Abstract
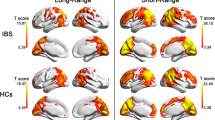
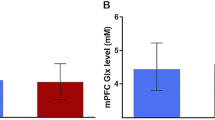
This resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (rs-fMRI) study investigated intrinsic brain abnormalities in irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and effect of anxiety and depression. Thirty IBS patients and 31 matched healthy controls underwent rs-fMRI scanning. Regional brain activity was evaluated by measuring the amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (ALFF) and compared between IBS patients and healthy controls with a two-sample t-test. Areas with abnormal ALFF were further used as seeds in subsequent inter-regional functional connectivity (FC) analysis. Statistical analyses were also performed by including anxiety and depression as covariates to evaluate their effect. Compared to healthy controls, IBS patients showed decreased ALFF in several core default mode network regions (medial prefrontal cortex [MPFC], posterior cingulate cortex [PCC], bilateral inferior parietal cortices [IPC]), and in middle frontal cortex, right orbital part of the superior frontal gyrus (ORBsup), dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (dACC), and ventral anterior cingulated cortex (vACC), while they showed increased ALFF in bilateral posterior insula and cuneus. In addition, IBS patients revealed decreased inter-regional positive FC between MPFC and right ORBsup, between vACC and PCC, as well as decreased negative FC between MPFC and left posterior insula, while they showed increased negative FC between MPFC and cuneus. The inclusion of anxiety and depression as covariates abolished ALFF differences in dACC and vACC, but none of the FC differences. In conclusion: IBS patients had disturbed intrinsic brain function. High levels of anxiety and depression in IBS patients could account for their decreased intrinsic brain activity in regions (the ACC) involved in affective processing.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Absinta, M., Rocca, M. A., Colombo, B., Falini, A., Comi, G., & Filippi, M. (2012). Selective decreased grey matter volume of the pain-matrix network in cluster headache. Cephalalgia, 32(2), 109–115.
Albert, J., Lopez-Martin, S., Tapia, M., Montoya, D., & Carretie, L. (2012). The role of the anterior cingulate cortex in emotional response inhibition. Human Brain Mapping, 33(9), 2147–2160.
Augustine, J. R. (1996). Circuitry and functional aspects of the insular lobe in primates including humans. Brain Research Reviews, 22(3), 229–244.
Baliki, M. N., Geha, P. Y., Apkarian, A. V., & Chialvo, D. R. (2008). Beyond feeling: chronic pain hurts the brain, disrupting the default-mode network dynamics. The Journal of Neuroscience, 28(6), 1398–1403.
Barthas, F., Sellmeijer, J., Hugel, S., Waltisperger, E., Barrot, M., & Yalcin, I. (2015). The anterior cingulate cortex is a critical hub for pain-induced depression. Biological Psychiatry, 77(3), 236–245.
Bush, G., Luu, P., & Posner, M. I. (2000). Cognitive and emotional influences in anterior cingulate cortex. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 4(6), 215–222.
Drossman, D. A. (2006). The functional gastrointestinal disorders and the rome III process. Gastroenterology, 130(5), 1377–1390.
Elsenbruch, S., Rosenberger, C., Enck, P., Forsting, M., Schedlowski, M., & Gizewski, E. R. (2010). Affective disturbances modulate the neural processing of visceral pain stimuli in irritable bowel syndrome: an fMRI study. Gut, 59(4), 489–495.
Fadgyas-Stanculete, M., Buga, A.-M., Popa-Wagner, A., & Dumitrascu, D. L. (2014). The relationship between irritable bowel syndrome and psychiatric disorders: from molecular changes to clinical manifestations. Journal of Molecular Psychiatry, 2(1), 4.
Folstein, M. F., Robins, L. N., & Helzer, J. E. (1983). The mini-mental state examination. Archives of General Psychiatry, 40(7), 812.
Fornito, A., Yoon, J., Zalesky, A., Bullmore, E. T., & Carter, C. S. (2011). General and specific functional connectivity disturbances in first-episode schizophrenia during cognitive control performance. Biological Psychiatry, 70(1), 64–72.
