Abstract
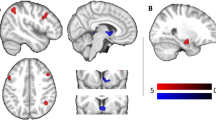
Eating behaviors are closely related to body weight, and eating traits are depicted in three dimensions: dietary restraint, disinhibition, and hunger. The current study aims to explore whether these aspects of eating behaviors are related to intrinsic brain activation, and to further investigate the relationship between the brain activation relating to these eating traits and body weight, as well as the link between function connectivity (FC) of the correlative brain regions and body weight. Our results demonstrated positive associations between dietary restraint and baseline activation of the frontal and the temporal regions (i.e., food reward encoding) and the limbic regions (i.e., homeostatic control, including the hypothalamus). Disinhibition was positively associated with the activation of the frontal motivational system (i.e., OFC) and the premotor cortex. Hunger was positively related to extensive activations in the prefrontal, temporal, and limbic, as well as in the cerebellum. Within the brain regions relating to dietary restraint, weight status was negatively correlated with FC of the left middle temporal gyrus and left inferior temporal gyrus, and was positively associated with the FC of regions in the anterior temporal gyrus and fusiform visual cortex. Weight status was positively associated with the FC within regions in the prefrontal motor cortex and the right ACC serving inhibition, and was negatively related with the FC of regions in the frontal cortical-basal ganglia-thalamic circuits responding to hunger control. Our data depicted an association between intrinsic brain activation and dietary restraint, disinhibition, and hunger, and presented the links of their activations and FCs with weight status.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, G., McColl, R., Barnard, H., Ringe, W. K., Fleckenstein, J., & Cullum, C. M. (2005). Magnetic resonance imaging of cerebellar–prefrontal and cerebellar–parietal functional connectivity. NeuroImage, 28(1), 39–48.
Beaver, J. D., Lawrence, A. D., van Ditzhuijzen, J., Davis, M. H., Woods, A., & Calder, A. J. (2006). Individual differences in reward drive predict neural responses to images of food. The Journal of Neuroscience, 26(19), 5160–5166.
Berthoud, H.-R., & Morrison, C. (2008). The brain, appetite, and obesity. Annual Review of Psychology, 59, 55–92.
Blundell, J. E., Caudwell, P., Gibbons, C., Hopkins, M., Naslund, E., King, N., et al. (2012). Role of resting metabolic rate and energy expenditure in hunger and appetite control: a new formulation. Disease Models & Mechanisms, 5(5), 608–613. doi:10.1242/dmm.009837.
Bond, M. J., McDowell, A. J., & Wilkinson, J. Y. (2001). The measurement of dietary restraint, disinhibition and hunger: an examination of the factor structure of the Three Factor Eating Questionnaire (TFEQ). International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders, 25(6), 900–906. doi:10.1038/sj.ijo.0801611.
Born, J. M., Lemmens, S. G., Rutters, F., Nieuwenhuizen, A. G., Formisano, E., Goebel, R., et al. (2010). Acute stress and food-related reward activation in the brain during food choice during eating in the absence of hunger. International Journal of Obesity, 34(1), 172–181. doi:10.1038/ijo.2009.221.
Born, J. M., Lemmens, S. G., Martens, M. J., Formisano, E., Goebel, R., & Westerterp-Plantenga, M. S. (2011). Differences between liking and wanting signals in the human brain and relations with cognitive dietary restraint and body mass index. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 94(2), 392–403.
Boschi, V., Iorio, D., Margiotta, N., D'Orsi, P., & Falconi, C. (2001). The three-factor eating questionnaire in the evaluation of eating behaviour in subjects seeking participation in a dietotherapy programme. Annals of Nutrition & Metabolism, 45(2), 72–77.
Bush, G., Vogt, B. A., Holmes, J., Dale, A. M., Greve, D., Jenike, M. A., et al. (2002). Dorsal anterior cingulate cortex: A role in reward-based decision making. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 99(1), 523–528. doi:10.1073/pnas.012470999.
