Abstract
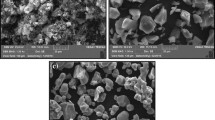
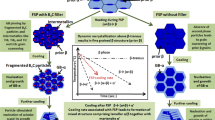
This article discusses the structural evolution, mechanical characteristics and tribological behaviors of CuAl9Mn2 + W surface composites containing 0, 5, 10 and 15 vol.% W prepared using both 1-pass and 4-pass friction stir processing. Homogeneous distribution of W-particles in the bronze matrix has been achieved using the 4-pass FSP. According to XRD, the following phases have been formed in the FSPed bronze matrix: α-Cu solid solution, α + β′-Cu3Al eutectoid, and γ-Al4Cu9 laths. Adding tungsten in FSP resulted in enriching the samples with γ-Al4Cu9. Formation of γ-Al4Cu9 occurred according to the well-known equilibrium reaction β → α + γ and may be related to some physical characteristic of the composite that changed with the addition of tungsten. In our opinion, this could be the reduced heat conductivity that made some β-Cu3Al grains to decompose into α-Cu and γ-Al4Cu9 ones instead of the β → β′ transformation. The mean sizes of the α-solid solution matrix grains after 1-pass and 4-pass FSP were at the level of 4.48-7.54 μm and 3.47-5.43 μm, respectively. The minimum grain size 3.47 μm was obtained after 4-pass FSP on CuAl9Mn2 + 10%W samples. The tensile strength of the composites, however, decreased as compared to that of the as-received and FSPed bronze, while microhardness was almost the same number for all samples. The maximum wear resistance was achieved on the 4-pass FSPed sample containing 5 vol.% W.


































Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article. All data necessary for the replication of results are provided within the paper.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
S. Wan, X. Cui, Q. Jin, J. Ma, X. Wen, W. Su, X. Zhang, G. Jin and H. Tian, Microstructure and Properties of Cold Sprayed Aluminum Bronze Coating on MBLS10A-200 Magnesium-Lithium Alloy, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2020, 281, p 125832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2022.125832
T. Lu, C. Chen, P. Li, Ch. Zhang, W. Han, Z. Ya, Ch. Suryanarayana and Zh. Guo, Enhanced Mechanical and Electrical Properties of In Situ Synthesized Nano-Tungsten Dispersion-Strengthened Copper Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2021, 799, p 140161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.140161
M.V. Lungu, D. Pătroi, V. Marinescu, S. Mitrea, I. Ion, M. Marin and P. Godeanu, Tungsten–Copper Composites for Arcing Contact Applications in High Voltage Circuit Breakers, Mater. Sci. Res. India, 2020, 17(3), p 214–229. https://doi.org/10.13005/msri/170304
L.L. Dong, M. Ahangarkani, W.G. Chen and Y.S. Zhang, Recent Progress in Development of Tungsten-Copper Composites: Fabrication, Modification and Applications, Intl. J. Refract. Hard Met., 2018, 75, p 30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2018.03.014
Q. Zhang, Sh. Liang and L. Zhuo, Fabrication and Properties of the W-30wt.%Cu Gradient Composite with W@WC Core-Shell Structure, J. Alloys Compd., 2017, 708, p 796–803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.03.064
Y. Huang, X. Zhou, N. Hua, W. Que and W. Chen, High Temperature Friction and Wear Behavior of Tungsten–Copper Alloys, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 2018, 77, p 105–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2018.08.001
F. Ren, W. Zhu, K. Chu and C. Zhao, Tribological and Corrosion Behaviors of Bulk Cu-W Nanocomposites Fabricated by Mechanical Alloying and Warm Pressing, J. Alloy. Compd., 2016, 676, p 164–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.03.141
W. Chen, P. Feng, L. Dong, M. Ahangarkani, Sh. Ren and Y. Fud, The Process of Surface Carburization and High Temperature Wear Behavior of Infiltrated W-Cu Composites, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2018, 353, p 300–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2018.08.088
M. Hashempour, H. Razavizadeh and H. Rezaie, Investigation on Wear Mechanism of Thermochemically Fabricated W-Cu Composites, Wear, 2010, 269(5–6), p 405–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2010.04.026
A. Pervikov, A. Filippov, Yu. Mironov, M. Kalashnikov, M. Krinitcyn, D. Eskin, M. Lerner and S. Tarasov, Microstructure and Properties of a Nanostructured W-31 wt.% Cu Composite Produced by Magnetic Pulse Compaction of Bimetallic Nanoparticles, Intl. J. Refract. Hard Met., 2022, 103, p 105735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2021.105735
H. Yo, X. Zhou, N. Hua, W. Que and W. Chen, High Temperature Friction and WEAR Behavior of Tungsten–Copper Alloys, Intl. J. Refract. Hard Met., 2018, 77, p 105–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2018.08.001
C.L. Wang, Y. Gao and G.Y. Zhang, Microstructure and wear Resistance of Cu-W Alloy Contact Material Prepared by Laser Shock Processing, T. Mater. Heat Treat., 2014, 35, p 153–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.03.141
F.M. Wang, J.P. Xie, Y. Li and A.Q. Wang, Dry-Sliding Tribological Characteristics of W80C20 Composite under of Magnetic Field, Chin. Sur. Eng., 2014, 27, p 76–79.
