Abstract
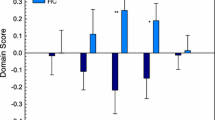
The thalamo-cortical resting state functional connectivity of seven sub-thalamic regions were examined in a prospectively recruited population of 77 acute mild TBI (mTBI) patients within the first 10 days (mean 6 ± 3 days) of injury and 35 neurologically intact control subjects using the Oxford thalamic connectivity atlas. Neuropsychological assessments were conducted using the Automated Neuropsychological Assessment Metrics (ANAM). A subset of participants received a magentic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) exam to determine metabolite concentrations in the thalamus and the posterior cingulate cortex. Results show that patients performed worse than the control group on various subtests of ANAM and the weighted throughput score, suggesting reduced cognitive performance at this early stage of injury. Both voxel and region of interest based analysis of the resting state fMRI data demonstrated that acute mTBI patients have increased functional connectivity between the various sub-thalamic regions and cortical regions associated with sensory processing and the default mode network (DMN). In addition, a significant reduction in NAA/Cr was observed in the thalamus in the mTBI patients. Furthermore, an increase in Cho/Cr ratio specific to mTBI patients with self-reported sensory symptoms was observed compared to those without self-reported sensory symptoms. These results provide novel insights into the neural mechanisms of the brain state related to internal rumination and arousal, which have implications for new interventions for mTBI patients with persistent symptoms. Furthermore, an understanding of heightened sensitivity to sensory related inputs during early stages of injury may facilitate enhanced prediction of safe return to work.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arfanakis, K., Haughton, V. M., Carew, J. D., Rogers, B. P., Dempsey, R. J., & Meyerand, M. E. (2002). Diffusion tensor MR imaging in diffuse axonal injury. AJNR. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 23, 794–802.
Bartnik-Olson, B. L., Holshouser, B., Wang, H., Grube, M., Tong, K., Wong, V., & Ashwal, S. (2014). Impaired neurovascular unit function contributes to persistent symptoms after concussion: a pilot study. Journal of Neurotrauma, 31, 1497–1506.
Bazarian, J. J., Zhong, J., Blyth, B., Zhu, T., Kavcic, V., & Peterson, D. (2007). Diffusion tensor imaging detects clinically important axonal damage after mild traumatic brain injury: a pilot study. Journal of Neurotrauma, 24, 1447–1459.
Behrens, T. E., Johansen-Berg, H., Woolrich, M. W., Smith, S. M., Wheeler-Kingshott, C. A., Boulby, P. A., Barker, G. J., Sillery, E. L., Sheehan, K., Ciccarelli, O., Thompson, A. J., Brady, J. M., & Matthews, P. M. (2003). Non-invasive mapping of connections between human thalamus and cortex using diffusion imaging. Nature Neuroscience, 6, 750–757.
Bey, T., & Ostick, B. (2009). Second impact syndrome. West Journal Emergency Medicine, 10, 6–10.
Biswal, B., Yetkin, F. Z., Haughton, V. M., & Hyde, J. S. (1995). Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 34, 537–541.
Callard, F., Smallwood, J., & Margulies, D. S. (2012). Default positions: how neuroscience's historical legacy has hampered investigation of the resting mind. Frontiers in Psychology, 3, 321.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2003). Report to congress on mild traumatic brain injury in the united states: steps to prevent a serious public health problem.
Cohen, B. A., Inglese, M., Rusinek, H., Babb, J. S., Grossman, R. I., & Gonen, O. (2007). Proton MR spectroscopy and MRI-volumetry in mild traumatic brain injury. AJNR. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 28, 907–913.
Davie, C. A., Hawkins, C. P., Barker, G. J., Brennan, A., Tofts, P. S., Miller, D. H., & McDonald, W. I. (1993). Detection of myelin breakdown products by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Lancet, 341, 630–631.
Di, X., & Biswal, B. B. (2014). Modulatory interactions between the default mode network and task positive networks in resting-state. PeerJ, 2, e367.
Dischinger, P. C., Ryb, G. E., Kufera, J. A., & Auman, K. M. (2009). Early predictors of postconcussive syndrome in a population of trauma patients with mild traumatic brain injury. Journal of Trauma, 66, 289–96. discussion 296–7.