Fox, M. D., & Greicius, M. (2010). Clinical applications of resting state functional connectivity. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 4, 19.
Fox, M. D., & Raichle, M. E. (2007). Spontaneous fluctuations in brain activity observed with functional magnetic resonance imaging. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience, 8(9), 700–711.
Francis, C. Y., Morris, J., & Whorwell, P. J. (1997). The irritable bowel severity scoring system: a simple method of monitoring irritable bowel syndrome and its progress. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 11(2), 395–402.
Friston, K. J., Frith, C. D., Liddle, P. F., & Frackowiak, R. S. (1993). Functional connectivity: the principal-component analysis of large (PET) data sets. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 13(1), 5–14.
Fulbright, R. K., Troche, C. J., Skudlarski, P., Gore, J. C., & Wexler, B. E. (2001). Functional MR imaging of regional brain activation associated with the affective experience of pain. AJR. American Journal of Roentgenology, 177(5), 1205–1210.
Hong, J.-Y., Kilpatrick, L. A., Labus, J., Gupta, A., Jiang, Z., Ashe-McNalley, C., et al. (2013). Patients with chronic visceral pain show sex-related alterations in intrinsic oscillations of the resting brain. The Journal of Neuroscience, 33(29), 11994–12002.
Huang, X., Huang, P., Li, D., Zhang, Y., Wang, T., Mu, J., et al. (2014). Early brain changes associated with psychotherapy in major depressive disorder revealed by resting-state fMRI: evidence for the top-down regulation theory. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 94(3), 437–444.
Jin, C., Qi, R., Yin, Y., Hu, X., Duan, L., Xu, Q., et al. (2014). Abnormalities in whole-brain functional connectivity observed in treatment-naive post-traumatic stress disorder patients following an earthquake. Psychological Medicine, 44(9), 1927–1936.
Labus, J. S., Gupta, A., Coveleskie, K., Tillisch, K., Kilpatrick, L., Jarcho, J., et al. (2013). Sex differences in emotion-related cognitive processes in irritable bowel syndrome and healthy control subjects. Pain, 154(10), 2088–2099.
Lee, M. H., Smyser, C. D., & Shimony, J. S. (2013). Resting-state fMRI: a review of methods and clinical applications. AJNR. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 34(10), 1866–1872.
Li, F., He, N., Li, Y., Chen, L., Huang, X., Lui, S., et al. (2014). Intrinsic brain abnormalities in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a resting-state functional MR imaging study. Radiology, 272(2), 514–523.
Liu, C. H., Li, F., Li, S. F., Wang, Y. J., Tie, C. L., Wu, H. Y., et al. (2012). Abnormal baseline brain activity in bipolar depression: a resting state functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Psychiatry Research, 203(2–3), 175–179.
Ma, X., Li, S., Tian, J., Jiang, G., Wen, H., Wang, T., et al. (2014). Altered brain spontaneous activity and connectivity network in irritable bowel syndrome patients: a resting-state fMRI study. Clinical Neurophysiology.
Mayer, E. A. (2008). Clinical practice. Irritable bowel syndrome. The New England Journal of Medicine, 358(16), 1692–1699.
Mayer, E. A., & Tillisch, K. (2011). The brain-gut axis in abdominal pain syndromes. Annual Review of Medicine, 62, 381–396.
Mayer, E. A., Aziz, Q., Coen, S., Kern, M., Labus, J. S., Lane, R., et al. (2009). Brain imaging approaches to the study of functional GI disorders: a Rome working team report. Neurogastroenterology and Motility, 21(6), 579–596.
Nagai, M., Kishi, K., & Kato, S. (2007). Insular cortex and neuropsychiatric disorders: a review of recent literature. European Psychiatry, 22(6), 387–394.
Nasreddine, Z. S., Phillips, N. A., Bedirian, V., Charbonneau, S., Whitehead, V., Collin, I., et al. (2005). The montreal cognitive assessment, MoCA: a brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 53(4), 695–699.
