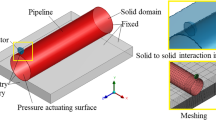
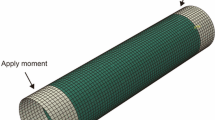
Abstract
Offshore pressurized pipelines are prone to rupture and perforation in several high-velocity impact conditions. Perforation failure combined with local shear plugging occurs when pressurized pipelines are subjected to flat-nosed impactors, such as torpedoes and explosive projectiles. In this paper, the perforation and plugging phenomena were systemically studied to reveal the failure features and impact limits. Qualitative descriptions of the plugging phenomenon were performed to understand the mode characteristics. The typical impact process for crack propagation and plug formation was analyzed. Effects of structural parameters on rupture and perforation limits were investigated to reveal the failure mechanisms. Simplified mechanical models considering strain rate and internal pressure were proposed to obtain the perforation limit and residual velocity. Critical shear strain and ultimate penetration depth were derived for the mechanical models. These results revealed the plugging phenomena and impact limits of pressurized pipelines impacted by flat-nosed impactors, which can provide the theoretical basis of critical impact conditions for protection design and experience reference of ultimate failure extent for damage assessment.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
M. Kristoffersen, F. Casadei, T. Børvik, M. Langseth, Impact against empty and water-filled X65 steel pipes - Experiments and simulations. Int. J. Impact Eng. 71, 73–88 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2014.04.004
Z. Yu, J. Amdahl, A review of structural responses and design of offshore tubular structures subjected to ship impacts. Ocean Eng. 154(15), 177–203 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2018.02.009
K.A. Macdonald, A. Cosham, C.R. Alexander, P. Hopkins, Assessing mechanical damage in offshore pipelines - Two case studies. Eng. Fail. Anal. 14(8), 1667–1679 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2006.11.074
DNV-ST-F101, Submarine Pipeline Systems, Norw. Det Nor. Verit. 2021.
G.Y. Lu, S.Y. Zhang, J.P. Lei, J.L. Yang, Dynamic responses and damages of water-filled pre-pressurized metal tube impacted by mass. Int. J. Impact Eng. 34(10), 1594–1601 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2006.07.006
A. Palmer, A. Neilson, S. Sivadasan, Pipe perforation by medium-velocity impact. Int. J. Impact Eng. 32(7), 1145–1157 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2004.09.010
N. Jones, R.S. Birch, Low-velocity impact of pressurised pipelines. Int. J. Impact Eng. 37(2), 207–219 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2009.05.006
M. Nishida, K. Tanaka, Experimental study of perforation and cracking of water-filled aluminum tubes impacted by steel spheres. Int. J. Impact Eng. 32(12), 2000–2016 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2005.06.010
Y. Zhou, S. Zhang, Rupture and perforation responses of pressurized tubular members subjected to medium-velocity transverse impact loading. Eng. Fail. Anal. 127, e105387 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2021.105387
M. Zeinoddini, H. Arabzadeh, M. Ezzati, G.A.R. Parke, Response of submarine pipelines to impacts from dropped objects: Bed flexibility effects. Int. J. Impact Eng. 62, 129–141 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2013.06.010
F. Jiang, S. Dong, Y. Zhao, Z. Xie, Investigation on the deformation response of submarine pipelines subjected to impact loads by dropped objects. Ocean Eng. 194(15), e106638 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.106638
X. Gao, Y. Shao, L. Xie, D. Yang, Behavior of API 5L X56 submarine pipes under transverse impact. Ocean Eng. 206, e107337 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.107337
A. Palmer, M. Touhey, S. Holder, M. Anderson, Full-scale impact tests on pipelines. Int. J. Impact Eng. 32(8), 1267–1283 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2004.09.003
T. de Vuyst, R. Vignjevic, A. AzorinAlbero, M. Anderson, The effect of the orientation of cubical projectiles on the ballistic limit and failure mode of AA2024-T351 sheets. Int. J. Impact Eng. 104, 21–37 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2017.01.026
