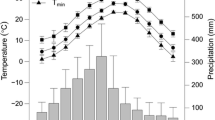
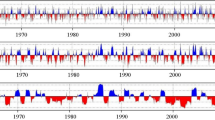
Abstract
The role of the temperate mixed broadleaf-Korean pine forest (BKF) in global biogeochemical cycles will depend on how the tree species community responds to climate; however, species-specific responses and vulnerabilities of common trees in BKF to extreme climates are poorly understood. Here we used dendrochronological methods to assess radial growth of seven main tree species (Pinus koraiensis, Picea jezoensis, Abies nephrolepis, Fraxinus mandshurica, Phellodendron amurense, Quercus mongolica, and Ulmus davidiana) in an old-growth BKF in response to climate changes in the Xiaoxing’an Mountains and to improve predictions of changes in the tree species composition. Temperature in most months and winter precipitation significantly negatively affected growth of P. jezoensis and A. nephrolepis, but positively impacted growth of P. koraiensis and the broadleaf species, especially F. mandshurica and U. davidiana. Precipitation and relative humidity in June significantly positively impacted the growth of most tree species. The positive effect of the temperature during the previous non-growing season (PNG) on growth of F. mandshurica and Q. mongolica strengthened significantly with rapid warming around 1981, while the impact of PNG temperature on the growth of P. jezoensis and A. nephrolepis changed from significantly negative to weakly negative or positive at this time. The negative response of radial growth of P. jezoensis and A. nephrolepis to precipitation during the growing season gradually weakened, and the negative response to PNG precipitation was enhanced. Among the studied species, P. koraiensis was the most resistant to drought, and U. davidiana recovered the best after extreme drought. Ulmus davidiana, P. jezoensis and A. nephrolepis were more resistant to extreme cold than the other species. Climate warming generally exacerbated the opposite growth patterns of conifer (decline) and broadleaf (increase) species. Deciduous broadleaf tree species in the old-growth BKF probably will gradually become dominant as warming continues. Species-specific growth-climate relationships should be considered in future models of biogeochemical cycles and in forestry management practices.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babst F, Alexander MR, Szejner P, Bouriaud O, Klesse S, Roden J, Ciais P, Poulter B, Frank D, Moore DJP, Trouet V (2014) A tree-ring perspective on the terrestrial carbon cycle. Oecologia 176(2):307–322. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-014-3031-6
Bansal S, St. Clair JB, Harrington CA, Gould PJ, (2015) Impact of climate change on cold hardiness of Douglas-fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii): environmental and genetic considerations. Glob Chang Biol 21(10):3814–3826. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.12958
Bose AK, Gessler A, Bolte A, Bottero A, Buras A, Cailleret M, Camarero JJ, Haeni M, Hereş AM, Hevia A, Lévesque M, Linares JC, Martinez-Vilalta J, Matías L, Menzel A, Sánchez-Salguero R, Saurer M, Vennetier M, Ziche D, Rigling A (2020) Growth and resilience responses of Scots pine to extreme droughts across Europe depend on predrought growth conditions. Glob Chang Biol 26(8):4521–4537. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.15153
Bottero A, Forrester DI, Cailleret M, Kohnle U, Gessler A, Michel D, Bose AK, Bauhus J, Bugmann H, Cuntz M (2021) Growth resistance and resilience of mixed silver fir and Norway spruce forests in central Europe: contrasting responses to mild and severe droughts. Glob Chang Biol 27(18):4403–4419. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.15737
Brodribb TJ, Bowman DJMS, Nichols S, Delzon S, Burlett R (2010) Xylem function and growth rate interact to determine recovery rates after exposure to extreme water deficit. New Phytol 188(2):1469–8137. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03393.x
Brodribb TJ, Pittermann J, Coomes DA (2012) Elegance versus speed: examining the competition between conifer and angiosperm trees. Int J Plant Sci 173(6):673–694. https://doi.org/10.1086/666005
Bunn AG (2008) A dendrochronology program library in R (dplR). Dendrochronologia 26(2):115–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dendro.2008.01.002