Drexel, M., Puhakka, N., Kirchmair, E., Hortnagl, H., Pitkanen, A., & Sperk, G. (2015). Expression of GABA receptor subunits in the hippocampus and thalamus after experimental traumatic brain injury. Neuropharmacology, 88, 122–133.
Faul, M., Xu, L., Wald, M., Coronado, V. (2010). Traumatic brain injury in the United States: emergency department visits, hospitalizations, and deaths. Center of Disease Control.
Folstein, M. F., Folstein, S. E., & McHugh, P. R. (1975). Mini-mental state". a practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 12, 189–198.
Friedman, S. D., Brooks, W. M., Jung, R. E., Hart, B. L., & Yeo, R. A. (1998). Proton MR spectroscopic findings correspond to neuropsychological function in traumatic brain injury. AJNR. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 19, 1879–1885.
Galarreta, M., & Hestrin, S. (2001). Electrical synapses between GABA-releasing interneurons. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 2, 425–433.
Garnett, M. R., Blamire, A. M., Corkill, R. G., Cadoux-Hudson, T. A., Rajagopalan, B., & Styles, P. (2000). Early proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in normal-appearing brain correlates with outcome in patients following traumatic brain injury. Brain, 123(Pt 10), 2046–2054.
Gasparovic, C., Yeo, R., Mannell, M., Ling, J., Elgie, R., Phillips, J., Doezema, D., & Mayer, A. R. (2009). Neurometabolite concentrations in gray and white matter in mild traumatic brain injury: an 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Journal of Neurotrauma, 26, 1635–1643.
Ge, Y., Patel, M. B., Chen, Q., Grossman, E. J., Zhang, K., Miles, L., Babb, J. S., Reaume, J., & Grossman, R. I. (2009). Assessment of thalamic perfusion in patients with mild traumatic brain injury by true FISP arterial spin labelling MR imaging at 3 T. Brain Injury, 23, 666–674.
George, E. O., Roys, S., Sours, C., Rosenberg, J., Zhuo, J., Shanmuganathan, K., & Gullapalli, R. P. (2014). Longitudinal and prognostic evaluation of mild traumatic brain injury: a 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Journal of Neurotrauma, 31, 1018–1028.
Govindaraju, V., Gauger, G. E., Manley, G. T., Ebel, A., Meeker, M., & Maudsley, A. A. (2004). Volumetric proton spectroscopic imaging of mild traumatic brain injury. AJNR. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 25, 730–737.
Greicius, M. D., Flores, B. H., Menon, V., Glover, G. H., Solvason, H. B., Kenna, H., Reiss, A. L., & Schatzberg, A. F. (2007). Resting-state functional connectivity in major depression: abnormally increased contributions from subgenual cingulate cortex and thalamus. Biological Psychiatry, 62, 429–437.
Grossman, E. J., Ge, Y., Jensen, J. H., Babb, J. S., Miles, L., Reaume, J., Silver, J. M., Grossman, R. I., & Inglese, M. (2012). Thalamus and cognitive impairment in mild traumatic brain injury: a diffusional kurtosis imaging study. Journal of Neurotrauma, 29, 2318–2327.
Grossman, E. J., Inglese, M., & Bammer, R. (2010). Mild traumatic brain injury: is diffusion imaging ready for primetime in forensic medicine? Topics in Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 21, 379–386.
Grossman, E. J., Jensen, J. H., Babb, J. S., Chen, Q., Tabesh, A., Fieremans, E., Xia, D., Inglese, M., & Grossman, R. I. (2013). Cognitive impairment in mild traumatic brain injury: a longitudinal diffusional kurtosis and perfusion imaging study. AJNR. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 34(951–7), S1–3.
Gusnard, D. A., Akbudak, E., Shulman, G. L., & Raichle, M. E. (2001). Medial prefrontal cortex and self-referential mental activity: relation to a default mode of brain function. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 98, 4259–4264.
Haacke, E. M., Xu, Y., Cheng, Y. C., & Reichenbach, J. R. (2004). Susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI). Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 52, 612–618.
Halbauer, J. D., Ashford, J. W., Zeitzer, J. M., Adamson, M. M., Lew, H. L., & Yesavage, J. A. (2009). Neuropsychiatric diagnosis and management of chronic sequelae of war-related mild to moderate traumatic brain injury. Journal of Rehabilitation Research and Development, 46, 757–796.
