Abstract
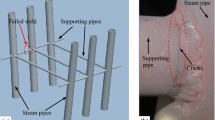
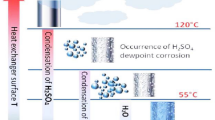
The present paper describes investigations of three failure cases of stainless steel 316/316L pipes handling moist H2S gas in a heavy water plant. The failure investigation included chemical composition determination, metallographic examination using an optical microscope, and a scanning electron microscopy equipped with energy dispersive spectroscopy and hardness testing. The first failure was related to leakage of H2S at the pipe-to-elbow weld joint. The failure was associated with weld misalignment that led to pitting and stress corrosion cracking in the weld heat-affected zone of the elbow. The other two failures also led to leakage of H2S from the filet welds of pipes. Filet welds in both these cases had insufficient weld penetration and fusion. These failures were caused by fatigue cracking that was initiated from the toe and root of the filet welds where the stress concentration is maximum. All the three cases of failures investigated were primarily related to poor workmanship during welding.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.L.N. Rao, Technology breakthrough by Heavy Water Board in material support to Indian nuclear power programme. Energy Procedia. 7, 177–185 (2011)
IS 15200:2002: Hydrogen Sulfide - Code of Safety, 2002, by Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS).
R.D. Kane, M.S. Cayard, Roles of H2S in the Behavior of Engineering Alloys: A Review of Literature and Experience, Paper no. 274, Corrosion 98, California, March 22 – 27, 1998.
A.J. Sedriks, Corrosion of Stainless Steels, The Corrosion Monograph Series, 1st edn. (Wiley, NJ, 1979), p. 9–11
ASM Handbook, Corrosion: Environments and Industries, Vol. 13C, first ed., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 2006, pp. 967-997.
R.J. Twigg, P. Eng, Corrosion of Steels in Sour Gas Environments, Research report no. INFO-0118, Atomic Energy Control Board, March 1984.
D.A. Jones, Principles and Prevention of Corrosion, second ed., Prentice Hall, NJ, 1996, pp. 249-254 309-314, 334-341.
W.T. Becker, R.J. Shipley, Failures related to welding, in: ASM Handbook, Failure Analysis and Prevention, Vol. 11, ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 2002, pp. 156–191.
ASTM A312/A312M-19, Standard Specification for Seamless, Welded, and Heavily Cold Worked Austenitic Stainless-Steel Pipes, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, 2019.
ASTM A403/A403M-20, Standard Specification for Wrought Austenitic Stainless Steel Piping Fittings, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, 2020.
A240/A240M-20a, Standard Specification for Chromium and Chromium-Nickel Stainless Steel Plate, Sheet, and Strip for Pressure Vessels and for General Applications. West Conshohocken, PA; ASTM International, 2020.
ASTM A351/A351M-00, Standard Specification for Castings, Austenitic, Austenitic-Ferritic (Duplex), for Pressure-Containing Parts, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, 2000.
W. Fricke, O. Doerk, Simplified approach to fatigue strength assessment of fillet-welded attachment ends. Int. J. Fatigue. 28, 141–150 (2006)
S. Xing, P. Dong, A. Threstha, Analysis of fatigue failure mode transition in load-carrying fillet-welded connections. Mar. Struct. 46, 102–126 (2016)
D.J. Thomas, Analyzing the failure of welded steel components in construction systems. J. Fail. Anal. Preven. 18, 304–314 (2018)
S.T. Adair, P.A. Attwood, In-service stress corrosion cracking of AISI 316L stainless steel in an H2S environment. Corros. Eng. Sci. Tech. 49, 396–400 (2014)
V. Singh, Performance of austenitic stainless steels in wet sour gas– Part 1. Mater. Perform. 43–8, 52–56 (2004)
V. Singh, Performance of austenitic stainless steels in wet sour gas – Part 2. Mater. Perform. 43–9, 46–50 (2004)
J. Hesketh, E.J.F. Dickinson, M.L. Martin, G. Hinds, A. Turnbull, Influence of H2S on the pitting corrosion of 316L stainless steel in oilfield brine. Corros. Sci. 182, 109265 (2021)
K. Chandra, A.P. Singh, V. Kain, N. Kumar, Sulfide stress cracking of a valve stem of duplex stainless steel. Eng. Fail. Anal. 94, 41–46 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chandra, K., Kain, V. & Kumar, N. Failure Cases of Stainless Steel 316/316L Pipe Welds in Moist Hydrogen Sulfide Environment. J Fail. Anal. and Preven. 22, 478–490 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-022-01354-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-022-01354-4