Yu. Li, Ch. Hou, L. Cao, Ch. Liu, Sh. Liang, F. Tang, X. Song and Z. Nie, Excellent Wear Resistance of Multicomponent Nanocrystalline W-Cu Based Composite, J. Alloys Compd., 2021, 861, p 158627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.158627
M. Jahangiri, M. Hashempour, H. Razavizadeh and H.R. Rezaie, A New Method to Investigate the Sliding Wear Behaviour of Materials based on Energy Dissipation: W–25 wt.%Cu Composite, Wear, 2012, 274–275, p 175–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2011.08.023
X. Wang, X. Zhang, L. Zhao, Ch. Zhao, H. Zhang, Du. Ye, W. Zhang, G. Ya and P. Cao, Tungsten/copper Composite Sheets Prepared by a Novel Encapsulation Rolling TECHNIQUE, J. Alloys Compd., 2021, 884, p 161051. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.161051
Ch. Hou, X. Song, F. Tang, L. Yurong, L. Cao, J. Wang and Z. Nie, W-Cu Composites with Submicron- and Nanostructures: Progress and Challenges, NPG Asia Mater., 2019, 11(1), p 74. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41427-019-0179-x
K.S. Mohammed, A. Rahmat and A. Aziz, Self-Compacting High Density Tungsten–Bronze Composites, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2013, 213, p 1088–1094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2013.02.006
M. Pezeshkian and I. Ebrahimzadeh, Investigating the Role of Metal Reinforcement Particles in Producing Cu/Ni/W Metal Matrix Composites via Friction Stir Processing: Microstructure, Microhardness, and Wear at High Temperature, Met. Mater. Int., 2023 https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-023-01488-6
V. Sharma, U. Prakash and B.V. Manoj Kumar, Surface Composites by Friction Stir Processing: A Review, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2015, 224, p 117–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2015.04.019
A. Zykova, A. Chumaevskii, A. Gusarova, D. Gurianov, T. Kalashnikova, N. Savchenko, E. Kolubaev and S. Tarasov, Evolution of Microstructure in friction Stir Processed Dissimilar CuZn37/AA5056 Stir Zone, Materials, 2021, 14(18), p 5208. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14185208
A.P. Zykova, S.Y. Tarasov, A.V. Chumaevskiy and E.A. Kolubaev, A Review of Friction Stir Processing of Structural Metallic Materials: Process, Properties, and Methods, Met., 2020, 10(6), p 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10060772
A. Zykova, A. Vorontsov, A. Chumaevskii, D. Gurianov, A. Gusarova, E. Kolubaev and S. Tarasov, Structural Evolution of Contact Parts of the Friction Stir Processing Heat-Resistant Nickel Alloy Tool Used for Multi-Pass Processing of Ti6Al4V/(Cu+Al) System, Wear, 2022, 488–489, p 204138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2021.204138
Y. Ahuja, R. Ibrahim, A. Paradowska and D. Riley, Friction Stir Forming to Fabricate Copper-Tungsten Composite, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2015, 217, p 222–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2014.11.024
M. Sabbaghian, M. Shamanian, H.R. Akramifard and M. Esmailzadeh, Effect of Friction Stir Processing on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Cu-TiC Composite, Ceram. In., 2014, 40(8), p 12969–12976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.04.158
M. Barmouz and M.K.B. Givi, Fabrication of In Situ Cu/SiC Composites using Multi-Pass Friction Stir Processing: Evaluation of Microstructural, Porosity, Mechanical and Electrical Behavior, Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf., 2011, 42, p 1445–1453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2011.06.010
V. Rubtsov, A. Chumaevskii, A. Gusarova, E. Knyazhev, D. Gurianov, A. Zykova, T. Kalashnikova, A. Cheremnov, N. Savchenko, A. Vorontsov, V. Utyaganova, E. Kolubaev and S. Tarasov, Macro- and Microstructure of In Situ Composites Prepared by Friction Stir Processing of AA5056 Admixed with Copper Powders, Mater., 2023, 16, p 1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16031070
Y.P. Mironov, L.L. Meisner and A.I. Lotkov, The Structure of Titanium Nickelide Surface Layers Formed by Pulsed Electron-Beam Melting, Tech. Phys., 2008, 53, p 934–942. https://doi.org/10.1134/s1063784208070189/metrics
R. Besson, M.-N. Avettand-Fenoel, L. Thuinet, J. Kwon, A. Addad, P. Roussel and A. Legris, Mechanisms of Formation of Al4Cu9 during Mechanical Alloying: An Experimental Study, Acta Mater. Mater., 2015, 87, p 216–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2014.12.050
Q. Zhang, W. Gong and W. Liu, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Dissimilar Al−Cu Joints by Friction Stir Welding, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2015, 25, p 1779–1786. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63783-9
A. Zykova, A. Panfilov, A. Chumaevskii, A. Vorontsov, D. Gurianov, N. Savchenko, E. Kolubaev and S. Tarasov, Decomposition of β′-Martensite in Annealing the Additively Manufactured Aluminum Bronze, Mater. Lett., 2023, 338, p 134064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2023.134064