Hattingen, E., Magerkurth, J., Pilatus, U., Mozer, A., Seifried, C., Steinmetz, H., Zanella, F., & Hilker, R. (2009). Phosphorus and proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy demonstrates mitochondrial dysfunction in early and advanced Parkinson's disease. Brain, 132, 3285–3297.
He, J. H., Cui, Y., Song, M., Yang, Y., Dang, Y. Y., Jiang, T. Z., Xu, R. X. (2014). Decreased functional connectivity between the mediodorsal thalamus and default mode network in patients with disorders of consciousness. Acta Neurol Scand.
Henry, L. C., Tremblay, S., Boulanger, Y., Ellemberg, D., & Lassonde, M. (2010). Neurometabolic changes in the acute phase after sports concussions correlate with symptom severity. Journal of Neurotrauma, 27, 65–76.
Henry, L. C., Tremblay, S., Leclerc, S., Khiat, A., Boulanger, Y., Ellemberg, D., Lassonde, M. (2011). Metabolic changes in concussed American football players during the acute and chronic post-injury phases. BMC Neurol 11: 105-2377-11-105.
Hoge, C. W., McGurk, D., Thomas, J. L., Cox, A. L., Engel, C. C., & Castro, C. A. (2008). Mild traumatic brain injury in U.S. Soldiers returning from Iraq. New England Journal of Medicine, 358, 453–463.
Holshouser, B. A., Tong, K. A., Ashwal, S., Oyoyo, U., Ghamsary, M., Saunders, D., & Shutter, L. (2006). Prospective longitudinal proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging in adult traumatic brain injury. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 24, 33–40.
Huusko, N., & Pitkanen, A. (2014). Parvalbumin immunoreactivity and expression of GABAA receptor subunits in the thalamus after experimental TBI. Neuroscience, 267, 30–45.
Inglese, M., Li, B. S., Rusinek, H., Babb, J. S., Grossman, R. I., & Gonen, O. (2003). Diffusely elevated cerebral choline and creatine in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 50, 190–195.
Iraji, A., Benson, R. R., Welch, R. D., O'Neil, B. J., Woodard, J. L., Ayaz, S. I., Kulek, A., Mika, V., Medado, P., Soltanian-Zadeh, H., Liu, T., Haacke, E. M., Kou, Z. (2014). Resting state functional connectivity in mild traumatic brain injury at the acute stage: independent component and seed based analyses. J Neurotrauma.
Iverson, G. L., Lovell, M. R., Smith, S., & Franzen, M. D. (2000). Prevalence of abnormal CT-scans following mild head injury. Brain Injury, 14, 1057–1061.
Johnson, B., Zhang, K., Gay, M., Horovitz, S., Hallett, M., Sebastianelli, W., & Slobounov, S. (2012). Alteration of brain default network in subacute phase of injury in concussed individuals: resting-state fMRI study. NeuroImage, 59, 511–518.
Kane, R. L., Roebuck-Spencer, T., Short, P., Kabat, M., & Wilken, J. (2007). Identifying and monitoring cognitive deficits in clinical populations using automated neuropsychological assessment metrics (ANAM) tests. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, 22(1), S115–26.
Kapogiannis, D., Reiter, D. A., Willette, A. A., & Mattson, M. P. (2013). Posteromedial cortex glutamate and GABA predict intrinsic functional connectivity of the default mode network. NeuroImage, 64, 112–119.
King, N. S., Crawford, S., Wenden, F. J., Moss, N. E., & Wade, D. T. (1995). The rivermead post concussion symptoms questionnaire: a measure of symptoms commonly experienced after head injury and its reliability. Journal of Neurology, 242, 587–592.
Kirov, I., Fleysher, L., Babb, J. S., Silver, J. M., Grossman, R. I., & Gonen, O. (2007). Characterizing 'mild' in traumatic brain injury with proton MR spectroscopy in the thalamus: initial findings. Brain Injury, 21, 1147–1154.
Kirov, I. I., Tal, A., Babb, J. S., Lui, Y. W., Grossman, R. I., & Gonen, O. (2013). Diffuse axonal injury in mild traumatic brain injury: a 3D multivoxel proton MR spectroscopy study. Journal of Neurology, 260, 242–252.
