Abstract
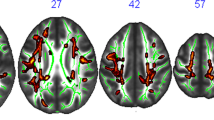
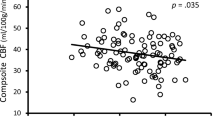
The objective of this study was to investigate the relationship between cardiorespiratory (CR) fitness and the brain’s white matter tract integrity using diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) in the Alzheimer’s disease (AD) population. We recruited older adults in the early stages of AD (n = 37; CDR = 0.5 and 1) and collected cross-sectional fitness and diffusion imaging data. We examined the association between CR fitness (peak oxygen consumption [VO2peak]) and fractional anisotropy (FA) in AD-related white matter tracts using two processing methodologies: a tract-of-interest approach and tract-based spatial statistic (TBSS). Subsequent diffusivity metrics (radial diffusivity [RD], mean diffusivity [MD], and axial diffusivity [A × D]) were also correlated with VO2peak. The tract-of-interest approach showed that higher VO2peak was associated with preserved white matter integrity as measured by increased FA in the right inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus (p = 0.035, r = 0.36). We did not find a significant correlation using TBSS, though there was a trend for a positive association between white matter integrity and higher VO2peak measures (p < 0.01 uncorrected). Our findings indicate that higher CR fitness levels in early AD participants may be related to preserved white matter integrity. However to draw stronger conclusions, further study on the relationship between fitness and white matter deterioration in AD is necessary.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, A. L., Lee, J. E., Lazar, M., & Field, A. S. (2007). Diffusion tensor imaging of the brain. Neurotherapeutics:The Journal of the American Society for Experimental NeuroTherapeutics, 4, 316–329.
Alexander, A. L., Hurley, S. A., Samsonov, A. A., Adluru, N., Hosseinbor, A. P., Mossahebi, P., PM, T. d., Zakszewski, E., & Field, A. S. (2011). Characterization of cerebral white matter properties using quantitative magnetic resonance imaging stains. Brain Connectivity, 1, 423–446.
Alves, G. S., O’Dwyer, L., Jurcoane, A., Oertel-Knochel, V., Knochel, C., Prvulovic, D., Sudo, F., Alves, C. E., Valente, L., Moreira, D., Fubetaer, F., Karakaya, T., Pantel, J., Engelhardt, E., & Laks, J. (2012). Different patterns of white matter degeneration using multiple diffusion indices and volumetric data in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer patients. PLoS ONE, 7, e52859.
Anderson, H. S., Kluding, P. M., Gajewski, B. J., Donnelly, J. E., & Burns, J. M. (2011). Reliability of peak treadmill exercise tests in mild Alzheimer disease. The International Journal of Neuroscience, 121, 450–456.
Andersson, J.L.R., Jenkinson, M., Smith, S. (2007) Non-linear optimisation. FMRIB Analysis Group Technical Reports: TR07JA02 from www fmrib ox ac uk/analysis/techrep.
Bach, M., Laun, F. B., Leemans, A., Tax, C. M., Biessels, G. J., Stieltjes, B., & Maier-Hein, K. H. (2014). Methodological considerations on tract-based spatial statistics (TBSS). NeuroImage, 100, 358–369.
Berg, L., McKeel, D. W., Jr., Miller, J. P., Storandt, M., Rubin, E. H., Morris, J. C., Baty, J., Coats, M., Norton, J., Goate, A. M., Price, J. L., Gearing, M., Mirra, S. S., & Saunders, A. M. (1998). Clinicopathologic studies in cognitively healthy aging and Alzheimer’s disease: relation of histologic markers to dementia severity, age, sex, and apolipoprotein E genotype. Archives of Neurology, 55, 326–335.
Boots EA, Schultz SA, Oh JM, Larson J, Edwards D, Cook D, Koscik RL, Dowling MN, Gallagher CL, Carlsson CM, Rowley HA, Bendlin BB, LaRue A, Asthana S, Hermann BP, Sager MA, Johnson SC, Okonkwo OC (2014) Cardiorespiratory fitness is associated with brain structure, cognition, and mood in a middle-aged cohort at risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Imaging and Behavior.
