Abstract
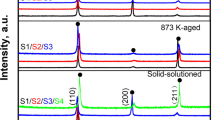
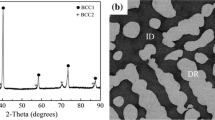
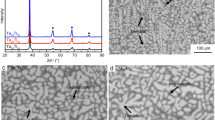
Alloying is a crucial and effective strategy for developing high-entropy alloys (HEAs) with enhanced mechanical properties. In this study, a series of (Ti1.5ZrNbMoV)100 − xOx refractory HEAs (x = 0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, and 3.0) were prepared using a vacuum arc melting method. Within the given range of O content, the single body-centered cubic (BCC) solid solution structure of the base alloy remained unchanged. However, the morphology of the dendrites displayed noticeable alterations with increase in oxygen content. The study revealed a positive correlation between the oxygen content and the hardness and yield strength of the alloys. This trend was attributed to the presence of oxygen atoms in the solid solution of the BCC matrix, which contributed to the alloy’s enhanced strength. The alloy containing 0.5 at.% oxygen exhibited the highest ductility among all the studied compositions. The improved ductility could be attributed to the relatively large fraction of the dendrites with smoother and blunt boundaries. These features effectively reduced stress concentration and increased the complexity of the facture surface, thereby enhancing the ductility of the alloy. These findings provide valuable insights for tailoring the properties of high-entropy alloys by carefully controlling their oxygen content.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, S.J. Lin, J.Y. Gan, T.S. Chin, T.T. Shun, C.H. Tsau and S.Y. Chang, Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2004, 6, p 299–303.
B. Cantor, I.T.H. Chang, P. Knight and A.J.B. Vincent, Microstructural Development in Equiatomic Multicomponent Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, 375–377, p 213-218.3.
J. Yi, L. Yang, L. Wang and M. Xu, Lightweight, Refractory High-Entropy Alloy, CrNbTa0.25TiZr, with High Yield Strength, Met. Mater. Int., 2022, 28(2), p 448–455.
L. Chen, B. Li, J. Guo, Y. Zhu and J. Feng, High-entropy Perovskite RETa3O9 Ceramics for High-temperature Environmental/Thermal Barrier Coatings, J. Adv. Ceram., 2022, 11(4), p 556–569.
L. Chen, K. Luo, B. Li, M. Hu and J. Feng, Mechanical Property Enhancements and Amorphous Thermal Transports of Ordered Weberite-Type RE3Nb/TaO7 High-entropy Oxides, J. Adv. Ceram., 2023, 12(2), p 399–413.
R. Wang, Y. Tang, Z. Lei, Y. Ai, Z. Tong, S. Li, Y. Ye and S. Bai, Achieving High Strength and Ductility in Nitrogen-Doped Refractory High-entropy Alloys, Mater. Des., 2022, 213, p 110356.
J. Yi, L. Yang, L. Wang, M. Xu and L. Liu, Equiatomic, Cu-Containing CrCuFeTiV 3d Transition Metal High Entropy Alloy with an Enhanced Strength and Hardness Synergy, Met. Mater. Int., 2021, 28(1), p 227–236.
D.D. Zhang, J.Y. Zhang, J. Kuang, G. Liu and J. Sun, Superior Strength-Ductility Synergy and Strain Hardenability of Al/Ta Co-doped NiCoCr Twinned Medium Entropy Alloy for Cryogenic Applications, Acta Mater., 2021, 220, p 117288.
N. Hua, W. Wang, Q. Wang, Y. Ye, S. Lin, L. Zhang, Q. Guo, J. Brechtl and P.K. Liaw, Mechanical, Corrosion, and Wear Properties of Biomedical Ti–Zr–Nb–Ta–Mo High Entropy Alloys, J. Alloys Compd., 2021, 861, p 157997.
B. Gludovatz, A. Hohenwarter, D. Catoor, E.H. Chang, E.P. George and R.O. Ritchie, A Fracture-Resistant High-Entropy Alloy for Cryogenic Applications, Science, 2014, 345(6201), p 1153–1158.
R.R. Eleti, T. Bhattacharjee, A. Shibata and N. Tsuji, Unique Deformation Behavior and Microstructure Evolution in High Temperature Processing of HfNbTaTiZr Refractory High Entropy Alloy, Acta Mater., 2019, 171, p 132–145.
H. Peng, Z. Kang, Y. Long and L. Zhou, A Two-Phase Ultrafine-Grained NbMoTaWV Refractory High Entropy Alloy with Prominent Compressive Properties, Vacuum, 2022, 199, p 110930.
F. Jiang, J. Wang, Q. Jiang, G. Yang, M. Xu, W. Xu, C. Tang and J. Yi, An Excellent Synergy in Yield Strength and Plasticity of NbTiZrTa0.25Cr0.4 Refractory High Entropy Alloy Through the Regulation of Cooling Rates, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater, 2023, 117, p 106409.