Kucyi, A., Moayedi, M., Weissman-Fogel, I., Goldberg, M. B., Freeman, B. V., Tenenbaum, H. C., & Davis, K. D. (2014). Enhanced medial prefrontal-default mode network functional connectivity in chronic pain and its association with pain rumination. Journal of Neuroscience, 34, 3969–3975.
Kumar, R., Husain, M., Gupta, R. K., Hasan, K. M., Haris, M., Agarwal, A. K., Pandey, C. M., & Narayana, P. A. (2009). Serial changes in the white matter diffusion tensor imaging metrics in moderate traumatic brain injury and correlation with neuro-cognitive function. Journal of Neurotrauma, 26, 481–495.
Laouchedi, M., Galanaud, D., Delmaire, C., Fernandez-Vidal, S., Messe, A., Mesmoudi, S., Oulebsir Boumghar, F., Pelegrini-Issac, M., Puybasset, L., Benali, H., Perlbarg, V. (2014). Deafferentation in thalamic and pontine areas in severe traumatic brain injury. J Neuroradiol.
Little, D. M., Kraus, M. F., Joseph, J., Geary, E. K., Susmaras, T., Zhou, X. J., Pliskin, N., & Gorelick, P. B. (2010). Thalamic integrity underlies executive dysfunction in traumatic brain injury. Neurology, 74, 558–564.
Lynall, M. E., Bassett, D. S., Kerwin, R., McKenna, P. J., Kitzbichler, M., Muller, U., & Bullmore, E. (2010). Functional connectivity and brain networks in schizophrenia. Journal of Neuroscience, 30, 9477–9487.
Mac Donald, C. L., Johnson, A. M., Cooper, D., Nelson, E. C., Werner, N. J., Shimony, J. S., Snyder, A. Z., Raichle, M. E., Witherow, J. R., Fang, R., Flaherty, S. F., & Brody, D. L. (2011). Detection of blast-related traumatic brain injury in U.S. military personnel. New England Journal of Medicine, 364, 2091–2100.
Marino, S., Zei, E., Battaglini, M., Vittori, C., Buscalferri, A., Bramanti, P., Federico, A., & De Stefano, N. (2007). Acute metabolic brain changes following traumatic brain injury and their relevance to clinical severity and outcome. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 78, 501–507.
Mason, M. F., Norton, M. I., Van Horn, J. D., Wegner, D. M., Grafton, S. T., & Macrae, C. N. (2007). Wandering minds: the default network and stimulus-independent thought. Science, 315, 393–395.
Mathias, J. L., Harman-Smith, Y., Bowden, S. C., Rosenfeld, J. V., & Bigler, E. D. (2014). Contribution of psychological trauma to outcomes after traumatic brain injury: assaults versus sporting injuries. Journal of Neurotrauma, 31, 658–669.
Mayer, A., Toulouse, T., Klimaj, S., Ling, J., Pena, A., Bellgowan, P. (2013). Investigating the properties of the hemodynamic response function following mild traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma.
Mayer, A. R., Ling, J., Mannell, M. V., Gasparovic, C., Phillips, J. P., Doezema, D., Reichard, R., & Yeo, R. A. (2010). A prospective diffusion tensor imaging study in mild traumatic brain injury. Neurology, 74, 643–650.
Mayer, A. R., Mannell, M. V., Ling, J., Elgie, R., Gasparovic, C., Phillips, J. P., Doezema, D., & Yeo, R. A. (2009). Auditory orienting and inhibition of return in mild traumatic brain injury: a FMRI study. Human Brain Mapping, 30, 4152–4166.
Mayer, A. R., Mannell, M. V., Ling, J., Gasparovic, C., & Yeo, R. A. (2011). Functional connectivity in mild traumatic brain injury. Human Brain Mapping, 32, 1825–1835.
McCrea, M., Kelly, J., Randolph, C. (2000). Standardized assessment of concussion (SAC): manual for adminstration, scoring, and interpretation, comprehensive neuropsychological services 2nd Eddition.
Messe, A., Caplain, S., Paradot, G., Garrigue, D., Mineo, J. F., Soto Ares, G., Ducreux, D., Vignaud, F., Rozec, G., Desal, H., Pelegrini-Issac, M., Montreuil, M., Benali, H., & Lehericy, S. (2011). Diffusion tensor imaging and white matter lesions at the subacute stage in mild traumatic brain injury with persistent neurobehavioral impairment. Human Brain Mapping, 32, 999–1011.