Castellanos, E. H., Charboneau, E., Dietrich, M. S., Park, S., Bradley, B. P., Mogg, K., et al. (2009). Obese adults have visual attention bias for food cue images: evidence for altered reward system function. International Journal of Obesity, 33(9), 1063–1073. doi:10.1038/ijo.2009.138.
Chao-Gan, Y., & Yu-Feng, Z. (2010). DPARSF: A MATLAB Toolbox for "Pipeline" Data Analysis of Resting-State fMRI. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 4, 13. doi:10.3389/fnsys.2010.00013.
Cornier, M.-A., Von Kaenel, S. S., Bessesen, D. H., & Tregellas, J. R. (2007). Effects of overfeeding on the neuronal response to visual food cues. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 86(4), 965–971.
de Castro, J. M., & Lilenfeld, L. R. R. (2005). Influence of heredity on dietary restraint, disinhibition, and perceived hunger in humans. Nutrition, 21(4), 446–455. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2004.07.010.
De Silva, A., Salem, V., Matthews, P. M., & Dhillo, W. S. (2012). The Use of Functional MRI to Study Appetite Control in the CNS. Experimental Diabetes Research, 2012, 13. doi:10.1155/2012/764017.
DelParigi, A., Chen, K., Salbe, A. D., Reiman, E. M., & Tataranni, P. A. (2005). Sensory experience of food and obesity: a positron emission tomography study of the brain regions affected by tasting a liquid meal after a prolonged fast. NeuroImage, 24(2), 436–443. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.08.035.
DelParigi, A., Chen, K., Salbe, A., Hill, J., Wing, R., Reiman, E., et al. (2007). Successful dieters have increased neural activity in cortical areas involved in the control of behavior. International Journal of Obesity, 31(3), 440–448.
Dietrich, A., Federbusch, M., Grellmann, C., Villringer, A., & Horstmann, A. (2014). Body weight status, eating behavior, sensitivity to reward/punishment, and gender: relationships and interdependencies. Frontiers in Psychology, 5, 1073.
Drapeau, V., Provencher, V., Lemieux, S., Despres, J. P., Bouchard, C., & Tremblay, A. (2003). Do 6-y changes in eating behaviors predict changes in body weight? Results from the Quebec Family Study. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders, 27(7), 808–814.
Elfhag, K. (2005). Personality correlates of obese eating behaviour: Swedish universities Scales of Personality and the Three Factor Eating Questionnaire. Eating and Weight Disorders-Studies on Anorexia, Bulimia and Obesity, 10(4), 210–215.
Fayet, F., Petocz, P., & Samman, S. (2012). Prevalence and correlates of dieting in college women: a cross sectional study. Int J Womens Health, 4, 405–411. doi:10.2147/ijwh.s33920.
Fineberg, N. A., Potenza, M. N., Chamberlain, S. R., Berlin, H. A., Menzies, L., Bechara, A., et al. (2009). Probing Compulsive and Impulsive Behaviors, from Animal Models to Endophenotypes: A Narrative Review. Neuropsychopharmacology, 35(3), 591–604.
Foster, G. D., Wadden, T. A., Swain, R. M., Stunkard, A. J., Platte, P., & Vogt, R. A. (1998). The Eating Inventory in obese women: clinical correlates and relationship to weight loss. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders, 22(8), 778–785.
Frank, G. K., Reynolds, J. R., Shott, M. E., Jappe, L., Yang, T. T., Tregellas, J. R., et al. (2012). Anorexia nervosa and obesity are associated with opposite brain reward response. Neuropsychopharmacology, 37(9), 2031–2046.
Fuhrer, D., Zysset, S., & Stumvoll, M. (2008). Brain activity in hunger and satiety: an exploratory visually stimulated FMRI study. Obesity (Silver Spring), 16(5), 945–950. doi:10.1038/oby.2008.33.
Gallant, A. R., Tremblay, A., Perusse, L., Despres, J. P., Bouchard, C., & Drapeau, V. (2013). Parental eating behavior traits are related to offspring BMI in the Quebec Family Study. International Journal of Obesity, 37(11), 1422–1426. doi:10.1038/ijo.2013.14.
