Abstract
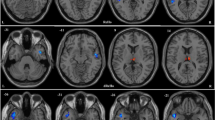
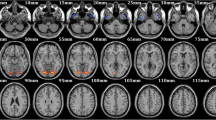
Déjà vu (DV) is an eerie phenomenon experienced frequently as an aura of temporal lobe epilepsy, but also reported commonly by healthy individuals. The former pathological manifestation appears to result from aberrant neural activity among brain structures within the medial temporal lobes. Recent studies also implicate medial temporal brain structures in the non-pathological experience of DV, but as one element of a diffuse neuroanatomical correlate; it remains to be seen if neural activity among the medial temporal lobes also underlies this benign manifestation. The present study set out to investigate this. Due to its unpredictable and infrequent occurrence, however, non-pathological DV does not lend itself easily to functional neuroimaging. Instead, we draw on research showing that brain structure covaries among regions that interact frequently as nodes of functional networks. Specifically, we assessed whether grey-matter covariance among structures implicated in non-pathological DV differs according to the frequency with which the phenomenon is experienced. This revealed two diverging patterns of structural covariation: Among the first, comprised primarily of medial temporal structures and the caudate, grey-matter volume becomes more positively correlated with higher frequency of DV experience. The second pattern encompasses medial and lateral temporal structures, among which greater DV frequency is associated with more negatively correlated grey matter. Using a meta-analytic method of co-activation mapping, we demonstrate a higher probability of functional interactions among brain structures constituting the former pattern, particularly during memory-related processes. Our findings suggest that altered neural signalling within memory-related medial temporal brain structures underlies both pathological and non-pathological DV.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi, N., Akanuma, N., Ito, M., Adachi, T., Takekawa, Y., Adachi, Y., Matsuura, M., Kanemoto, K., & Kato, M. (2010). Two forms of déjà vu experiences in patients with epilepsy. Epilepsy & Behavior, 18(3), 218–222.
Aggleton, J. P., & Brown, M. W. (1999). Episodic memory, amnesia, and the hippocampal–anterior thalamic axis. Behavioral and brain sciences, 22(03), 425--444.
Aggleton, J. P., Dumont, J. R., & Warburton, E. C. (2011). Unraveling the contributions of the diencephalon to recognition memory: a review. Learning & Memory, 18(6), 384--400.
Alexander-Bloch, A., Raznahan, A., Bullmore, E., & Giedd, J. (2013). The convergence of maturational change and structural covariance in human cortical networks. The Journal of Neuroscience, 33(7), 2889–2899.
Ashburner, J. (2007). A fast diffeomorphic image registration algorithm. NeuroImage, 38(1), 95–113.
Ashburner, J., & Friston, K. J. (2005). Unified segmentation. NeuroImage, 26(3), 839–851.
Augustine, J. R. (1996). Circuitry and functional aspects of the insular lobe in primates including humans. Brain Research Reviews, 22(3), 229--244.
Bancaud, J., Brunet-Bourgin, F., Chauvel, P., & Halgren, E. (1994). Anatomical origin of déjà vu and vivid ‘memories’ in human temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain, 117(1), 71–90.
Bartolomei, F., Barbeau, E., Gavaret, M., Guye, M., McGonigal, A., Regis, J., & Chauvel, P. (2004). Cortical stimulation study of the role of rhinal cortex in deja vu and reminiscence of memories. Neurology, 63(5), 858–864.
Bartolomei, F., Barbeau, E. J., Nguyen, T., McGonigal, A., Régis, J., Chauvel, P., & Wendling, F. (2012). Rhinal–hippocampal interactions during déjà vu. Clinical Neurophysiology, 123(3), 489–495.
Berntson, G. G., Norman, G. J., Bechara, A., Bruss, J., Tranel, D., & Cacioppo, J. T. (2011). The insula and evaluative processes. Psychological science, 22(1), 80--86.
Brázdil, M., & Zeman, A. (2013). The boundaries of epilepsy: where is the limit? A reply to Labate and Gambardella. Cortex, 49(4), 1163–1164.
Brázdil, M., Mareček, R., Fojtíková, D., Mikl, M., Kuba, R., Krupa, P., & Rektor, I. (2009). Correlation study of optimized voxel-based morphometry and 1 H MRS in patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy and hippocampal sclerosis. Human Brain Mapping, 30, 1226–1235.
