Abstract
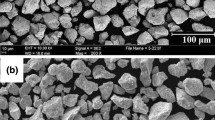
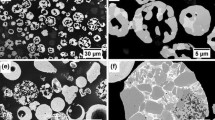
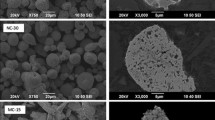
In this paper, high-velocity oxy-fuel sprayed coatings from experimental Cr3C2-Ni powder produced by mechanically activated thermal synthesis and disintegrator milling are compared with coatings from commercial Cr3C2-NiCr powder under room- and elevated-temperature abrasive-erosive wear (AEW) conditions. In a room-temperature AEW test, the coating made from the experimental powder had wear rates that were 1.1-5.3 times higher than the coating from the commercial powder; this difference was the lowest at the highest impact velocity (80 m s−1). Under AEW tests at elevated temperature (300 and 550 °C), the coating made from the experimental powder exhibited wear rates that were 1.2-2.8 times higher in comparison with that made from the commercial powder, but this difference was smaller under an oblique impact angle (30°) and higher temperature conditions. The reasons for the lower resistance against AEW of the coating made from the experimental powder were found to be its lower ability to resist plastic indentation and deformation as well as lower indentation fracture toughness at room temperature, weaker bonding between the matrix and reinforcement and probably lower mechanical properties as well as unfavourable residual stresses at elevated temperatures.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.-F. Wang and Z.-G. Yang, Finite Element Model of Erosive Wear on Ductile and Brittle Materials, Wear, 2008, 265(5-6), p 871-878
K.G. Budinksi, Solid Particle Erosion Testing with a Gas-Jet Apparatus, in Proc. STLE Annu. Meet. Exhib., May 5-9, 2013 (Detroit, the USA), p 10-12
J.R. Davis, Ed., Applications for Thermal Spray Processing, Handbook of Thermal Spray Technology, 1st ed., ASM International, Materials Park, 2004, p 171-174
J. Zhang, Z. Han, W. Yin, H. Wang, C. Ge, and J. Jiang, Numerical Experiment of the Solid Particle Erosion of Bionic Configuration Blade of Centrifugal Fan, Acta Metall. Sin. Engl. Lett., 2013, 26(1), p 16-24
M.M. Trabulsi, Black Powder in Sales-Gas Transmission Pipelines, J. Pipeline Eng., 2007, 6, p 245-250
C.B. Solnordal, C.Y. Wong, and J. Boulandger, An Experimental and Numerical Analysis of Erosion Caused by Sand Pneumatically Conveyed Through a Standard Pipe Elbow, Wear, 2015, 336(337), p 43-57
P.N. Walsh, J.M. Quets, and R.C. Tucker, Coatings for The Protection of Turbine Blades from Erosion, J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power, 1995, 117(1), p 152-155
K. Brun, M. Nored, and R. Kurz, Particle Transport Analysis of Sand Ingestion in Gas Turbine Engines, J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power, 2012, 134(1), p 012402
G. Stachowiak and A.W. Batchelor, Engineering Tribology, Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2013, p 525-576
E. Bousser, L. Martinu, and J.E. Klemberg-Sapieha, Solid Particle Erosion Mechanisms of Hard Protective Coatings, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2013, 235, p 383-393
G. Wang, X. Jia, J. Li, F. Li, Z. Liu, and B. Gang, Current State and Development of the Research on Solid Particle Erosion and Repair of Turbomachine Blades, Re-engineering Manufacturing for Sustainability, A.Y.C. Nee, B. Song, and S.-K. Ong, Eds., Springer, Singapore, 2013, p 633-638