Bosch, B., Arenaza-Urquijo, E. M., Rami, L., Sala-Llonch, R., Junque, C., Sole-Padulles, C., Pena-Gomez, C., Bargallo, N., Molinuevo, J. L., & Bartres-Faz, D. (2012). Multiple DTI index analysis in normal aging, amnestic MCI and AD. Relationship with neuropsychological performance. Neurobiology of Aging, 33, 61–74.
Bouchard, C. (2012). Genomic predictors of trainability. Experimental Physiology, 97, 347–352.
Braak, H., & Braak, E. (1991). Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathologica, 82, 239–259.
Brun, A., & Englund, E. (1986). A white matter disorder in dementia of the Alzheimer type: a pathoanatomical study. Annals of Neurology, 19, 253–262.
Burggren, A., & Brown, J. (2014). Imaging markers of structural and functional brain changes that precede cognitive symptoms in risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 8, 251–261.
Burns, J. M., Cronk, B. B., Anderson, H. S., Donnelly, J. E., Thomas, G. P., Harsha, A., Brooks, W. M., & Swerdlow, R. H. (2008a). Cardiorespiratory fitness and brain atrophy in early Alzheimer disease. Neurology, 71, 210–216.
Burns, J. M., Mayo, M. S., Anderson, H. S., Smith, H. J., & Donnelly, J. E. (2008b). Cardiorespiratory fitness in early-stage Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Disease and Associated Disorders, 22, 39–46.
Burzynska, A. Z., Preuschhof, C., Backman, L., Nyberg, L., Li, S. C., Lindenberger, U., & Heekeren, H. R. (2010). Age-related differences in white matter microstructure: region-specific patterns of diffusivity. NeuroImage, 49, 2104–2112.
Colcombe, S. J., Erickson, K. I., Raz, N., Webb, A. G., Cohen, N. J., McAuley, E., & Kramer, A. F. (2003). Aerobic fitness reduces brain tissue loss in aging humans. The Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences, 58, 176–180.
Colcombe, S. J., Erickson, K. I., Scalf, P. E., Kim, J. S., Prakash, R., McAuley, E., Elavsky, S., Marquez, D. X., Hu, L., & Kramer, A. F. (2006). Aerobic exercise training increases brain volume in aging humans. Journals of Gerontology. Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences, 61, 1166–1170.
Erickson, K. I., Prakash, R. S., Voss, M. W., Chaddock, L., Hu, L., Morris, K. S., White, S. M., Wojcicki, T. R., McAuley, E., & Kramer, A. F. (2009). Aerobic fitness is associated with hippocampal volume in elderly humans. Hippocampus, 19, 1030–1039.
Erickson, K. I., Leckie, R. L., & Weinstein, A. M. (2014). Physical activity, fitness, and gray matter volume. Neurobiology of Aging, 35(Suppl 2), S20–S28.
Fleg, J. L., Morrell, C. H., Bos, A. G., Brant, L. J., Talbot, L. A., Wright, J. G., & Lakatta, E. G. (2005). Accelerated longitudinal decline of aerobic capacity in healthy older adults. Circulation, 112, 674–682.
Gold, B. T., Powell, D. K., Andersen, A. H., & Smith, C. D. (2010). Alterations in multiple measures of white matter integrity in normal women at high risk for Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage, 52, 1487–1494.
Gons, R.A., Tuladhar, A.M., de Laat, K.F., van Norden, A.G., van Dijk, E.J., Norris, D.G., Zwiers, M.P., de Leeuw, F.E. (2013). Physical activity is related to the structural integrity of cerebral white matter. Neurology.
Hayes, S. M., Hayes, J. P., Cadden, M., & Verfaellie, M. (2013). A review of cardiorespiratory fitness-related neuroplasticity in the aging brain. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 5, 31.
Hayes, S. M., Salat, D. H., Forman, D. E., Sperling, R. A., & Verfaellie, M. (2015). Cardiorespiratory fitness is associated with white matter integrity in aging. Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology, 2, 688–698.