García-García, I., Jurado, M. Á., Garolera, M., Segura, B., Sala-Llonch, R., Marqués-Iturria, I., et al. (2013). Alterations of the salience network in obesity: A resting-state fMRI study. Human Brain Mapping, 34(11), 2786–2797. doi:10.1002/hbm.22104.
Gearhardt, A. N., Yokum, S., Stice, E., Harris, J. L., & Brownell, K. D. (2013). Relation of obesity to neural activation in response to food commercials. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience. doi:10.1093/scan/nst059.
Gearhardt, A. N., Yokum, S., Stice, E., Harris, J. L., & Brownell, K. D. (2014). Relation of obesity to neural activation in response to food commercials. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 9(7), 932–938.
Goldstone, A. P., Prechtl de Hernandez, C. G., Beaver, J. D., Muhammed, K., Croese, C., Bell, G., et al. (2009). Fasting biases brain reward systems towards high-calorie foods. European Journal of Neuroscience, 30(8), 1625–1635.
Green, E., Jacobson, A., Haase, L., & Murphy, C. (2015). Neural correlates of taste and pleasantness evaluation in the metabolic syndrome. Brain Research, 1620, 57–71.
Gu, H., Salmeron, B. J., Ross, T. J., Geng, X., Zhan, W., Stein, E. A., et al. (2010). Mesocorticolimbic circuits are impaired in chronic cocaine users as demonstrated by resting-state functional connectivity. NeuroImage, 53(2), 593–601. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.06.066.
Haase, L., Cerf-Ducastel, B., & Murphy, C. (2009). Cortical activation in response to pure taste stimuli during the physiological states of hunger and satiety. NeuroImage, 44(3), 1008–1021.
Harden, C. J., Corfe, B. M., Richardson, J. C., Dettmar, P. W., & Paxman, J. R. (2009). Body mass index and age affect Three-Factor Eating Questionnaire scores in male subjects. Nutrition Research, 29(6), 379–382. doi:10.1016/j.nutres.2009.04.001.
Hare, T. A., Camerer, C. F., & Rangel, A. (2009). Self-control in decision-making involves modulation of the vmPFC valuation system. Science, 324(5927), 646–648. doi:10.1126/science.1168450.
Hays, N. P., Bathalon, G. P., McCrory, M. A., Roubenoff, R., Lipman, R., & Roberts, S. B. (2002). Eating behavior correlates of adult weight gain and obesity in healthy women aged 55–65 y. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 75(3), 476–483.
Hays, N. P., Bathalon, G. P., Roubenoff, R., McCrory, M. A., & Roberts, S. B. (2006). Eating Behavior and Weight Change in Healthy Postmenopausal Women: Results of a 4-Year Longitudinal Study. The Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences, 61(6), 608–615.
Hinkle, W., Cordell, M., Leibel, R., Rosenbaum, M., & Hirsch, J. (2013). Effects of Reduced Weight Maintenance and Leptin Repletion on Functional Connectivity of the Hypothalamus in Obese Humans. PloS One, 8(3), e59114. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0059114.
Hinton, E. C., Parkinson, J. A., Holland, A. J., Arana, F. S., C. Roberts, A., & Owen, A. M. (2004). Neural contributions to the motivational control of appetite in humans. European Journal of Neuroscience, 20(5), 1411–1418, doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2004.03589.x.
Hon, N., Epstein, R. A., Owen, A. M., & Duncan, J. (2006). Frontoparietal activity with minimal decision and control. The Journal of Neuroscience, 26(38), 9805–9809, doi:10.1523/jneurosci.3165-06.2006.
Kelley, A. E., Baldo, B. A., & Pratt, W. E. (2005). A proposed hypothalamic–thalamic–striatal axis for the integration of energy balance, arousal, and food reward. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 493(1), 72–85. doi:10.1002/cne.20769.
Kenny, P. J. (2011). Reward Mechanisms in Obesity: New Insights and Future Directions. Neuron, 69(4), 664–679.
Khazaal, Y., Billieux, J., Fresard, E., Huguelet, P., Van der Linden, M., & Zullino, D. (2010). A measure of dysfunctional eating-related cognitions in people with psychotic disorders. Psychiatric Quarterly, 81(1), 49–56.