D. Wang, Z. Tian, L. Shen, Z. Liu, and Y. Huang, Effects of Laser Remelting on Microstructure and Solid Particle Erosion Characteristics of ZrO2-7 wt.% Y2O3 Thermal Barrier Coating Prepared by Plasma Spraying, Ceram. Int., 2014, 40(6), p 8791-8799
E. Bousser, L. Martinu, and J.E. Klemberg-Sapieha, Solid Particle Erosion Mechanisms of Protective Coatings for Aerospace Applications, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2014, 257, p 165-181
I. Finnie, Erosion of Surfaces by Solid Particles, Wear, 1960, 3, p 87-103
D.A. Woodford, R.T. Wood, Effect of particle size and hardness on materials erosion in fluidized beds, in Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Erosion by Liquid and Solid Impact, J.E. Field and N.S. Corney, Eds., Sept 5-8, 1983 (Cambridge, UK), Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge, p 56.1-56.9
M.M. Stack and D. Peña, Particle Size Effects on the Elevated Temperature Erosion Behaviour of Ni-Cr/WC MMC-Based Coatings, Surf. Coat. Technol., 1999, 113, p 5-12
M. Antonov, R. Veinthal, E. Huttunen-Saarivirta, I. Hussainova, A. Vallikivi, M. Lelis, and J. Priss, Effect of Oxidation on Erosive Wear Behaviour of Boiler Steels, Tribol. Int., 2013, 68, p 35-44
S. Matthews, B. James, and M. Hyland, High Temperature Erosion-Oxidation of Cr3C2-NiCr Thermal Spray Coatings under Simulated Turbine Conditions, Corros. Sci., 2013, 70, p 203-211
J.B. Cheng, X.B. Liang, Y.X. Chen, Z.H. Wang, and B.S. Xu, High-Temperature Erosion Resistance of FeBSiNB Amorphous Coatings Deposited by Arc Spraying for Boiler Applications, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2013, 22(5), p 820-827
H. Arabnejad, A. Mansouri, S.A. Shirazi, and B.S. McLauri, Development of Mechanistic Erosion Equation for Solid Particles, Wear, 2015, 332-333, p 1044-1050
K. Szymański, A. Hernas, G. Moskal, and H. Myalska, Thermally Sprayed Coatings Resistant to Erosion and Corrosion for Power Plant Boilers—A Review, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2015, 268, p 153-164
A.S. Praveen, J. Sarangan, S. Suresh, and J. Siva Subramanian, Erosion Wear Behaviour of Plasma Sprayed NiCrSiB/Al2O3 Composite Coating, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 2015, 52, p 209-218
D.A.J. Ramm, T.W. Clyne, A.J. Sturgeon, and S. Dunkerton, Correlations between Spraying Conditions and Microstructure for Alumina Coatings Produced by HVOF and VPS, Thermal spray industrial applications, C.C. Berndt and S. Sampath, Ed., ASM International, Materials Park, 1994, p 239-243
V. Matikainen, K. Niemi, H. Koivuluoto, and P. Vuoristo, Abrasion, Erosion and Cavitation Erosion Wear Properties of Thermally Sprayed Alumina Based Coatings, Coatings, 2014, 4(1), p 18-36
L.-X. Cai, J.-R. Mao, S.-S. Wang, J. Di, and Z.-P. Feng, Experimental Investigation on Erosion Resistance of Iron Boride Coatings for Steam Turbines at High Temperatures, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J, 2015, 229(5), p 636-645
S.S. Chatha, H.S. Sidhu, and B.S. Sidhu, High-Temperature Behaviour of a NiCr-Coated T91 Boiler Steel in the Platen Superheater of Coal-Fired Boiler, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2013, 22(5), p 838-847
V. Pokhmurski, M. Student, V. Gvozdeckii, T. Stypnutskyy, O. Student, B. Wielage, and H. Pokhmurska, Arc-Sprayed Iron-Based Coatings for Erosion-Corrosion Protection of Boiler Tubes at Elevated Temperatures, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2013, 22(5), p 808-819