A. Zykova, A. Nikolaeva, A. Panfilov, A. Vorontsov, A. Nikonenko, A. Dobrovolsky, A. Chumaevskii, D. Gurianov, A. Filippov, N. Semenchuk, N. Savchenko, E. Kolubaev and S. Tarasov, Microstructures and Phases in Electron Beam Additively Manufactured Ti-Al-Mo-Zr-V/CuAl9Mn2, Alloy Mater., 2023, 16, p 4279. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16124279
J. Schell, P. Heilmann and D.A. Rigney, Friction and Wear of Cu–Ni Alloys, Wear, 1982, 75, p 205–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(82)90149-1
B. Venkataraman and G. Sundararajan, The Sliding Wear Behaviour of Al–SiC Particulate Composites. II. The Characterization of Subsurface Deformation and Correlation with Wear Behavior, Acta Mater. Mater., 1996, 44, p 461–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/1359-6454(95)00218-9
W. Czupryk, Frictional Transfer of Iron in Oxidative Wear Conditions during Lubricated Sliding, Wear, 2000, 237, p 288–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1648(99)00360-9
J.B. Singh, J.G. Wen and P. Bellon, Nanoscale Characterization of the Transfer Layer Formed During Dry Sliding of Cu–15wt.% Ni–8wt.% Sn Bronze Alloy, Acta Mater. Mater., 2008, 56(13), p 3053–3064. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(82)90149-1
W. Cai and P. Bellon, Subsurface Microstructure Evolution and Deformation Mechanism of Ag–Cu Eutectic Alloy After Dry Sliding Wear, Wear, 2013, 303(1), p 602–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2013.04.006
P.K. Wong, C.T. Kwok, H.C. Ma and D. Guo, Laser Fabrication of W-Reinforced Cu Layers II. Electrical Wear Behavior in Air and Synthetic Acid Rain, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2016, 177, p 118–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2016.04.00
S. Tarasov, V. Rubtsov and A. Kolubaev, Subsurface Shear Instability and Nanostructuring of Metals in Sliding, Wear, 2010, 268(1–2), p 59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2009.06.027
K.N. Kalashnikov, SYu. Tarasov, A.V. Chumaevskii, S.V. Fortuna, A.A. Eliseev and A.N. Ivanov, Towards Aging in a Multipass Friction Stir–Processed AA2024, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2019, 103, p 2121–2132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03631-3
Y. Li, H. Fu, T. Ma, K. Wang, X. Yang and J. Lin, Microstructure and Wear Resistance of AlCoCrFeNi-WC/TiC Composite Coating by Laser Cladding, Mater Charact, 2022, 194, p 112479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2022.112479
Y.D. Kim, N.L. Oh, S.-T. Oh and I.-H. Moon, Thermal Conductivity of W-Cu Composites at Various Temperatures, Mater. Lett., 2001, 51, p 420–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-577X(01)00330-5
M. Jamil, N. He, W. Zhao, A.M. Khan, H. Xiang, M.K. Gupta and A. Iqbal, A Novel Low-Pressure Hybrid Dry Ice Blasting System For Improving the Tribological and Machining Characteristics of AISI-52100 Tool STEEL, J. Manuf. Process., 2022, 80, p 152–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JMAPRO.2022.05.056
B. Denkena, A. Krödel and A. Heckemeyer, Numerical and Experimental Analysis of Thermal and Mechanical Tool Load When Turning AISI 52100 with Ground Cutting Edge Microgeometries, CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol., 2021, 35, p 494–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CIRPJ.2021.08.006
Acknowledgments
The investigations have been carried out using the equipment of Share Use Centre “Nanotech” of the ISPMS SB RAS.
Funding
This research was funded by Government research assignment for ISPMS SB RAS, project FWRW-2024-0001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.Z., N.S., A.C. and S.T. were involved in the conceptualization; A.Z., N.S., and A.C. contributed to the methodology; A.V. and N.S. contributed to the software; A.C., A.Z., and N.S. assisted in the validation; A.Z., N.S., A.C. and S.T. performed the formal analysis; A.Z., E.K., N. S., D.G., A.V., V.U., N.S. and A.C. contributed to the investigation; A. Chum. and E.K. contributed to the resources; A.C., A.Z., N.S., and A.C. curated the data; A.C., A.Z., N.S., and S.T. contributed to writing—original draft preparation; A.Z., N.S., and S.T. assisted in writing—review and editing; A.Z., E.K., N. S., D.G., A.V., V.U., N. S. and A.C. contributed to the visualization; A.Z. and S.T. contributed to the supervision; A.Z. and A.C. were involved in the project administration; A.C. acquired the funding. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participation
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cheremnov, A., Zykova, A., Savchenko, N. et al. Surface CuAl9Mn2/W Composites Prepared by Multipass Friction Stir Processing: Microstructures, Phases, and Mechanical and Tribological Properties. J. of Materi Eng and Perform (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-024-09388-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-024-09388-5