Cabon A, DeRose RJ, Shaw JD, Anderegg WRL (2023) Declining tree growth resilience mediates subsequent forest mortality in the US Mountain West. Glob Chang Biol 29:4826–4841. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.16826
Cao J, Liu HY, Zhao B, Li ZS, Liang BY, Shi L, Wu L, Cressey EL, Quine TA (2021) High forest stand density exacerbates growth decline of conifers driven by warming but not broad-leaved trees in temperate mixed forest in northeast Asia. Sci Total Environ 795:148875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148875
Carnicer J, Barbeta A, Sperlich D, Coll M, Peñuelas J (2013) Contrasting trait syndromes in angiosperms and conifers are associated with different responses of tree growth to temperature on a large scale. Front Plant Sci 4:409. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2013.00409
Choat B, Jansen S, Brodribb TJ, Cochard H, Delzon S, Bhaskar R, Bucci SJ, Feild TS, Gleason SM, Hacke UG, Jacobsen AL, Lens F, Maherali H, Martínez-Vilalta J, Mayr S, Mencuccini M, Mitchell PJ, Nardini A, Pittermann J, Pratt RB, Sperry JS, Westoby M, Wright IJ, Zanne AE (2012) Global convergence in the vulnerability of forests to drought. Nature 491(7426):752–755. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11688
Chu K, He HY, Chen QY, Cai FK, Song G, Ye J (2022) Effects of species interactions on tree growth and survival of mixed broadleaved Korean pine forest on Changbai Mountain. Chin J Ecol 41(06):1050–1055. https://doi.org/10.13292/j.1000-4890.202206.025. ((in Chinese))
Cook ER (1985) A time series analysis approach to tree-ring standardization. University of Arizona, Tucson
D’Orangeville L, Itter M, Kneeshaw D, Munger JW, Richardson AD, Dyer JM, Orwig DA, Pan Y, Pederson N (2022) Peak radial growth of diffuse-porous species occurs during periods of lower water availability than for ring-porous and coniferous trees. Tree Physiol 42(2):304–316. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpab101
DeSoto L, Cailleret M, Sterck F, Jansen S, Kramer K, Robert EMR, Aakala T, Amoroso MM, Bigler C, Camarero JJ, Čufar K, Gea-Izquierdo G, Gillner S, Haavik LJ, Hereş A-M, Kane JM, Kharuk VI, Kitzberger T, Klein T, Levanič T, Linares JC, Mäkinen H, Oberhuber W, Papadopoulos A, Rohner B, Sangüesa-Barreda G, Stojanovic DB, Suárez ML, Villalba R, Martínez-Vilalta J (2020) Low growth resilience to drought is related to future mortality risk in trees. Nat Commun 11(1):545. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-14300-5
Epron D, Bahn M, Derrien D, Lattanzi FA, Pumpanen J, Gessler A, Högberg P, Maillard P, Dannoura M, Gérant D, Buchmann N (2012) Pulse-labelling trees to study carbon allocation dynamics: a review of methods, current knowledge and future prospects. Tree Physiol 32(6):776–798. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tps057
Fang OY, Zhang QB (2019) Tree resilience to drought increases in the Tibetan Plateau. Glob Chang Biol 25(1):245–253. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.14470
Fisichelli N, Vor T, Ammer C (2014) Broadleaf seedling responses to warmer temperatures “chilled” by late frost that favors conifers. Eur J for Res 133:587–596. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-014-0786-6
Fonti P, von Arx G, García-González I, Eilmann B, Sass-Klaassen U, Gärtner H, Eckstein D (2010) Studying global change through investigation of the plastic responses of xylem anatomy in tree rings. New Phytol 185(1):42–53. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.03030.x
Fritts H (1976) Tree rings and climate. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Gazol A, Camarero JJ, Vicente-Serrano SM, Sánchez-Salguero R, Gutiérrez E, Luis M, Sangüesa-Barreda G, Novak K, Rozas V, Tíscar PA, Linares JC, Martín-Hernández N, Castillo EMd, Ribas M, García-González I, Silla F, Camisón A, Génova M, Olano JM, Longares LA, Hevia A, Tomás-Burguera M, Galván JD (2018) Forest resilience to drought varies across biomes. Glob Chang Biol 24(5):2143–2158. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.14082
Giardina F, Konings AG, Kennedy D, Alemohammad S, Hamed, (2018) Tall Amazonian forests are less sensitive to precipitation variability. Nat Geosci 11:405–409. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-018-0133-5