Patrick, D. L., Drossman, D. A., Frederick, I. O., DiCesare, J., & Puder, K. L. (1998). Quality of life in persons with irritable bowel syndrome: development and validation of a new measure. Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 43(2), 400–411.
Phan, K. L., Wager, T. D., Taylor, S. F., & Liberzon, I. (2004). Functional neuroimaging studies of human emotions. CNS Spectrums, 9(4), 258–266.
Posserud, I., Ersryd, A., & Simren, M. (2006). Functional findings in irritable bowel syndrome. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 12(18), 2830–2838.
Price, D. D., Bush, F. M., Long, S., & Harkins, S. W. (1994). A comparison of pain measurement characteristics of mechanical visual analogue and simple numerical rating scales. Pain, 56(2), 217–226.
Raichle, M. E., MacLeod, A. M., Snyder, A. Z., Powers, W. J., Gusnard, D. A., & Shulman, G. L. (2001). A default mode of brain function. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 98(2), 676–682.
Rapps, N., van Oudenhove, L., Enck, P., & Aziz, Q. (2008). Brain imaging of visceral functions in healthy volunteers and IBS patients. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 64(6), 599–604.
Thijssen, A. Y., Jonkers, D. M., Leue, C., van der Veek, P. P., Vidakovic-Vukic, M., van Rood, Y. R., et al. (2010). Dysfunctional cognitions, anxiety and depression in irritable bowel syndrome. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology, 44(10), e236–e241.
van de Ven, V. G., Formisano, E., Prvulovic, D., Roeder, C. H., & Linden, D. E. (2004). Functional connectivity as revealed by spatial independent component analysis of fMRI measurements during rest. Human Brain Mapping, 22(3), 165–178.
Van Oudenhove, L. (2010). Visceral sensory and cognitive-affective neuroscience: towards integration? Gut, 59(4), 431–432.
Verne, G. N., Himes, N. C., Robinson, M. E., Gopinath, K. S., Briggs, R. W., Crosson, B., et al. (2003). Central representation of visceral and cutaneous hypersensitivity in the irritable bowel syndrome. Pain, 103(1–2), 99–110.
Yuan, Y. Z., Tao, R. J., Xu, B., Sun, J., Chen, K. M., Miao, F., et al. (2003). Functional brain imaging in irritable bowel syndrome with rectal balloon-distention by using fMRI. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 9(6), 1356–1360.
Zang, Y. F., He, Y., Zhu, C. Z., Cao, Q. J., Sui, M. Q., Liang, M., et al. (2007). Altered baseline brain activity in children with ADHD revealed by resting-state functional MRI. Brain and Development, 29(2), 83–91.
Zhou, G., Qin, W., Zeng, F., Liu, P., Yang, X., von Deneen, K. M., et al. (2013). White-matter microstructural changes in functional dyspepsia: a diffusion tensor imaging study. The American Journal of Gastroenterology, 108(2), 260–269.
Zung, W. W. (1971). A rating instrument for anxiety disorders. Psychosomatics, 12(6), 371–379.
Zung, W. W., Richards, C. B., & Short, M. J. (1965). Self-rating depression scale in an outpatient clinic. Further validation of the SDS. Archives of General Psychiatry, 13(6), 508–515.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the Natural Scientific Foundation of China [Grant Nos. 81322020, 81230032 and 81171313 for Long Jiang Zhang, Grant No. 81301209 for Rongfeng Qi], the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in the University (NCET-12-0260 for Long Jiang Zhang), and the Chinese Key Program (Grant Nos. BWS11J063 and 10z026 for Guang Ming Lu).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Rongfeng Qi declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Chang Liu declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Jun Ke declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Qiang Xu declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Jianhui Zhong declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Fangyu Wang declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Long Jiang Zhang declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Guang Ming Lu declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Rongfeng Qi, Chang Liu and Jun Ke contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, R., Liu, C., Ke, J. et al. Intrinsic brain abnormalities in irritable bowel syndrome and effect of anxiety and depression. Brain Imaging and Behavior 10, 1127–1134 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9478-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9478-1