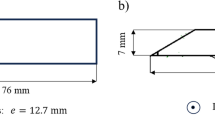
Abstract
Three similarly-manufactured but differently-employed pellet mill dies of X46Cr13 (420C) stainless steel were broken into several parts. To determine the causes of fracture, material characteristics (such as microstructure) and features of crack faces were investigated. It is figured out that sensitization, which is the existence of continuous carbides on the prior-austenite grain boundaries, has taken place both in the dies and the as-received primary rings. In addition, studies on the crack faces reveal the occurrence of fatigue, corrosion, and intergranular fracture. It can be concluded that corroded sites of die 1 and sharp edges of dies 2 and 3 act as fatigue initiation spots, and final crack growth takes place mostly by intergranular fracture, owing to the presence of continuous carbides. The results show the importance of microstructure control for primary rings, design modification for the dies to reduce stress concentration, and cleanliness of the dies in non-operating periods.






















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Corresponding data will be made available upon reasonable requests.
References
A. Awny, M.N. Radwan, M.A. Nour, S.S. Fouda, S.A. Al-Dhumri, S.M. Soliman, A.M. El-Tahan, M.T. El-Saadony, R.S.A. Faid-Allah, Finite element modeling of the breakage behavior of agricultural biomass pellets under different heights during handling and storage, Saudi. J. Biol. Sci. 29, 1407–1415 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.11.034
J. Soh, S. Sarkar, P. Heng, C. Liew, Pelletization techniques. Encycl. Pharm. Sci. Technol. Fourth Ed. 4, 2515–2524 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1081/e-ept4-120050321
M.E. Mostafa, S. Hu, Y. Wang, S. Su, X. Hu, S.A. Elsayed, J. Xiang, The significance of pelletization operating conditions: an analysis of physical and mechanical characteristics as well as energy consumption of biomass pellets. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 105, 332–348 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.01.053
R. Turner, Chap. 4: Pellet mill die and roll design, Feed Pelleting Reference Guide, In C. Stark, C. Jones, and A. Fahrenholz, Kansas State University, (2014)
S.K. Nielsen, M. Mandø, A.B. Rosenørn, Review of die design and process parameters in the biomass pelleting process. Powder Technol. 364, 971–985 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2019.10.051
J. Chojnacki, P. Kaldunski, S. Nagnajewicz, R. Patyk, Simulation tests of pelleting process in aspect of obtained stresses contact pressure and fatigue strength for granulator flat die. Eng. Mech. (2018). https://doi.org/10.21495/91-8-157
U.P. Onochie, O.O. Ighodaro, C.C. Kwasi-Effah, K.O. Otomi, One dimensional simulation of extrusion channel of biomass pelleting machine. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 22(8), 1213–1217 (2018). https://doi.org/10.4314/jasem.v22i8.11
M.F. Buchely, H.A. Colorado, Failure analysis of a pellet-mill die. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 16, 285–292 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-016-0085-2
H. Bai, B. Zheng, W. Li, X. Tu, Failure analysis of ring die of a feed pellet machine. China Foundry. 17(2), 167–172 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41230-020-9104-8
C.W. Wegst, Key to steel. (Verlag Stahlschlüssel Wegst, Marbach, 2004)
G.E. Dieter, Mechanical metallurgy, 5th edn. (McGraw-Hill, New York, 2000)
ASM Handbook v. 11. Failure Analysis and Prevention, ASM International, Ohio, (2002). https://doi.org/10.31399/asm.hb.v11.9781627081801
J.S. Tumuluru, Effect of process variables on the density and durability of the pellets made from high moisture corn stover. Biosyst. Eng. 119, 44–57 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2013.11.012
C.R. Brooks, A. Choudhury, Failure analysis of engineering materials. (McGraw-Hill, New York, 2002)
ASM Handbook v. 9. Metallography and microstructure, ASM International, Ohio, (2004). https://doi.org/10.31399/asm.hb.v09.9781627081771
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Academic Center for Education, Culture and Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
No competing interest exists to be declared.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kalani, A.R., Ghiasi, H. & Tayefeh, S. Causes of the Fracture of Some Rotary Pelletization Dies: A Case Study. J Fail. Anal. and Preven. 23, 660–670 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-023-01621-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-023-01621-y