T.G. Zhang, W.J. Stronge, Theory for ballistic limit of thin ductile tubes hit by blunt missiles. Int. J. Impact Eng. 18(7–8), 735–752 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0734-743X(96)00033-4
A. Rusinek, J.A. Rodríguez-Martínez, R. Zaera, J.R. Klepaczko, Experimental and numerical study on the perforation process of mild steel sheets subjected to perpendicular impact by hemispherical projectiles. Int. J. Impact Eng. 36(4), 565–587 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2008.09.004
T. Børvik, M. Langseth, O.S. Hopperstad, J.R. Klepaczko, Ballistic penetration of steel plates, 22(9), 855-886 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0734-743X(99)00011-1
C. Palomby, W.J. Stronge, Blunt missile perforation of thin plates and shells by discing. Int. J. Impact Eng. 7(1), 85–100 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1016/0734-743X(88)90014-0
C.A. Calder, W. Goldsmith, Plastic deformation and perforation of thin plates resulting from projectile impact. Int. J. Solids Struct. 7, 863–881 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-7683(71)90096-5
X.W. Chen, Q.M. Li, Perforation of a thick plate by rigid projectiles. Int. J. Impact Eng. 28(7), 743–759 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0734-743X(02)00152-5
S.R. Reid, T.Y. Reddy, Effect of strain hardening on the lateral compression of tubes between rigid plates. Int. J. Solid Struct. 14, 213–225 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-7683(78)90026-4
M. Burley, J.E. Campbell, J. Dean, T.W. Clyne, Johnson-Cook parameter evaluation from ballistic impact data via iterative FEM modelling. Int. J. Impact Eng. 112, 180–192 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2017.10.012
G.R. Johnson, T.J. Holmquist, Evaluation of cylinder-impact test data for constitutive model constants. J. Appl. Phys. 64(8), 3901–3910 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.341344
H. Arabzadeh, M. Zeinoddini, Dynamic response of pressurized submarine pipelines subjected to transverse impact loads. Procedia Eng. 14, 648–655 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2011.07.082
M. Kristoffersen, T. Børvik, I. Westermann, M. Langseth, Impact against X65 steel pipes - An experimental investigation. Int. J. Solids Struct. 50(20–21), 3430–3445 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2013.06.013
D. Liu, W.J. Stronge, Ballistic limit of metal plates struck by blunt deformable missiles: experiments. Int. J. Solids Struct. 37(10), 1403–1423 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7683(98)00322-9
R. Masri, D. Durban, Ballistic limit predictions for perforation of aluminium armour plates by rigid nose-pointed projectiles. Int. J. Impact Eng. 131, 291–303 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2019.05.006
T. Jankowiak, K.M. Alexis Rusinek, R.P. Kpenyigba, Ballistic behavior of steel sheet subjected to impact and perforation. Steel Comp. Struct. 16(6), 595–609 (2014). https://doi.org/10.12989/scs.2014.16.6.595
M.J. Forrestal, T.L. Warren, Perforation equations for conical and ogival nose rigid projectiles into aluminum target plates. Int. J. Impact Eng. 36(2), 220–225 (2009)
H.M. Wen, N. Jones, Low-velocity perforation of punch-impact-loaded metal plates. J. Press. Vessel Technol. - Trans. ASME. 118, 181–187 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2842178
X.W. Chen, Q.M. Li, Perforation of a thick plate by rigid projectiles. Int. J. Impact Eng. 28, 743–759 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0734-743X(02)00152-5
N. Jones, S.-B. Kim, Q.M. Li, Response and failure of ductile circular plates struck by a mass. J. Press. Vessel Technol. 119(3), 332–342 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2842313
Y.L. Bai, W. Johnson, Plugging: Physical understanding and energy absorption. Met. Technol. 9, 182–190 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmps.2017.06.016
H.M. Wen, W.H. Sun, Transition of plugging failure modes for ductile metal plates under impact by flat-nosed projectiles. Mech. Based Des. Struct. Mech. 38, 86–104 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1080/15397730903415892