Killgore, W. D., & Yurgelun-Todd, D. A. (2006). Affect modulates appetite-related brain activity to images of food. International Journal of Eating Disorders, 39(5), 357–363.
Killgore, W. D. S., Young, A. D., Femia, L. A., Bogorodzki, P., Rogowska, J., & Yurgelun-Todd, D. A. (2003). Cortical and limbic activation during viewing of high- versus low-calorie foods. NeuroImage, 19(4), 1381–1394, doi:10.1016/S1053-8119(03)00191-5.
Kishinevsky, F. I., Cox, J. E., Murdaugh, D. L., Stoeckel, L. E., Cook Iii, E. W., & Weller, R. E. (2012). fMRI reactivity on a delay discounting task predicts weight gain in obese women. Appetite, 58(2), 582–592. doi:10.1016/j.appet.2011.11.029.
Kullmann, S., Pape, A. A., Heni, M., Ketterer, C., Schick, F., Haring, H. U., et al. (2013). Functional network connectivity underlying food processing: disturbed salience and visual processing in overweight and obese adults. Cerebral Cortex, 23(5), 1247–1256. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhs124.
Langlois, F., Langlois, M.-F., Carpentier, A. C., Brown, C., Lemieux, S., & Hivert, M.-F. (2011). Ghrelin levels are associated with hunger as measured by the Three-Factor Eating Questionnaire in healthy young adults. Physiology & Behavior, 104(3), 373–377.
Laurenius, A., Larsson, I., Bueter, M., Melanson, K. J., Bosaeus, I., Forslund, H. B., et al. (2012). ing Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. International Journal of Obesity, 36(3), 348–355. doi:10.1038/ijo.2011.217.
Lee, Y., Chong, M. F., Liu, J. C., Libedinsky, C., Gooley, J. J., Chen, S., et al. (2013). Dietary disinhibition modulates neural valuation of food in the fed and fasted states. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 97(5), 919–925. doi:10.3945/ajcn.112.053801.
Lemoine, S., Rossell, N., Drapeau, V., Poulain, M., Garnier, S., Sanguignol, F., et al. (2007). Effect of weight reduction on quality of life and eating behaviors in obese women. Menopause, 14(3 Pt 1), 432–440. doi:10.1097/gme.0b013e31802e46c2.
Lindroos, A. K., Lissner, L., Mathiassen, M. E., Karlsson, J., Sullivan, M., Bengtsson, C., et al. (1997). Dietary intake in relation to restrained eating, disinhibition, and hunger in obese and nonobese Swedish women. Obesity Research, 5(3), 175–182.
Maayan, L., Hoogendoorn, C., Sweat, V., & Convit, A. (2011). Disinhibited eating in obese adolescents is associated with orbitofrontal volume reductions and executive dysfunction. Obesity (Silver Spring), 19(7), 1382–1387. doi:10.1038/oby.2011.15.
Martin, L. E., Holsen, L. M., Chambers, R. J., Bruce, A. S., Brooks, W. M., Zarcone, J. R., et al. (2010). Neural Mechanisms Associated With Food Motivation in Obese and Healthy Weight Adults. Obesity, 18(2), 254–260. doi:10.1038/oby.2009.220.
Matthews, S. C., Paulus, M. P., Simmons, A. N., Nelesen, R. A., & Dimsdale, J. E. (2004). Functional subdivisions within anterior cingulate cortex and their relationship to autonomic nervous system function. NeuroImage, 22(3), 1151–1156. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.03.005.
Molnar-Szakacs, I., Iacoboni, M., Koski, L., & Mazziotta, J. C. (2005). Functional Segregation within Pars Opercularis of the Inferior Frontal Gyrus: Evidence from fMRI Studies of Imitation and Action Observation. Cerebral Cortex, 15(7), 986–994. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhh199.