Brázdil, M., Mareček, R., Urbánek, T., Kašpárek, T., Mikl, M., Rektor, I., & Zeman, A. (2012). Unveiling the mystery of déjà vu: The structural anatomy of déjà vu. Cortex, 48(9), 1240–1243.
Brown, A. S. (2003). A review of the deja vu experience. Psychological Bulletin, 129(3), 394–413.
Burwell, R. D. (2000). The parahippocampal region: corticocortical connectivity. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 911(1), 25–42.
Chase, H. W., Clos, M., Dibble, S., Fox, P., Grace, A. A., Phillips, M. L., & Eickhoff, S. B. (2015). Evidence for an anterior–posterior differentiation in the human hippocampal formation revealed by meta-analytic parcellation of fMRI coordinate maps: focus on the subiculum. NeuroImage, 113, 44–60.
Clos, M., Rottschy, C., Laird, A. R., Fox, P. T., & Eickhoff, S. B. (2014). Comparison of structural covariance with functional connectivity approaches exemplified by an investigation of the left anterior insula. NeuroImage, 99, 269–280.
Cohen, M. X., Lombardo, M. V., & Blumenfeld, R. S. (2008). Covariance-based subdivision of the human striatum using T1-weighted MRI. European Journal of Neuroscience, 27(6), 1534–1546.
Craig, A. D. (2009). How do you feel—now? The anterior insula and human awareness. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 10, 59–70.
Dogan, I., Eickhoff, C. R., Fox, P. T., Laird, A. R., Schulz, J. B., Eickhoff, S. B., & Reetz, K. (2015). Functional connectivity modeling of consistent cortico-striatal degeneration in Huntington’s disease. NeuroImage: Clinical, 7, 640–652.
Duerden, E. G., Arsalidou, M., Lee, M., & Taylor, M. J. (2013). Lateralization of affective processing in the insula. NeuroImage, 78, 159–175.
Eichenbaum, H., Yonelinas, A. R., & Ranganath, C. (2007). The medial temporal lobe and recognition memory. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 30, 123–152.
Eickhoff, S. B., Laird, A. R., Grefkes, C., Wang, L. E., Zilles, K., & Fox, P. T. (2009). Coordinate-based activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis of neuroimaging data: a random-effects approach based on empirical estimates of spatial uncertainty. Human Brain Mapping, 30(9), 2907–2926.
Eickhoff, S. B., Jbabdi, S., Caspers, S., Laird, A. R., Fox, P. T., Zilles, K., & Behrens, T. E. (2010). Anatomical and functional connectivity of cytoarchitectonic areas within the human parietal operculum. The Journal of Neuroscience, 30(18), 6409–6421.
Eickhoff, S. B., Bzdok, D., Laird, A. R., Kurth, F., & Fox, P. T. (2012). Activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis revisited. NeuroImage, 59(3), 2349–2361.
Evans, A. C. (2013). Networks of anatomical covariance. NeuroImage, 80, 489–504.
Gloor, P. (1990). Experiential phenomena of temporal lobe epilepsy: facts and hypotheses. Brain, 113(6), 1673–1694.
Gloor, P., Olivier, A., Quesney, L. F., Andermann, F., & Horowitz, S. (1982). The role of the limbic system in experiential phenomena of temporal lobe epilepsy. Annals of Neurology, 12(2), 129–144.
Groenewegen, H. J., Wright, C. I., Beijer, A. V., & Voorn, P. (1999). Convergence and segregation of ventral striatal inputs and outputs. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 877(1), 49–63.
Guedj, E., Aubert, S., McGonigal, A., Mundler, O., & Bartolomei, F. (2010). Déjà-vu in temporal lobe epilepsy: metabolic pattern of cortical involvement in patients with normal brain MRI. Neuropsychologia, 48(7), 2174–2181.
Halgren, E., Walter, R. D., Cherlow, D. G., & Crandall, P. H. (1978). Mental phenomena evoked by electrical stimulation of the human hippocampal formation and amygdala. Brain, 101(1), 83–115.
Havekes, R., Abel, T., & Van der Zee, E. A. (2011). The cholinergic system and neostriatal memory functions. Behavioural Brain Research, 221(2), 412–423.
Hoffstaedter, F., Grefkes, C., Caspers, S., Roski, C., Palomero-Gallagher, N., Laird, A. R., Fox, P. T., & Eickhoff, S. B. (2014). The role of anterior midcingulate cortex in cognitive motor control. Human Brain Mapping, 35(6), 2741–2753.