Morey, R. A., Haswell, C. C., Selgrade, E. S., Massoglia, D., Liu, C., Weiner, J., Marx, C. E., MIRECC Work Group, Cernak, I., & McCarthy, G. (2013). Effects of chronic mild traumatic brain injury on white matter integrity in Iraq and Afghanistan war veterans. Human Brain Mapping, 34, 2986–2999.
Ommaya, A. K., Goldsmith, W., & Thibault, L. (2002). Biomechanics and neuropathology of adult and paediatric head injury. British Journal of Neurosurgery, 16, 220–242.
Pop, V., & Badaut, J. (2011). A neurovascular perspective for long-term changes after brain trauma. Translation Stroke Research, 2, 533–545.
Povlishock, J. T., Becker, D. P., Cheng, C. L., & Vaughan, G. W. (1983). Axonal change in minor head injury. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology, 42, 225–242.
Provencher, S. W. (2001). Automatic quantitation of localized in vivo 1H spectra with LCModel. NMR Biomed, 14, 260–264.
Ramlackhansingh, A. F., Brooks, D. J., Greenwood, R. J., Bose, S. K., Turkheimer, F. E., Kinnunen, K. M., Gentleman, S., Heckemann, R. A., Gunanayagam, K., Gelosa, G., & Sharp, D. J. (2011). Inflammation after trauma: microglial activation and traumatic brain injury. Annals of Neurology, 70, 374–383.
Reich, S., Short, P., Kane, R., Weiner, W., Shulman, L., Anderson, K. (2005). Validation of the ANAM test battery in parkinson's disease. Ft. Belvoir: Defense technical information center.
Robinson, M. E., Lindemer, E. R., Fonda, J. R., Milberg, W. P., McGlinchey, R. E., Salat, D. H. (2014). Close-range blast exposure is associated with altered functional connectivity in Veterans independent of concussion symptoms at time of exposure. Hum Brain Mapp.
Sarmento, E., Moreira, P., Brito, C., Souza, J., Jevoux, C., & Bigal, M. (2009). Proton spectroscopy in patients with post-traumatic headache attributed to mild head injury. Headache, 49, 1345–1352.
Sonuga-Barke, E. J., & Castellanos, F. X. (2007). Spontaneous attentional fluctuations in impaired states and pathological conditions: a neurobiological hypothesis. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 31, 977–986.
Sours, C., Rosenberg, J., Kane, R., Roys, S., Zhuo, J., Shanmuganathan, K., Gullapalli, R. P. (2014). Associations between interhemispheric functional connectivity and the automated neuropsychological assessment metrics (ANAM) in civilian mild TBI. Brain Imaging Behav.
Sours, C., Zhuo, J., Janowich, J., Aarabi, B., Shanmuganathan, K., & Gullapalli, R. P. (2013). Default mode network interference in mild traumatic brain injury - a pilot resting state study. Brain Research, 1537, 201–215.
Squarcina, L., Bertoldo, A., Ham, T. E., Heckemann, R., & Sharp, D. J. (2012). A robust method for investigating thalamic white matter tracts after traumatic brain injury. NeuroImage, 63, 779–788.
Stokum, J., Sours, C., Zhuo, J., Shanmuganathan, K., Gullapalli, R. (2014). A longitudinal evaluation of diffusion kurtosis imaging in patients with mild traumatic brain injury. Brain injury. [BI] In press.
Tang, L., Ge, Y., Sodickson, D. K., Miles, L., Zhou, Y., Reaume, J., & Grossman, R. I. (2011). Thalamic resting-state functional networks: disruption in patients with mild traumatic brain injury. Radiology, 260, 831–840.
Vagnozzi, R., Signoretti, S., Cristofori, L., Alessandrini, F., Floris, R., Isgro, E., Ria, A., Marziali, S., Zoccatelli, G., Tavazzi, B., Del Bolgia, F., Sorge, R., Broglio, S. P., McIntosh, T. K., & Lazzarino, G. (2010). Assessment of metabolic brain damage and recovery following mild traumatic brain injury: a multicentre, proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic study in concussed patients. Brain, 133, 3232–3242.