Nooner, K. B., Colcombe, S., Tobe, R., Mennes, M., Benedict, M., Moreno, A., et al. (2012). The NKI-Rockland Sample: A Model for Accelerating the Pace of Discovery Science in Psychiatry. [Review]. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 6, doi:10.3389/fnins.2012.00152.
Ochner, C. N., Laferrère, B., Afifi, L., Atalayer, D., Geliebter, A., & Teixeira, J. (2012). Neural responsivity to food cues in fasted and fed states pre and post gastric bypass surgery. Neuroscience Research, 74(2), 138–143. doi:10.1016/j.neures.2012.08.002.
Piech, R. M., Lewis, J., Parkinson, C. H., Owen, A. M., Roberts, A. C., Downing, P. E., et al. (2009). Neural correlates of appetite and hunger-related evaluative judgments. PloS One, 4(8), e6581. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0006581.
Provencher, V., Drapeau, V., Tremblay, A., Despres, J. P., & Lemieux, S. (2003). Eating behaviors and indexes of body composition in men and women from the Quebec family study. Obesity Research, 11(6), 783–792. doi:10.1038/oby.2003.109.
Riou, M.-È., Doucet, É., Provencher, V., Weisnagel, S. J., Piché, M.-È., Dubé, M.-C., et al. (2011). Influence of physical activity participation on the associations between eating behaviour traits and body mass index in healthy postmenopausal women. Journal of Obesity, 2011, 9. doi:10.1155/2011/465710.
Rolls, E. T. (2004). The functions of the orbitofrontal cortex. Brain and Cognition, 55(1), 11–29. doi:10.1016/S0278-2626(03)00277-X.
Rolls, E. T. (2005). Taste, olfactory, and food texture processing in the brain, and the control of food intake. Physiology & Behavior, 85(1), 45–56.
Rothemund, Y., Preuschhof, C., Bohner, G., Bauknecht, H.-C., Klingebiel, R., Flor, H., et al. (2007). Differential activation of the dorsal striatum by high-calorie visual food stimuli in obese individuals. NeuroImage, 37(2), 410–421. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.05.008.
Santel, S., Baving, L., Krauel, K., Münte, T. F., & Rotte, M. (2006). Hunger and satiety in anorexia nervosa: fMRI during cognitive processing of food pictures. Brain Research, 1114(1), 138–148. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2006.07.045.
Scharmüller, W., Übel, S., Ebner, F., & Schienle, A. (2012). Appetite regulation during food cue exposure: a comparison of normal-weight and obese women. Neuroscience Letters, 518(2), 106–110. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2012.04.063.
Siep, N., Roefs, A., Roebroeck, A., Havermans, R., Bonte, M. L., & Jansen, A. (2009). Hunger is the best spice: an fMRI study of the effects of attention, hunger and calorie content on food reward processing in the amygdala and orbitofrontal cortex. Behavioural Brain Research, 198(1), 149–158. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2008.10.035.
Stunkard, A. J., & Messick, S. (1985). The three-factor eating questionnaire to measure dietary restraint, disinhibition and hunger. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 29(1), 71–83.
Swick, D., Ashley, V., & Turken, A. U. (2008). Left inferior frontal gyrus is critical for response inhibition. BMC Neuroscience, 9, 102. doi:10.1186/1471-2202-9-102.
Tang, D. W., Fellows, L. K., Small, D. M., & Dagher, A. (2012). Food and drug cues activate similar brain regions: a meta-analysis of functional MRI studies. Physiology & Behavior, 106(3), 317–324. doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2012.03.009.
Tataranni, P. A., Gautier, J.-F., Chen, K., Uecker, A., Bandy, D., Salbe, A. D., et al. (1999). Neuroanatomical correlates of hunger and satiation in humans using positron emission tomography. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 96(8), 4569–4574. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.8.4569.
Tomasi, D., Wang, G.-J., Wang, R., Backus, W., Geliebter, A., Telang, F., et al. (2009). Association of body mass and brain activation during gastric distention: implications for obesity. PloS One, 4(8), e6847. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0006847.
Vaidya, C. J., & Gordon, E. M. (2013). Phenotypic variability in resting-state functional connectivity: current status. Brain Connectivity, 3(2), 99–120. doi:10.1089/brain.2012.0110.