Hollenberg, M., Ngo, L. H., Turner, D., & Tager, I. B. (1998). Treadmill exercise testing in an epidemiologic study of elderly subjects. Journals of Gerontology. Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences, 53, B259–B267.
Honea, R. A., Thomas, G. P., Harsha, A., Anderson, H. S., Donnelly, J. E., Brooks, W. M., & Burns, J. M. (2009). Cardiorespiratory fitness and preserved medial temporal lobe volume in Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Disease and Associated Disorders, 23, 188–197.
Hua, K., Zhang, J., Wakana, S., Jiang, H., Li, X., Reich, D. S., Calabresi, P. A., Pekar, J. J., van Zijl, P. C., & Mori, S. (2008). Tract probability maps in stereotaxic spaces: analyses of white matter anatomy and tract-specific quantification. NeuroImage, 39, 336–347.
Johansen-Berg, H., & Rushworth, M. F. (2009). Using diffusion imaging to study human connectional anatomy. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 32, 75–94.
Johnson, N. F., Kim, C., Clasey, J. L., Bailey, A., & Gold, B. T. (2012). Cardiorespiratory fitness is positively correlated with cerebral white matter integrity in healthy seniors. NeuroImage, 59, 1514–1523.
Keihaninejad, S., Zhang, H., Ryan, N. S., Malone, I. B., Modat, M., Cardoso, M. J., Cash, D. M., Fox, N. C., & Ourselin, S. (2013). An unbiased longitudinal analysis framework for tracking white matter changes using diffusion tensor imaging with application to Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage, 72, 153–163.
Keppel, G., & Wickens, T. D. (2004). Design and analysis : A researcher’s handbook. Upper Saddle River: Pearson Prentice Hall.
Krafft, C. E., Schaeffer, D. J., Schwarz, N. F., Chi, L, Weinberger, A. L., Pierce, J. E., Rodrigue, A. L., Allison, J. D., Yanasak, N. E., Liu, T, Davis, C. L., McDowell, J. E. (2014). Improved frontoparietal white matter integrity in overweight children is associated with attendance at an after-school exercise program. Developmental Neuroscience, 36, 1–9.
Liu, Y., Spulber, G., Lehtimaki, K. K., Kononen, M., Hallikainen, I., Grohn, H., Kivipelto, M., Hallikainen, M., Vanninen, R., & Soininen, H. (2011). Diffusion tensor imaging and tract-based spatial statistics in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiology of Aging, 32, 1558–1571.
Madden, D. J., Spaniol, J., Costello, M. C., Bucur, B., White, L. E., Cabeza, R., Davis, S. W., Dennis, N. A., Provenzale, J. M., & Huettel, S. A. (2009). Cerebral white matter integrity mediates adult age differences in cognitive performance. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 21, 289–302.
Marks, B. L., Madden, D. J., Bucur, B., Provenzale, J. M., White, L. E., Cabeza, R., & Huettel, S. A. (2007). Role of aerobic fitness and aging on cerebral white matter integrity. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1097, 171–174.
Marks, B. L., Katz, L. M., Styner, M., & Smith, J. K. (2011). Aerobic fitness and obesity: relationship to cerebral white matter integrity in the brain of active and sedentary older adults. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 45, 1208–1215.
Mayer, C. J., Steinman, L., Williams, B., Topolski, T. D., & LoGerfo, J. (2008). Developing a telephone assessment of physical activity (TAPA) questionnaire for older adults. Preventing Chronic Disease, 5, A24.
McKhann, G., Drachman, D., Folstein, M., Katzman, R., Price, D., & Stadlan, E. M. (1984). Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA work group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology, 34, 939–944.
Mori, S., Wakana, S., Van Zijl, P.C., Nagae-Poetscher, L. (2005). MRI atlas of human white matter.
Morris, J. C. (1993). The clinical dementia rating (CDR): current version and scoring rules. Neurology, 43, 2412b–2414b.