Gou XH, Zhou FF, Zhang YX, Chen QY, Zhang JZ (2013) Forward modeling analysis of regional scale tree-ring patterns around the northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Northwest China Biogeosci Discuss 10(6):9969–9988. https://doi.org/10.5194/bgd-10-9969-2013
Granda E, Gazol A, Camarero JJ (2018) Functional diversity differently shapes growth resilience to drought for co-existing pine species. J Veg Sci 29(2):265–275. https://doi.org/10.1111/jvs.12617
Gruber A, Strobl S, Veit B, Oberhuber W (2010) Impact of drought on the temporal dynamics of wood formation in Pinus sylvestris. Tree Physiol 30(4):490–501. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpq003
Harvey JE, Smiljanić M, Scharnweber T, Buras A, Cedro A, Cruz-García R, Drobyshev I, Janecka K, Jansons Ā, Kaczka R (2020) Tree growth influenced by warming winter climate and summer moisture availability in northern temperate forests. Glob Chang Biol 26(4):2505–2518. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.14966
Holmes RL (1983) Computer-assisted quality control in tree-ring dating and measurement. Tree-Ring Bullet 43:51–67
IPCC (2021) Climate change 2021: the physical science basis. In: Masson-Delmotte PZV, Pörtner HO, Roberts D, Skea J, Shukla PR, Pirani A, Moufouma-Okia W, Péan C, Pidcock R, Connors S, Matthews JBR, Chen Y, Zhou X, Gomis MI, Lonnoy E, Maycock T, Tignor M, Waterfield T (eds.): United Kingdom
Jiao L, Chen K, Wang SJ, Liu XP (2020) Stability evaluation of radial growth of Picea schrenkiana in different age groups in response to climate change in the eastern Tianshan Mountains. J Mt Sci 17(14):1735–1748. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-019-5703-5
Jing MD, Zhu LJ, Liu SG, Cao Y, Zhu Y, Yan WD (2022) Warming-induced drought leads to tree growth decline in subtropics: Evidence from tree rings in central China. Front Plant Sci 13:964400. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.964400
Keitel C, Matzarakis A, Rennenberg H, Gessler A (2006) Carbon isotopic composition and oxygen isotopic enrichment in phloem and total leaf organic matter of European beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) along a climate gradient. Plant Cell Environ 29(8):1492–1507. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2006.01520.x
Kosugi Y, Matsuo N (2006) Seasonal fluctuations and temperature dependence of leaf gas exchange parameters of co-occurring evergreen and deciduous trees in a temperate broad-leaved forest. Tree Physiol 26(9):1173–1184. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/26.9.1173
Lens F, Gleason SM, Bortolami G, Brodersen C, Delzon S, Jansen S (2022) Functional xylem characteristics associated with drought-induced embolism in angiosperms. New Phytol 236(6):2019–2036. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.18447
Lenz A, Hoch G, Körner C (2013) Early season temperature controls cambial activity and total tree ring width at the alpine treeline. Plant Ecol Divers 6(3–4):365–375. https://doi.org/10.1080/17550874.2012.711864
Li J (1997) Korean pine mixed forest ecology and management. Northeast Forestry University Press, Harbin ((in Chinese))
Liu XD, Yin ZY, Shao XM, Qin NS (2006) Temporal trends and variability of daily maximum and minimum, extreme temperature events, and growing season length over the eastern and central Tibetan Plateau during 1961–2003. J Geophys Res Atmos 111:D19109. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JD006915
Lloret F, Keeling EG, Sala A (2011) Components of tree resilience: effects of successive low-growth episodes in old ponderosa pine forests. Oikos 120(12):1909–1920. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0706.2011.19372.x
Lyu SN, Wang XC, Zhang YD, Li ZS (2017) Different responses of Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis) and Mongolia oak (Quercus mongolica) growth to recent climate warming in northeast China. Dendrochronologia 45:113–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dendro.2017.08.002
Marquis B, Bergeron Y, Houle D, Leduc M, Rossi S (2022) Variability in frost occurrence under climate change and consequent risk of damage to trees of western Quebec. Canada Sci Rep 12(1):7220. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-11105-y