H.J. Kim, Y.G. Kweoun, and R.W. Chang, Wear and Erosion Behaviour of Plasma-Sprayed WC-Co Coatings, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 1994, 3(2), p 169-178
S. Matthews and L.-M. Berger, Long-Term Compositional/Microstructural Development of Cr3C2-NiCr Coatings at 500 °C, 700 °C and 900 °C, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 2016, 59, p 1-18
S. Matthews, B. James, and M. Hyland, The Role of Microstructure in the Mechanism of High Velocity Erosion of Cr3C2-NiCr Thermal Spray Coatings: Part 1 - As-Sprayed Coatings, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2009, 203(8), p 1086-1093
L. Thakur and N. Arora, Solid Particle Erosion Behaviour of WC-CoCr Nanostructured Coating, Tribol. Trans., 2013, 56(5), p 781-788
M. Manjunatha, R.S. Kulkarni, and M. Krishna, Investigation of HVOF Thermal Sprayed Cr3C2-NiCr Cermet Carbide Coatings on Erosive Performance of AISI 316 Molybdenum Steel, Proced. Mater. Sci., 2014, 5, p 622-629
A. Surzhenkov, P. Kulu, R. Tarbe, V. Mikli, H. Sarjas, and J. Latokartano, Wear Resistance of Laser Remelted Thermally Sprayed Coatings, Est. J. Eng., 2009, 15(4), p 318-328
A. Surženkov, D. Goljandin, R. Traksmaa, M. Viljus, K. Talviste, A. Aruniit, J. Latokartano, and P. Kulu, High-Temperature Erosion Wear of Cermet Particles Reinforced Self-Fluxing Alloy Matrix HVOF Sprayed Coatings, Mater. Sci. (Medžiagotyra), 2015, 21(3), p 386-390
A. Surzhenkov, M. Antonov, D. Goljandin, P. Kulu, M. Viljus, R. Traksmaa, and A. Mere, High-Temperature Erosion of Fe-Based Coatings Reinforced with Cermet Particles, Surf. Eng., 2016, 32(8), p 624-630
H. Sarjas, P. Kulu, K. Juhani, M. Viljus, V. Matikainen, and P. Vuoristo, Wear Resistance of HVOF Sprayed Coatings from Mechanically Activated Thermally Synthesized Cr3C2-Ni Spray Powder, Proc. Est. Acad. Sci., 2016, 65(2), p 101-106
I. Hussainova, J. Kübarsepp, and J. Pirso, Mechanical Properties and Features of Erosion of Cermets, Wear, 2001, 250(1-2), p 818-825
H. Sarjas, P. Kulu, K. Juhani, and P. Vuoristo, Novel WC-Co Spray Powders and HVOF Sprayed Coatings on Their Basis, in Proceedings of 28th International Conference on Surface Modification Technologies, T.S. Sudarsan, P. Vuoristo, and H. Koivuluoto, Eds., June 16-18, 2014 (Tampere, Finland), Valardoc, 2014, p 35-42
R. Ren, Z. Yang, L.L. Shaw, A Novel Process for Synthesizing Nanostructured Carbides: Mechanically Activated Synthesis, in Ceramic Engineering and Science Proceedings, 19(4), D.E. Bray, Ed., Jan. 20-24, 1998 (Cocoa Beach, FL, the USA), John Wiley & Sons, 1998, p 461-468
J. Pirso, M. Viljus, S. Letunovitš, and K. Juhani, Reactive Carburizing Sintering—A Novel Production Method for High Quality Chromium Carbide-Nickel Cermets, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 2006, 24(3), p 263-270
Z.-G. Ban and L.L. Shaw, Characterization of Thermal Sprayed Nanostructured WC-Co Coatings Derived from Nanocrystalline WC-18 wt.% Co powders, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2003, 12(1), p 112-119
M. Jõeleht, J. Pirso, K. Juhani, M. Viljus, and R. Traksmaa, The Formation of Reactive Sintered (Ti, Mo)C-Ni Cermet from Nanocrystalline Powders, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 2014, 43, p 284-290