Morris, J. C., Storandt, M., Miller, J. P., McKeel, D. W., Price, J. L., Rubin, E. H., & Berg, L. (2001). Mild cognitive impairment represents early-stage Alzheimer disease. Archives of Neurology, 58, 397–405.
Petersen, S. E., & Posner, M. I. (2012). The attention system of the human brain: 20 years after. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 35, 73–89.
Salat, D. H. (2011). The declining infrastructure of the aging brain. Brain Connectivity, 1, 279–293.
Sexton, C. E., Kalu, U. G., Filippini, N., Mackay, C. E., & Ebmeier, K. P. (2011). A meta-analysis of diffusion tensor imaging in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiology of Aging, 32(2322), e2325–2318.
Shirk, S. D., Mitchell, M. B., Shaughnessy, L. W., Sherman, J. C., Locascio, J. J., Weintraub, S., & Atri, A. (2011). A web-based normative calculator for the uniform data set (UDS) neuropsychological test battery. Alzheimer’s Research & Therapy, 3, 32.
Smith, S. M., Jenkinson, M., Woolrich, M. W., Beckmann, C. F., Behrens, T. E., Johansen-Berg, H., Bannister, P. R., De Luca, M., Drobnjak, I., Flitney, D. E., Niazy, R. K., Saunders, J., Vickers, J., Zhang, Y., De Stefano, N., Brady, J. M., & Matthews, P. M. (2004). Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. NeuroImage, 23(Suppl 1), S208–S219.
Smith, S. M., Jenkinson, M., Johansen-Berg, H., Rueckert, D., Nichols, T. E., Mackay, C. E., Watkins, K. E., Ciccarelli, O., Cader, M. Z., Matthews, P. M., & Behrens, T. E. (2006). Tract-based spatial statistics: voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. NeuroImage, 31, 1487–1505.
Song, S. K., Yoshino, J., Le, T. Q., Lin, S. J., Sun, S. W., Cross, A. H., & Armstrong, R. C. (2005). Demyelination increases radial diffusivity in corpus callosum of mouse brain. NeuroImage, 26, 132–140.
Talbot, L. A., Metter, E. J., & Fleg, J. L. (2000). Leisure-time physical activities and their relationship to cardiorespiratory fitness in healthy men and women 18–95 years old. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 32, 417–425.
Teipel, S. J., Meindl, T., Wagner, M., Stieltjes, B., Reuter, S., Hauenstein, K. H., Filippi, M., Ernemann, U., Reiser, M. F., & Hampel, H. (2010). Longitudinal changes in fiber tract integrity in healthy aging and mild cognitive impairment: a DTI follow-up study. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 22, 507–522.
Thies, W., Bleiler, L., & Alzheimer’s, A. (2013). 2013 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement, 9, 208–245.
Thompson, P. M., Hayashi, K. M., de Zubicaray, G., Janke, A. L., Rose, S. E., Semple, J., Herman, D., Hong, M. S., Dittmer, S. S., Doddrell, D. M., & Toga, A. W. (2003). Dynamics of gray matter loss in Alzheimer’s disease. The Journal of Neuroscience:The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 23, 994–1005.
Tian, Q., Erickson, K. I., Simonsick, E. M., Aizenstein, H. J., Glynn, N. W., Boudreau, R. M., Newman, A. B., Kritchevsky, S. B., Yaffe, K., Harris, T. B., & Rosano, C. (2014). Physical activity predicts microstructural integrity in memory-related networks in very old adults. Journals of Gerontology. Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences, 69, 1284–1290.
Tseng, B.Y., Gundapuneedi, T., Khan, M.A., Diaz-Arrastia, R., Levine, B.D., Lu, H., Huang, H., Zhang, R. (2013). White matter integrity in physically fit older adults. NeuroImage.
Vidoni, E. D., Honea, R. A., Billinger, S. A., Swerdlow, R. H., & Burns, J. M. (2012a). Cardiorespiratory fitness is associated with atrophy in Alzheimer’s and aging over 2 years. Neurobiology of Aging, 33, 1624–1632.