Montwé D, Isaac-Renton M, Hamann A, Spiecker H (2018) Cold adaptation recorded in tree rings highlights risks associated with climate change and assisted migration. Nat Commun 9(1):1574. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04039-5
Pederson N, Cook E, Jacoby G, Peteet D, Griffin K (2004) The influence of winter temperatures on the annual radial growth of six northern range margin tree species. Dendrochronologia 22:7–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dendro.2004.09.005
Peng ZT, Zhang YD, Zhu LJ, Guo MM, Lu QA, Xu K, Shao H, Mo QF, Liu SR (2023) Spatial and temporal patterns of the sensitivity of radial growth response by to regional climate change in the Tianshan Mountains. J Forestry Res 34(6):1669–1681. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-023-01629-y
Pettitt AN (1979) A non-parametric approach to the change-point problem. J R Stat Soc Ser C Appl Stat 28(2):126–135. https://doi.org/10.2307/2346729
Poyatos R, Aguadé D, Galiano L, Mencuccini M, Martínez-Vilalta J (2013) Drought-induced defoliation and long periods of near-zero gas exchange play a key role in accentuating metabolic decline of Scots pine. New Phytol 200(2):388–401. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12278
Prado-Junior JA, Schiavini I, Vale VS, Diego R, Lopes SF, Poorter L (2017) Functional traits shape size-dependent growth and mortality rates of dry forest tree species. J Plant Ecol 10(6):895–906. https://doi.org/10.1093/jpe/rtw103
R Core Team (2020) R: a language and environment for statistical computing (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, 2020)
Rahman M, Islam M, Bräuning A (2019) Species-specific growth resilience to drought in a mixed semi-deciduous tropical moist forest in South Asia. For Ecol Manage 433:487–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2018.11.034
Rennenberg H, Loreto F, Polle A, Brilli F, Fares S, Beniwal RS, Gessler A (2006) Physiological responses of forest trees to heat and drought. Plant Biol 8(5):556–571. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2006-924084
Rozendaal DMA, Phillips OL, Lewis SL, Affum-Baffoe K, Alvarez-Davila E, Andrade A, Aragão LEOC, Araujo-Murakami A, Baker TR, Bánki O, Brienen RJW, Camargo JLC, Comiskey JA, Djuikouo Kamdem MN, Fauset S, Feldpausch TR, Killeen TJ, Laurance WF, Laurance SGW, Lovejoy T, Malhi Y, Marimon BS, Marimon Junior B-H, Marshall AR, Neill DA, Núñez Vargas P, Pitman NCA, Poorter L, Reitsma J, Silveira M, Sonké B, Sunderland T, Taedoumg H, ter Steege H, Terborgh JW, Umetsu RK, van der Heijden GMF, Vilanova E, Vos V, White LJT, Willcock S, Zemagho L, Vanderwel MC (2020) Competition influences tree growth, but not mortality, across environmental gradients in Amazonia and tropical Africa. Ecology 101(7):e03052. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecy.3052
Seiwa K (1999) Ontogenetic changes in leaf phenology of Ulmus davidiana var. japonica, a deciduous broad-leaved tree. Tree Physiol 19(12):793–797. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/19.12.793
Shen YX, Guo QX, Liang YL (2011) Application of catchment scale forest dynamic model to prediction of successional process of natural secondary forests in Northeast China. J Northeast for Univ. https://doi.org/10.13759/j.cnki.dlxb.2011.07.024. ((in Chinese))
Shi L, Liu HY, Wang L, Peng RN, He HL, Liang BY, Cao J (2024) Transitional responses of tree growth to climate warming at the southernmost margin of high latitudinal permafrost distribution. Sci Total Environ 908:168503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.168503
Stokes MA, Smiley TL (1968) An introduction to tree-ring dating. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Vicente-Serrano SM, Beguería S, López-Moreno JI (2010) A multiscalar drought index sensitive to global warming: the standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index. J Clim 23(7):1696–1718. https://doi.org/10.1175/2009jcli2909.1
Vitasse Y, Bottero A, Cailleret M, Bigler C, Fonti P, Gessler A, Lévesque M, Rohner B, Weber P, Rigling A, Wohlgemuth T (2019) Contrasting resistance and resilience to extreme drought and late spring frost in five major European tree species. Glob Chang Biol 25(11):3781–3792