Hoffstaedter, F., Grefkes, C., Roski, C., Caspers, S., Zilles, K., & Eickhoff, S. B. (2015). Age-related decrease of functional connectivity additional to gray matter atrophy in a network for movement initiation. Brain Structure and Function, 220(2), 999–1012.
Honey, C. J., Thivierge, J. P., & Sporns, O. (2010). Can structure predict function in the human brain? NeuroImage, 52(3), 766–776.
Ickes, B. R., Pham, T. M., Sanders, L. A., Albeck, D. S., Mohammed, A. H., & Granholm, A. C. (2000). Long-term environmental enrichment leads to regional increases in neurotrophin levels in rat brain. Experimental Neurology, 164, 45–52.
Illman, N. A., Butler, C. R., Souchay, C., & Moulin, C. J. (2012). Deja experiences in temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Research and Treatment. doi:10.1155/2012/539567.
Kelly, C., Toro, R., Di Martino, A., Cox, C. L., Bellec, P., Castellanos, F. X., & Milham, M. P. (2012). A convergent functional architecture of the insula emerges across imaging modalities. NeuroImage, 61(4), 1129–1142.
Khundrakpam, B. S., Reid, A., Brauer, J., Carbonell, F., Lewis, J., Ameis, S., Karama, S., Lee, J., Chen, Z., Das, S., & Evans, A. C. (2013). Developmental changes in organization of structural brain networks. Cerebral Cortex, 23(9), 2072–2085. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhs187.
Krishnan, A., Williams, L. J., McIntosh, A. R., & Abdi, H. (2011). Partial least squares (PLS) methods for neuroimaging: a tutorial and review. NeuroImage, 56(2), 455–475.
Labate, A., Cerasa, A., Mumoli, L., Ferlazzo, E., Aguglia, U., Quattrone, A., & Gambardella, A. (2015). Neuro-anatomical differences among epileptic and non-epileptic déjà-vu. Cortex, 64, 1–7.
Laird, A. R., Eickhoff, S. B., Li, K., Robin, D. A., Glahn, D. C., & Fox, P. T. (2009). Investigating the functional heterogeneity of the default mode network using coordinate-based meta-analytic modeling. The Journal of Neuroscience, 29(46), 14496–14505.
McIntosh, A. R., & Lobaugh, N. J. (2004). Partial least squares analysis of neuroimaging data: applications and advances. NeuroImage, 23, S250–S263.
McIntosh, A. R., Bookstein, F. L., Haxby, J. V., & Grady, C. L. (1996). Spatial pattern analysis of functional brain images using partial least squares. NeuroImage, 3, 143–157.
Moulin, C. J. (2014). The strange sensation of déjà vu: not so strange in temporal lobe epilepsy. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 85(2), 132–132.
Mullan, S., & Penfield, W. (1959). Illusions of comparative interpretation and emotion: production by epileptic discharge and by electrical stimulation in the temporal cortex. Archives of Neurology and Psychiatry, 81(3), 269–284.
O’Connor, A. R., & Moulin, C. J. (2010). Recognition without identification, erroneous familiarity, and déjà vu. Current Psychiatry Reports, 12(3), 165–173.
O’Connor, A. R., & Moulin, C. J. A. (2013). Déjà vu experiences in healthy subjects are unrelated to laboratory tests of recollection and familiarity for word stimuli. Frontiers in Psychology, 4(881). doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00881.
Packard, M. G., & Knowlton, B. J. (2002). Learning and memory functions of the basal ganglia. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 25(1), 563–593.
Pail, M., Brázdil, M., Mareček, R., & Mikl, M. (2010). An optimized voxel-based morphometric study of gray matter changes in patients with left-sided and right-sided mesial temporal lobe epilepsy and hippocampal sclerosis (MTLE/HS). Epilepsia, 51(4), 511–518.
Penfield, W., & Perot, P. (1963). The brain’s record of auditory and visual experience. A final summary and discussion. Brain, 86, 595–696.
Pollock, G. S., Vernon, E., Forbes, M. E., Yan, Q., Ma, Y. T., Hsieh, T., et al. (2001). Effects of early visualexperience and diurnal rhythms on BDNF mRNA and protein levels in the visual system, hippocampus, and cerebellum. Journal of Neuroscience, 21, 3923–3931.
Power, J. D., Fair, D. A., Schlaggar, B. L., & Petersen, S. E. (2010). The development of human functional brain networks. Neuron, 67(5), 735–748.
