : Official Journal of the Movement Disorder Society, 25(14), 2318–2325. doi:10.1002/mds.23268.
Schrag, A., & Schott, J. M. (2006). Epidemiological, clinical, and genetic characteristics of early-onset parkinsonism. The Lancet Neurology, 5(4), 355–363. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(06)70411-2.
Sehm, B., Taubert, M., Conde, V., Weise, D., Classen, J., Dukart, J., Draganski, B., Villringer, A., & Ragert, P. (2014). Structural brain plasticity in Parkinson's disease induced by balance training. Neurobiology of Aging, 35(1), 232–239. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.06.021.
Sheng, K., Fang, W., Zhu, Y., Shuai, G., Zou, D., Su, M., Han, Y., & Cheng, O. (2016). Different alterations of cerebral regional homogeneity in early-onset and late-onset Parkinson's disease. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 8, 165. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2016.00165.
Shih, M. C., Franco de Andrade, L. A., Amaro Jr., E., Felicio, A. C., Ferraz, H. B., Wagner, J., Hoexter, M. Q., Lin, L. F., Fu, Y. K., Mari, J. J., Tufik, S., & Bressan, R. A. (2007). Higher nigrostriatal dopamine neuron loss in early than late onset Parkinson's disease?--a [99mTc]-TRODAT-1 SPECT study. Movement Disorders : Official Journal of the Movement Disorder Society, 22(6), 863–866. doi:10.1002/mds.21315.
Song, S. K., Lee, J. E., Park, H. J., Sohn, Y. H., Lee, J. D., & Lee, P. H. (2011). The pattern of cortical atrophy in patients with Parkinson's disease according to cognitive status. Movement Disorders : Official Journal of the Movement Disorder Society, 26(2), 289–296. doi:10.1002/mds.23477.
Tam, C. W., Burton, E. J., McKeith, I. G., Burn, D. J., & O'Brien, J. T. (2005). Temporal lobe atrophy on MRI in Parkinson disease with dementia: A comparison with Alzheimer disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurology, 64(5), 861–865. doi:10.1212/01.WNL.0000153070.82309.D4.
Tanner, C. M., & Aston, D. A. (2000). Epidemiology of Parkinson's disease and akinetic syndromes. Current Opinion in Neurology, 13(4), 427–430.
Tomlinson, C. L., Stowe, R., Patel, S., Rick, C., Gray, R., & Clarke, C. E. (2010). Systematic review of levodopa dose equivalency reporting in Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders : Official journal of the Movement Disorder Society, 25(15), 2649–2653. doi:10.1002/mds.23429.
Tsai, C. H., Lo, S. K., See, L. C., Chen, H. Z., Chen, R. S., Weng, Y. H., Chang, F. C., & Lu, C. S. (2002). Environmental risk factors of young onset Parkinson's disease: A case-control study. Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery, 104(4), 328–333.
Wu, T., & Hallett, M. (2008). Neural correlates of dual task performance in patients with Parkinson's disease. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 79(7), 760–766. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2007.126599.
Wu, T., & Hallett, M. (2013). The cerebellum in Parkinson's disease. Brain : A Journal of Neurology, 136(Pt 3), 696–709. doi:10.1093/brain/aws360.
Wu, T., Wang, L., Hallett, M., Li, K., & Chan, P. (2010). Neural correlates of bimanual anti-phase and in-phase movements in Parkinson's disease. Brain : A Journal of Neurology, 133(Pt 8), 2394–2409. doi:10.1093/brain/awq151.
Yu, H., Sternad, D., Corcos, D. M., & Vaillancourt, D. E. (2007). Role of hyperactive cerebellum and motor cortex in Parkinson's disease. NeuroImage, 35(1), 222–233. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.11.047.
Zhang, J., Zhang, Y. T., Hu, W. D., Li, L., Liu, G. Y., & Bai, Y. P. (2015). Gray matter atrophy in patients with Parkinson's disease and those with mild cognitive impairment: A voxel-based morphometry study. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, 8(9), 15383–15392.
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank all the Parkinson’s disease patients and normal controls who participated in our research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to report.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Funding
This study was funded by the 12th Five-year Plan for National Science and Technology Supporting Program of China (Grant No. 2012BAI10B04) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81571654, 81371519 and 81301190).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xuan, M., Guan, X., Huang, P. et al. Different patterns of gray matter density in early- and middle-late-onset Parkinson’s disease: a voxel-based morphometry study. Brain Imaging and Behavior 13, 172–179 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-017-9745-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-017-9745-4