Wang XC, Pederson N, Chen ZJ, Lawton K, Zhu C, Han SJ (2019) Recent rising temperatures drive younger and southern Korean pine growth decline. Sci Total Environ 649:1105–1116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.393
Wigley TML, Briffa KR, Jones PD (1984) On the average value of correlated time series, with applications in dendroclimatology and hydrometeorology. J Clim Appl Meteor 23(2):201–213
Wu XC, Li XY, Liu HY, Ciais P, Li YQ, Xu CY, Babst F, Guo WC, Hao BY, Wang P, Huang YM, Liu SM, Tian YH, He B, Zhang CC (2019) Uneven winter snow influence on tree growth across temperate China. Glob Chang Biol 25(1):144–154. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.14464
Ye HC, Yang DQ, Robinson D (2008) Winter rain on snow and its association with air temperature in northern Eurasia. Hydrol Process 22(15):2728–2736. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.7094
Yuan DY, Zhu LJ, Cherubini P, Li ZS, Zhang YD, Wang XC (2021) Species-specific indication of 13 tree species growth on climate warming in temperate forest community of northeast China. Ecol Indic 133:108389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108389
Zang C, Biondi F (2015) Treeclim: an R package for the numerical calibration of proxy-climate relationships. Ecography 38(4):431–436. https://doi.org/10.1111/ecog.01335
Zhang R, Hu ZH, Cherubini P, Cooper DJ, Zhu LJ, Lei PF (2023) Tree-ring data reveal trees are suffering from severe drought stress in the humid subtropical forest. For Ecol Manage 546:121330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2023.121330
Zhu LJ, Jin GZ, Wang XC (2015) Reconstruction of disturbance history of a typical broad-leaved Pinus koraiensis forest and mechanisms of disturbance occurrence. Chin J Plant Ecol 39:125–139. https://doi.org/10.17521/cjpe.2015.0013. ((in Chinese))
Zhu LJ, Li ZS, Wang XC (2017) Anatomical characteristics of xylem in tree rings and its relationship with environments. Chin J Plant Ecol 41(2):238–251. https://doi.org/10.17521/cjpe.2016.0198. ((in Chinese))
Zhu LJ, Wang XC, Pederson N, Chen ZJ, Cooper DJ, Zhang YD, Li ZS (2018) Spatial variability in growth-climate relationships of Amur cork tree (Phellodendron amurense) and their connections with PDO in Northeast China. J Geophys Res Biogeosci 123:1625–1636. https://doi.org/10.1029/2017jg004292
Zhu LJ, Cooper DJ, Yuan DY, Li ZS, Zhang YD, Liang HX, Wang XC (2020) Regional scale temperature rather than precipitation determines vessel features in earlywood of Manchurian ash in temperate forests. J Geophys Res Biogeosci 125(11):e2020JG005955. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020JG005955
Zhu LJ, Liu SG, Zhu HF, Cooper DJ, Yuan DY, Zhu Y, Li ZS, Zhang YD, Liang HX, Zhang X, Song WQ, Wang XC (2022) Multi-species approach strengthens the reliability of dendroclimatic reconstructions in monsoonal Northeast China. Clim Change 171(1):7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-022-03328-9
Zhu LJ, Zhang J, Camarero JJ, Cooper DJ, Cherubini P, Yuan DY, Wang XC (2023) Drivers and spatiotemporal patterns of post-drought growth resilience of four temperate broad-leaved trees. Agric Meteorol 342:109741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2023.109741
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the Forestry Bureau staff for field assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Project funding: This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42107476, 41877426), the Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (2021JJ41075), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2020M682600), the Science and Technology Innovation Program of Hunan Province (2020RC2058), the Research Foundation of the Bureau of Education in Hunan Province (20B627) and China Scholarship Council (CSC, no. 202206600004, to DY).
The online version is available at https://link.springer.com/.
Corresponding editor: Tao Xu.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, X., Yuan, D., Zhu, L. et al. Long-term changes in radial growth of seven tree species in the mixed broadleaf-Korean pine forest in Northeast China: Are deciduous trees favored by climate change?. J. For. Res. 35, 70 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-024-01725-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-024-01725-7