Vidoni, E. D., Van Sciver, A., Johnson, D. K., He, J., Honea, R., Haines, B., Goodwin, J., Laubinger, M. P., Anderson, H. S., Kluding, P. M., Donnelly, J. E., Billinger, S. A., & Burns, J. M. (2012b). A community-based approach to trials of aerobic exercise in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Contemporary Clinical Trials, 33, 1105–1116.
Voss, M. W., Erickson, K. I., Prakash, R. S., Chaddock, L., Kim, J. S., Alves, H., Szabo, A., Phillips, S. M., Wojcicki, T. R., Mailey, E. L., Olson, E. A., Gothe, N., Vieira-Potter, V. J., Martin, S. A., Pence, B. D., Cook, M. D., Woods, J. A., McAuley, E., & Kramer, A. F. (2013a). Neurobiological markers of exercise-related brain plasticity in older adults. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity, 28, 90–99.
Voss, M. W., Heo, S., Prakash, R. S., Erickson, K. I., Alves, H., Chaddock, L., Szabo, A. N., Mailey, E. L., Wojcicki, T. R., White, S. M., Gothe, N., McAuley, E., Sutton, B. P., & Kramer, A. F. (2013b). The influence of aerobic fitness on cerebral white matter integrity and cognitive function in older adults: results of a one-year exercise intervention. Human Brain Mapping, 34, 2972–2985.
Walhovd, K. B., Johansen-Berg, H., & Karadottir, R. T. (2014). Unraveling the secrets of white matter - bridging the gap between cellular, animal and human imaging studies. Neuroscience, 276C, 2–13.
Winkler, A. M., Ridgway, G. R., Webster, M. A., Smith, S. M., & Nichols, T. E. (2014). Permutation inference for the general linear model. NeuroImage, 92, 381–397.
Xie, S., Xiao, J. X., Wang, Y. H., Wu, H. K., Gong, G. L., & Jiang, X. X. (2005). Evaluation of bilateral cingulum with tractography in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroreport, 16, 1275–1278.
Yu, J. T., Tan, L., & Hardy, J. (2014). Apolipoprotein E in Alzheimer’s disease: an update. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 37, 79–100.
Zalesky, A. (2011). Moderating registration misalignment in voxelwise comparisons of DTI data: a performance evaluation of skeleton projection. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 29, 111–125.
Zhang, Y., Schuff, N., Jahng, G. H., Bayne, W., Mori, S., Schad, L., Mueller, S., Du, A. T., Kramer, J. H., Yaffe, K., Chui, H., Jagust, W. J., Miller, B. L., & Weiner, M. W. (2007). Diffusion tensor imaging of cingulum fibers in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease. Neurology, 68, 13–19.
Zhang, B., Xu, Y., Zhu, B., & Kantarci, K. (2014). The role of diffusion tensor imaging in detecting microstructural changes in prodromal Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics, 20, 3–9.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge Charles Henry and Michael Hulet and the rest of the Information and Telecommunication Technology Center (ITTC) staff at The University of Kansas for their support with our high performance computing.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to analysis design, results interpretation and manuscript preparation.
Funding
Drs. Burns, Vidoni, Morris, Honea, and Rasinio Graves are supported by the University of Kansas Alzheimer’s Disease Center (P30AG035982). Supported by the National Institute on Aging (NIA) R01AG033673. Dr. Burns was also supported by grants from the NIA and NINDS (R01AG034614 & U10NS077356). Dr. Vidoni was supported in part by Frontiers: The Heartland Institute for Clinical and Translational Research (University of Kansas Medical Center’s CTSA (KL2TR000119). Dr. Honea and Rodrigo Perea are supported by a grant from NIA (K01AG035042). Work conducted in the project is supported by the National Center for Research Resources (M01RR023940), and is now at the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (UL1TR000001). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH. The KU Grayhawk Database provided contact information for potential participants.
Disclosures
None of the authors have relevant disclosures to mention.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Table 1
(PDF 12 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perea, R.D., Vidoni, E.D., Morris, J.K. et al. Cardiorespiratory fitness and white matter integrity in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Imaging and Behavior 10, 660–668 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9431-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9431-3