P. Peetsalu, S. Zimakov, J. Pirso, V. Mikli, R. Tarbe, and P. Kulu, Technology and Characterization of Composite Thermal Spray Powders, Mater. Sci. (Medžiagotyra), 2005, 11(4), p 385-389
D.K. Shetty and I.G. Wright, Indentation Fracture of WC-Co Cermets, J. Mater. Sci., 1985, 20, p 1873-1883
M. Antonov, I. Hussainova, J. Pirso, and O. Volobueva, Assessment of Mechanically Mixed Layer Developed during High Temperature Erosion of Cermets, Wear, 2007, 263(7-12), p 878-886
M. Antonov, J. Pirso, A. Vallikivi, D. Goljandin, and I. Hussainova, The Effect of Fine Erodent Retained on the Surface During Erosion of Metals, Ceramics, Plastic, Rubber and Hardmetal, Wear, 2016, 354-355, p 53-68
D.L. Joslin and W.C. Oliver, A New Method for Analysing Data from Continuous Depth-Sensing Microindentation Tests, J. Mater. Res., 1990, 5(1), p 123-126
T.Y. Tsui, G.M. Pharr, W.C. Oliver, C.S. Bhatia, R.L. White, S. Anders, A. Anders, and I.G. Brown, Nanoindentation and Nanoscratching of Hard Carbon Coatings for Magnetic Discs, Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol 383, D.B. Bogy, M.S. Donley, M.D. Drory, and J.E. Field, Eds., 1995, p 447-452
I. Hussainova, J. Jasiuk, M. Sardela, and M. Antonov, Micromechanical Properties and Erosive Wear Performance of Chromium Carbide Based Cermets, Wear, 2009, 267(1-4), p 152-159
R.J.K. Wood, J.C. Walker, T.J. Harvey, S. Wang, and S.S. Rajahram, Influence of Microstructure on the Erosion and Erosion-Corrosion Characteristics of 316 Stainless Steel, Wear, 2013, 306(1-2), p 254-262
I. Kleis and P. Kulu, Solid Particle Erosion. Occurrence, Prediction and Control, Springer, London, 2008, p 134-156
A.V. Levi, Solid Particle Erosion and Erosion-Corrosion of Materials, ASM International, Materials Park, 1995, p 35-60
S. Kuroda and T.W. Clyne, The Quenching Stress in Thermally Sprayed Coatings, Thin Solid Films, 1991, 200(1), p 49-66
I. Hussainova, Effect of Microstructure on the Erosive Wear of Titanium Carbide-Based Cermets, Wear, 2003, 255(1-6), p 121-128
P. Kulu, I. Hussainova, and R. Veinthal, Solid Particle Erosion of Thermal Spray Coatings, Wear, 2005, 258(1-4), p 488-496
I. Hussainova, On Micromechanical Problems of Erosive Wear of Particle Reinforced Composites, Proc. Estonian Acad. Sci. Eng., 2005, 11(1), p 46-58
M.M. Stack and F.H. Stott, An Approach to Modelling Erosion-Corrosion of Alloys Using Erosion-Corrosion Maps, Corros. Sci., 1993, 35(5-8), p 1027-1034
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dmitri Goljandin, Ph.D., for his help with the manufacture of the experimental Cr3C2-Ni powder and Deniss Tšernobajev, M.Sc., for his help with the wear tests. This work was supported by the Institutional Research Funding IUT19-29 “Multi-Scale Structured Ceramic-Based Composites for Extreme Applications” of the Estonian Ministry of Education and Research and by the base funding provided to R&D institutions by the Estonian Ministry of Education and Research, Project Number B56, “Innovative Polycrystalline Diamond (PDC) Drag Bit for Soft Ground Tunnel Boring Machines”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarjas, H., Surzhenkov, A., Juhani, K. et al. Abrasive-Erosive Wear of Thermally Sprayed Coatings from Experimental and Commercial Cr3C2-Based Powders. J Therm Spray Tech 26, 2020–2029 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-017-0638-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-017-0638-2