Abstract
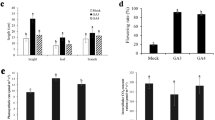
The effects of exogenous gibberellic acid (GA3) and abscisic acid (ABA) on the total respiratory rate, percentages of total respiratory rate contributed by respiratory pathways [Embden-Meyerhof- Parnas Pathway (EMP), Pentose Phosphate Pathway (PPP), and Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle (TCA)], and conversion of starch to soluble sugars in the buds of black currants during secondary bud burst were investigated to determine the relationship between respiratory rates and secondary bud burst. ‘Adelinia’, a black currant cultivar that is prone to secondary bud burst after the first harvest, was used in this study. Mature bushes of Adelinia were sprayed with 30 mg/L GA3 and 50 mg/L ABA to manipulate bud burst. The results showed that exogenous applications of GA3 and ABA had opposite effects on bud respiratory rate. Generally, GA3 treatment increased the total respiratory rate and respiratory rate of the TCA and PPP, and the respiratory rates after GA3 treatment were higher than those of control. While ABA treatment mostly decreased the total respiratory rate and the respiratory rate of TCA and PPP in buds in comparison to control. In terms of the percentage of the three respiratory rates in comparison to the total respiratory rate, GA3 treatment significantly increased the percentage of TCA and PPP respiratory rate in comparison to the control (P < 0.01), whereas ABA decreased the rates. GA3 significantly increased the content of soluble sugars and decreased the starch content, while the starch content in buds after ABA treatment was significantly higher than that of the control. All results showed that PPP is a critical process for the second bud burst in black currants. While the EMP–TCA pathway is still dominant in bud respiration, provides a series of basic materials and energy (ATP). The conversion of starch to soluble sugars is essential for bud burst. Thus, we conclude that an energy shortage is a main contributor in ABA inhibition of the secondary bud burst of black currants.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiko I, Daisuke S, Takaya M (2012) Carbohydrate metabolism and its possible roles in endo-dormancy transition in Japanese pear. Sci Hortic 144:187–194
Anderson JV, Gesch RW, Jia Y, Chao WS, Horvath DP (2005) Seasonal shifts in dormancy status, carbohydrate metabolism, and related gene expression in crown buds of leafy spurge. Plant Cell Environ 28:1567–1578
Bi L (2009) Study on changes of inclusions and metabolism during dormant period of Qiyuesu Pear. Agricultural University of Hebei, Baoding, China, Thesis (MS)
Bogatek KA (1984) Respiratory activity of apple seeds during dormancy removal and germination. Physiol Veg 22(2):181–189
Campoy JA, Ruiz D, Egea J (2011) Dormancy in temperate fruit trees in a global warming context: a review. Sci Hortic 130:357–372
Carvajal ME, Gardea AA, Rascon CA, Orozco J, Ponce L, Marquez E (2007) Respiratory response of apple buds treated with bud breaking agents. Thermochim Acta 457:109–112
Cong S, Wang HB, Wang XD, Wang BL, Zheng XC, Shi XB (2013) Respiratory changes during dormancy of grape buds. Sci Agric Sin 46(6):1201–1207
Frank G, Anthony AM, John VJ (2005) Dormancy release ABA and pre-harvest sprouting. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8:183–187
Gao DS, Xia N, Wang XA (1999) Changes of carbohydrate content and effect of exogenous growth regulators on dormancy-breaking during dormant period of peach shoots. Plant Physiol Commun 35(1):10–12
Gao DS, Shu HR, Li XL (2001) A study on bud chilling requirements of fruit trees in green house. Acta Hortic Sin 28(4):283–289
Gao DS, Li XL, Shu HR, Wang Y (2002a) Effects of some chemicals on dormancy breaking of grape and peach trees. J Fruit Sci 19(6):385–388
Gao DS, Shu HR, Li XL (2002b) Effect of exogenous plant growth hormones on the changes of carbohydrates in peach bud during dormant period. J Fruit Sci 18(2):104–107
Hans L (2005) Plant respiration: from cell to ecosystem. Springer, New York, pp 1–15
Hatem BM, Ahmedou MV, Jan MC, Habib K (2012) Carbohydrate changes during dormancy release in Superior Seedless grapevine cuttings following hydrogen cyanamide treatment. Sci Hortic 140:19–25
Huang J, Zhang HS, Wang JF (2003) Molecular cloning and characterization of rice 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase gene that is up-regulated by salt stress. Mol Biol Rep 30:223–227
Huo JW, Li ZH, Qin D (2011) Review of nutritional ingredients and health protectable function of black currant fruit and its prospect in industrial development. J Northeast Agric Univ 42(2):139–144
Lang GA (1987) Endo-, para-, and ecodormancy: physiological terminology and classification for dormancy research. Hortic Sci 22(5):371–377
Li HS (2006) Modern plant physiology. Higher Education Press, Beijing, pp 107–143
Li ZH, Gao DS, Li XL (2006) The relation between en-dormancy and changes in two main electron transport pathways of Nectarine (Prunus persica var. nectariana) buds. J Plant Physiol Mol Biol 32(2):156–162