Vagnozzi, R., Signoretti, S., Tavazzi, B., Floris, R., Ludovici, A., Marziali, S., Tarascio, G., Amorini, A. M., Di Pietro, V., Delfini, R., & Lazzarino, G. (2008). Temporal window of metabolic brain vulnerability to concussion: a pilot 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopic study in concussed athletes--part III. Neurosurgery, 62, 1286–95. discussion 1295–6.
Wang, X., Xu, M., Song, Y., Li, X., Zhen, Z., Yang, Z., & Liu, J. (2014). The network property of the thalamus in the default mode network is correlated with trait mindfulness. Neuroscience, 278, 291–301.
Warner, M. A., Marquez de la Plata, C., Spence, J., Wang, J. Y., Harper, C., Moore, C., Devous, M., & Diaz-Arrastia, R. (2010a). Assessing spatial relationships between axonal integrity, regional brain volumes, and neuropsychological outcomes after traumatic axonal injury. Journal of Neurotrauma, 27, 2121–2130.
Warner, M. A., Youn, T. S., Davis, T., Chandra, A., Marquez de la Plata, C., Moore, C., Harper, C., Madden, C. J., Spence, J., McColl, R., Devous, M., King, R. D., & Diaz-Arrastia, R. (2010b). Regionally selective atrophy after traumatic axonal injury. Archives of Neurology, 67, 1336–1344.
Whitfield-Gabrieli, S., & Nieto-Castanon, A. (2012). Conn: a functional connectivity toolbox for correlated and anticorrelated brain networks. Brain Connectivity, 2, 125–141.
Yeh, P. H., Wang, B., Oakes, T. R., French, L. M., Pan, H., Graner, J., Liu, W., & Riedy, G. (2014). Postconcussional disorder and PTSD symptoms of military-related traumatic brain injury associated with compromised neurocircuitry. Human Brain Mapping, 35, 2652–2673.
Yeo, R. A., Phillips, J. P., Jung, R. E., Brown, A. J., Campbell, R. C., & Brooks, W. M. (2006). Magnetic resonance spectroscopy detects brain injury and predicts cognitive functioning in children with brain injuries. Journal of Neurotrauma, 23, 1427–1435.
Yin, Y., Jin, C., Hu, X., Duan, L., Li, Z., Song, M., Chen, H., Feng, B., Jiang, T., Jin, H., Wong, C., Gong, Q., & Li, L. (2011). Altered resting-state functional connectivity of thalamus in earthquake-induced posttraumatic stress disorder: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Brain Research, 1411, 98–107.
Yuh, E. L., Mukherjee, P., Lingsma, H. F., Yue, J. K., Ferguson, A. R., Gordon, W. A., Valadka, A. B., Schnyer, D. M., Okonkwo, D. O., Maas, A. I., Manley, G. T., & Investigators, T. R. A. C. K.-T. B. I. (2013). Magnetic resonance imaging improves 3-month outcome prediction in mild traumatic brain injury. Annals of Neurology, 73, 224–235.
Zhou, Y., Milham, M. P., Lui, Y. W., Miles, L., Reaume, J., Sodickson, D. K., Grossman, R. I., & Ge, Y. (2012). Default-mode network disruption in mild traumatic brain injury. Radiology, 265, 882–892.
Zhou Y, Lui YW, Zuo XN, Milham MP, Reaume J, Grossman RI, Ge Y (2013) Characterization of thalamo-cortical association using amplitude and connectivity of functional MRI in mild traumatic brain injury. J Magn Reson Imaging.
Zhuo, J., Xu, S., Proctor, J. L., Mullins, R. J., Simon, J. Z., Fiskum, G., & Gullapalli, R. P. (2012). Diffusion kurtosis as an in vivo imaging marker for reactive astrogliosis in traumatic brain injury. NeuroImage, 59, 467–477.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Joshua Betz, Jacqueline Janowich, Teodora Stoica and Joseph Rosenberg for their help with patient recruitment, Dr. Robert Kane for providing access to ANAM, and and George Makris for his help with acquiring and processing the data. Support for this work was in part provided by the Department of Defense (W81XWH-08-1-0725 & W81XWH-12-1-0098 to RPG).
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Informed Consent
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, and the applicable revisions at the time of the investigation. Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table 1
(DOC 124 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sours, C., George, E.O., Zhuo, J. et al. Hyper-connectivity of the thalamus during early stages following mild traumatic brain injury. Brain Imaging and Behavior 9, 550–563 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9424-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9424-2