Raznahan, A., Shaw, P., Lalonde, F., Stockman, M., Wallace, G. L., Greenstein, D., Clasen, L., Gogtay, N., & Giedd, J. N. (2011). How does your cortex grow? The Journal of Neuroscience, 31(19), 7174–7177.
Rottschy, C., Caspers, S., Roski, C., Reetz, K., Dogan, I., Schulz, J. B., Zilles, K., Laird, A. R., Fox, P. T., & Eickhoff, S. B. (2013). Differentiated parietal connectivity of frontal regions for “what” and “where” memory. Brain Structure and Function, 218(6), 1551–1567.
Rykhlevskaia, E., Gratton, G., & Fabiani, M. (2008). Combining structural and functional neuroimaging data for studying brain connectivity: a review. Psychophysiology, 45(2), 173--187.
Seeley, W. W., Crawford, R. K., Zhou, J., Miller, B. L., & Greicius, M. D. (2009). Neurodegenerative diseases target large-scale human brain networks. Neuron, 62(1), 42–52.
Sno, H. N., Schalken, H. F., de Jonghe, F., & Koeter, M. W. (1994). The inventory for déjà vu experiences assessment: development, utility, reliability, and validity. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 182(1), 27–33.
Takeda, Y., Kurita, T., Sakurai, K., Shiga, T., Tamaki, N., & Koyama, T. (2011). Persistent déjà vu associated with hyperperfusion in the entorhinal cortex. Epilepsy & Behavior, 21(2), 196–199.
Ullsperger, M., Harsay, H. A., Wessel, J. R., & Ridderinkhof, K. R. (2010). Conscious perception of errors and its relation to the anterior insula. Brain Structure and Function, 214(5-6), 629--643.
Vignal, J. P., Maillard, L., McGonigal, A., & Chauvel, P. (2007). The dreamy state: hallucinations of autobiographic memory evoked by temporal lobe stimulations and seizures. Brain, 130(1), 88–99.
Warren-Gash, C., & Zeman, A. (2014). Is there anything distinctive about epileptic déjà vu? Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 85(2), 143–147.
Weinand, M. E., Hermann, B., Wyler, A. R., Carter, L. P., Oommen, K. J., Labiner, D., Ahern, G., & Herring, A. (1994). Long-term subdural strip electrocorticographic monitoring of ictal deja vu. Epilepsia, 35(5), 1054–1059.
Winkler, A. M., Kochunov, P., Blangero, J., Almasy, L., Zilles, K., Fox, P. T., Duggirala, R., & Glahn, D. C. (2009). Cortical thickness or grey matter volume? The importance of selecting the phenotype for imaging genetics studies. NeuroImage, 53(3), 1135–1146.
Wolf, R. C., Sambataro, F., Vasic, N., Depping, M. S., Thomann, P. A., Landwehrmeyer, G. B., Süssmuth, S. D., & Orth, M. (2014). Abnormal resting-state connectivity of motor and cognitive networks in early manifest Huntington’s disease. Psychological Medicine, 44(15), 3341–3356.
Zielinski, B. A., Gennatas, E. D., Zhou, J., & Seeley, W. W. (2010). Network-level structural covariance in the developing brain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 107(42), 18191–18196.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the project “CEITEC – Central European Institute of Technology” (CZ.1.05/1.1.00/02.0068) from European Regional Development Fund. We wish to thank Natasa Kovacevic for her assistance with our structural PLS pipelines.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was supported by the project “CEITEC – Central European Institute of Technology” (CZ.1.05/1.1.00/02.0068) from European Regional Development Fund.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the Ethics Review Board of St. Anne’s Hospital, Brno, and conformed to the Declaration of Helsinki (1964). Written informed consent was obtained from every participant prior to the experiment.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Figure 1
Meta-analytic co-activation matrix. Meta-analytic connectivity modelling (MACM) was employed to compare the probability of co-activation between cells comprising the positive and negative pattern of structural covariance, and perform a behavioral characterisation of each pattern. The matrix presents the standardized probability of co-activation among each VOI (rows) when each other VOI served as a seed (columns; see Multi-analytic Connectivity Modelling). For abbreviations see Table 1. (JPEG 215 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shaw, D.J., Mareček, R. & Brázdil, M. Structural covariance mapping delineates medial and medio-lateral temporal networks in déjà vu. Brain Imaging and Behavior 10, 1068–1079 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9471-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9471-8