N. Jones, R.S. Birch, Influence of internal pressure on the impact behavior of steel pipelines. J. Press. Vessel Technol. - Trans. ASME. 118(4), 464–471 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2842215
N. Jones, R.S. Birch, Influence of internal pressure on the impact behavior of steel pipelines. J Pressure Vessel Technol. 118(4), 464–471 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2842215
G.R. Johnson, W.H. Cook, Fracture characteristics of three metals subjected to various strains, strain rates, temperatures and pressures. Eng. Fract. Mech. 21(1), 31–48 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-7944(85)90052-9
Y. Cao, Y. Zhen, M. Song, H. Yi, Determination of Johnson-Cook parameters and evaluation of Charpy impact test performance for X80 pipeline steel. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 179, e105627 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-7944(85)90052-9
O. Obeid, G. Alfano, H. Bahai, H. Jouhara, Mechanical response of a lined pipe under dynamic impact. Eng. Fail. Anal. 88, 35–53 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2018.02.013
M.E. Backman, W. Goldsmith, The mechanics of penetration of projectiles into targets. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 16, 1–99 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2018.02.013
Y. Zhou, S. Zhang, Perforation analysis and limit prediction of submarine pipelines subjected to extreme impact loadings. Ocean Eng. 246, e110651 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.110651
T. Fras, C.C. Roth, D. Mohr, Dynamic perforation of ultra-hard high-strength armor steel: Impact experiments and modeling. Int. J. Impact Eng. 131, 256–271 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2019.05.008
W.Q. Shen, N.O. Rieve, B. Baharun, A study on the failure of circular plates struck by masses. Part 1: experimental results. Int. J. Impact Eng. 27, 399–412 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0734-743X(01)00146-4
Z.Y. Wang, Y. Zhao, G.W. Ma, A numerical study on the high-velocity impact behavior of pressure pipes. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A. 17(6), 443–453 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A1500112
Q.M. Li, N. Jones, Shear and adiabatic shear failures in an impulsively loaded fully clamped beam. Int. J. Impact Eng. 22(6), 589–607 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A1500112
D. Rittel, L.H. Zhang, S. Osovski, The dependence of the Taylor-Quinney coefficient on the dynamic loading mode. J. Mech. Phys. Solids. 107, 96–114 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmps.2017.06.016
X.W. Chen, Q.M. Li, S.C. Fan, Initiation of adiabatic shear failure in a clamped circular plate struck by a blunt projectile. Int. J. Impact Eng. 31(7), 877–893 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2004.04.011
X. Teng, T. Wierzbicki, Dynamic shear plugging of beams and plates with an advancing crack. Int. J. Impact Eng. 31(6), 667–698 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2004.03.013
T. Børvik, O.S. Hopperstad, M. Langseth, H. Jouhara, Effect of target thickness in blunt projectile penetration of Weldox 460 E steel plates. Int. J. Impact Eng. 28(4), 413–464 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0734-743X(02)00072-6
Y. Bai, T.P. Preben, Elastic-plastic behaviour of offshore steel structures under impact loads. Int. J. Impact Eng. 13(1), 99–115 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1016/0734-743X(93)90110-S
T. de Sousa Antonino, P.B. Guimarães, R. de AraújoAlécio, Y.P. Yadava, Measurements of the Thermophysical Properties of the API 5L X80. Mater. Sci. Appl. 5, 617–627 (2014). https://doi.org/10.4236/msa.2014.58064
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. B220203031).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors do not have any possible conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Zhang, S. Plugging Analysis and Shear Model of Pressurized Pipeline Struck by Destructive Flat-Nosed Impactors. J Fail. Anal. and Preven. 23, 711–727 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-023-01600-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-023-01600-3