Volkow, N. D., & Fowler, J. S. (2000). Addiction, a disease of compulsion and drive: involvement of the orbitofrontal cortex. Cerebral Cortex, 10(3), 318–325. doi:10.1093/cercor/10.3.318.
Walsh, B. T., Wilson, G. T., Loeb, K. L., Devlin, M. J., Pike, K. M., Roose, S. P., et al. (1997). Medication and psychotherapy in the treatment of bulimia nervosa. American Journal of Psychiatry, 154(4), 523–531.
Westenhoefer, J., Stunkard, A. J., & Pudel, V. (1999). Validation of the flexible and rigid control dimensions of dietary restraint. International Journal of Eating Disorders, 26(1), 53–64. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-108X(199907)26:1<53::AID-EAT7>3.0.CO;2-N.
Weston, C. S. (2012). Another major function of the anterior cingulate cortex: the representation of requirements. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 36(1), 90–110. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2011.04.014.
Williamson, D. A., Martin, C. K., York-Crowe, E., Anton, S. D., Redman, L. M., Han, H., et al. (2007). Measurement of dietary restraint: validity tests of four questionnaires. Appetite, 48(2), 183–192. doi:10.1016/j.appet.2006.08.066.
Wing, R. R., & Phelan, S. (2005). Long-term weight loss maintenance. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 82(1), 222S–225S.
Yu-Feng, Z., Yong, H., Chao-Zhe, Z., Qing-Jiu, C., Man-Qiu, S., Meng, L., et al. (2007). Altered baseline brain activity in children with ADHD revealed by resting-state functional MRI. Brain and Development, 29(2), 83–91. doi:10.1016/j.braindev.2006.07.002.
Zou, Q., Ross, T. J., Gu, H., Geng, X., Zuo, X.-N., Hong, L. E., et al. (2013). Intrinsic resting-state activity predicts working memory brain activation and behavioral performance. Human Brain Mapping, 34(12), 3204–3215. doi:10.1002/hbm.22136.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, and the applicable revisions at the time of the investigation. Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Funding
This paper is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 61473235, 81271549, 61131003, 81470816, 61431013, 81201081, 81227901, 81120108005; the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities No. QN2012031; the Shaanxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation under Grant No. 2015JM3117.
Data collection and sharing project was funded in part by the New York State Office of Mental Health and Research Foundation for Mental Hygiene. Additional project support provided by the NKI Center for Advanced Brain Imaging (CABI), the Brain Research Foundation (Chicago, IL), the Stavros Niarchos Foundation, and NIH grant P50 MH086385-S1. The project Directors were F. Xavier Castellanos, Bennett Leventhal, and Michael Milham. The Project Coordinator was Kate Nooner. David Gutman and Maarten Mennes finished Computational Infrastructure and Data Analytic Development/Support. The NKI/Rockland Sample Team included Melissa Benedict, Bharat Biswal, Barbara Coffey, Stan Colcombe, David Guilfoyle, David Gutman, Harold S. Koplewicz, Matthew Hoptman, Dan Javitt, Larry Maayan, Maarten Mennes, Kate Nooner, Nunzio Pomara. I would like to express my gratitude to Heather S. Pixley for the English editing of this paper.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained when study participants joined the International Neuroimaging Data-sharing Initiative (INDI) database.
Additional information
NKI/Rockland data Sample used in preparation of this article was obtained from the International Neuroimaging Data-sharing Initiative (INDI) online database NKI/Rockland Sample (http://fcon_1000.projects.nitrc.org/indi/pro/nki.html). The investigators within the INDI project contributed to the design and implementation of INDI and provided data but did not take part in the data analysis or the writing of this paper. A complete listing of INDI investigators can be found at: http://fcon_1000.projects.nitrc.org/indi/pro/nki.html
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, J., Li, M., Zhang, Y. et al. Intrinsic brain subsystem associated with dietary restraint, disinhibition and hunger: an fMRI study. Brain Imaging and Behavior 11, 264–277 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9491-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9491-4