Li J, Gao DS, Li XL (2008) Effect of photoperiod treatments on dormancy induction and changes in correlated respiratory rate of nectarine peach bud. Agric Sci China 7(12):1445–1450
Li FX, Qin D, Li SL, Zhan G, Huo JW, Wang HH (2014) Ascorbic acid content and difference of related enzyme activities in fruit of blackcurrant. J South Agric 45(7):1237–1241
Ma HY, Liu GC (2012) Responsive characteristics of respiratory metabolism pathway activity in ‘Hanfu’ apple flower buds under cold stress. J Fruit Sci 29(3):317–321
McPherson HG, Snelgar WP, Manson PJ, Snowball AM (1997) Bud respiration and dormancy of Kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa). Ann Bot 80:411–418
Mostafa MR, Mohamed AS, Ei Y (2013) Response of “Anna” apple dormant buds and carbohydrate metabolism during floral bud break to onion extract. Sci Hortic 155:78–84
Pu XC, Han JG, Li M, Du GP (1996) Studies on respiratory pathway of seed when breaking dormancy. Acta Pratac Sin 5(3):56–60
Qin D (2009) Study on the physiological and biochemical changes in Avrolles (Malus domestica) after natural dormancy releasing, Shandong Agricultural University, Taían, China, Thesis (PhD)
Qin D, Huo JW, Sui W, Zhang ZF (2012) Black currant production, breeding and processing in China. Acta Hortic 926:119–122
Rehman S, Park IH (2000) Effect of scarification, GA and chilling on the germination of goldenrain-tree (Koelreuteria paniculata Laxm.) seeds. Sci Hortic 85:319–324
Roberts EH (1973) Oxidative processes and the control of seed germination. In: Heydecker W (ed) Seed ecology, Butterworth, London, p 189–218
Rose GA, Cameron RW (2009) Chill unit models for blackcurrant (Ribes nigrum L.) cultivars ‘Ben Gairn’, ‘Ben Hope’ and ‘Ben Tirran’. Sci Hortic 122:654–657
Tan Y, Gao DS, Li L, Chen XD (2010) Respiratory response of dormant nectarine floral buds on chilling deficiency. Agric Sci China 9(10):1448–1454
Tang PS (1979) Regulation and control of multiple pathways of respiratory metabolism in relation to other physiological functions. Acta Bot Sin 21:93–106
Wang HB (2006) Study on the mechanisms of endo-dormancy induction and short-term heating releasing endo-dormancy in peach bud, Xinjiang Agricultural Universit,Wulumuqi, China, Thesis (MS)
Wang HB, Gao DS, Wang XD, Li J (2005) Relationship between the content of starch and soluble sugar and the dormancy release in peach bud treated by short-term heating. J Fruit Sci 22(6):615–619
Wang HB, Gao DS, Wang XD, Li J (2006a) Research achievement on bud endo-dormancy induction in deciduous fruit trees. J Fruit Sci 23(1):91–95
Wang HB, Gao DS, Wang XD, Li J (2006b) Role of gibberellin and abscisic acid in peach bud endo -dormancy induction. J Fruit Sci 23(4):599–601
Wang HB, Gao DS, Wang XD, Li J (2006c) Effects of short term heating on bud dormancy in ‘shuguang’ nectarine tree. Acta Hortic Sin 33(3):601–604
Wang HH, Huo JW, Qin D, Xie FC, Zhang YH, Li XG (2015) Effect of GA3 and ABA on morphological indexes of secondary germination in Ribes nigrum L. North Hortic 18:13–17
Xu RY, Yoshiji N, Han DS (2006) Changes in endogenous abscisic acid and soluble sugars levels during dormancy-release in bulbs of Lilium rubellum. Sci Hortic 111:68–72
Xue YL (1980) Physiological and regulatory mechanism of respiration respiratory metabolisms. Plant Physiol Commun 1:60–72
Yang RC, Zhang HJ, Wang J (2012) Regulatory mechanism of plant hormones on seed dormancy and germination. Acta Agrestia Sin 20(1):1–9
Yeam DY, Murray JJ, Portz HL (1981) Physiology of Seed Germination in Zoysia grass (Zoysia japonica Steud). Proc. Int. in Turfgrass Res. Conf., 4th, Guelph, Canada 467-476
Yeam DY, Mandava NB, Terry PH, Murray JJ, Portz HL (1988) Identification and quantification of abscisic acid in Zoysia grass seeds and its inhibitory effect on germination. Crop Sci 28:317–332
Yoshiko K, Toshio T, Tatsushi O, Akihiko G (1999) Involvement of endogenous plant hormones (IAA, ABA, GAs) in leaves and flower bud formation of satsuma mandarin (Citrus unshiu Marc.). Sci Hortic 79:185–194
Young E (1990) Changes in respiration rate and energy of activation after chilling and forcing dormant apple trees. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 115(5):809–814
Zhao SJ (1998) The experimental principles and techniques of plant physiology. China Agricultural Science and Technique Press, Beijing, pp 98–107
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project funding
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31201584), ‘Yong Talents’ Project of Northeast Agricultural University (16QC07), the Postdoctoral Fund of Heilongjiang Province (LBH-Z11236), the Science and Technology Research Project by Education Department of Heilongjiang Province (12511050) and the Doctoral Fund Project of the Northeast Agricultural University (2010RCB21).
The online version is available at http://www.springerlink.com
Corresponding editor: Hu Yanbo
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, D., Wang, H., Zhang, C. et al. Effects of GA3 and ABA on the respiratory pathways during the secondary bud burst in black currants. J. For. Res. 28, 705–712 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-016-0354-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-016-0354-7