L. Wang, J. Wang, H. Niu, G. Yang, L. Yang, M. Xu and J. Yi, BCC+L21 Dual-Phase Cu40Al20Ti20V20 Near-Eutectic High-Entropy Alloy with a Combination of Strength and Plasticity, J. Alloys Compd., 2022, 908, p 164683.
X. Zhang, B. Li, L. Zeng, J. Yi, B. Wang, C. Hu and M. Xia, Effect of Re Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AlCoCrFeNi2.1 Eutectic High-Entropy Alloy, Intermetallics, 2023, 154, p 107808.
P.-J. Yang, Q.-J. Li, W.-Z. Han, J. Li and E. Ma, Designing Solid Solution Hardening to Retain Uniform Ductility While Quadrupling Yield Strength, Acta Mater., 2019, 179, p 107–118.
A. Fu, W. Guo, B. Liu, Y. Cao, L. Xu, Q. Fang, H. Yang and Y. Liu, A Particle Reinforced NbTaTiV Refractory High Entropy Alloy Based Composite with Attractive Mechanical Properties, J. Alloys Compd., 2020, 815, p 152466.
D.E. Jodi, N. Choi, J. Park and N. Park, Mechanical Performance Improvement by Nitrogen Addition in N-CoCrNi Compositionally Complex Alloys, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2020, 51(6), p 3228–3237.
Y. Guo, J. He, Z. Li, L. Jia, X. Wu and C. Liu, Strengthening and Dynamic Recrystallization Mediated by Si-Alloying in a Refractory High Entropy Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2022, 832, p 142480.
Z. Lei, X. Liu, Y. Wu, H. Wang, S. Jiang, S. Wang, X. Hui, Y. Wu, B. Gault, P. Kontis, D. Raabe, L. Gu, Q. Zhang, H. Chen, H. Wang, J. Liu, K. An, Q. Zeng, T.G. Nieh and Z. Lu, Enhanced Strength and Ductility in a High-Entropy Alloy Via Ordered Oxygen Complexes, Nature, 2018, 563(7732), p 546–550.
S. Lv, Y. Zu, G. Chen, B. Zhao, X. Fu and W. Zhou, A Multiple Nonmetallic Atoms Co-doped CrMoNbWTi Refractory High-Entropy Alloy with Ultra-high Strength and Hardness, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2020, 795, p 140035.
R.L. Klueh, P.J. Maziasz and I.S. Kim, Tensile and Creep Properties of an Oxide Dispersion-Strengthened Ferritic Steel, J. Nucl. Mater., 2002, 307, p 773–777.
T. Saito, T. Furuta and J. Hwang, Multifunctional Alloys Obtained via a Dislocation-Free Plastic Deformation Mechanism, Science, 2003, 300, p 464–467.
L. Chen, M. Hu and J. Feng, Defect-Dominated Phonon Scattering Processes and Thermal Transports of Ferroelastic (Sm1-XYbX)TaO4 Solid Solutions, Mater. Today Phys., 2023, 35, p 101118.
L. Chen, M. Hu, X. Zheng and J. Feng, Characteristics of Ferroelastic Domains and Thermal Transport Limits in HfO2 Alloying YTaO4 Ceramics, Acta Mater., 2023, 251, p 118870.
Y. Zhang, Y.J. Zhou, J.P. Lin, G.L. Chen and P.K. Liaw, Solid-Solution Phase Formation Rules for Multi-component Alloys, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2008, 10(6), p 534–538.
X. Yang and Y. Zhang, Prediction of High-Entropy Stabilized Solid-Solution in Multi-component Alloys, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2012, 132(2–3), p 233–238.
S. Guo and C.T. Liu, Phase Stability in High Entropy Alloys: Formation of Solid-Solution Phase or Amorphous Phase, Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int., 2011, 21(6), p 433–446.
S. Guo, C. Ng, J. Lu and C.T. Liu, Effect of Valence Electron Concentration on Stability of fcc or bcc Phase in High Entropy Alloys, J. Appl. Phys., 2011, 109(10), p 103505.
Y.X. Ye, B. Ouyang, C.Z. Liu, G.J. Duscher and T.G. Nieh, Effect of Interstitial Oxygen and Nitrogen on Incipient Plasticity of NbTiZrHf High-entropy Alloys, Acta Mater., 2020, 199, p 413–424.
Z.D. Han, N. Chen, S.F. Zhao, L.W. Fan, G.N. Yang, Y. Shao and K.F. Yao, Effect of Ti Additions on Mechanical Properties of NbMoTaW and VNbMoTaW Refractory High Entropy Alloys, Intermetallics, 2017, 84, p 153–157.
Y.D. Wu, Y.H. Cai, X.H. Chen, T. Wang, J.J. Si, L. Wang, Y.D. Wang and X.D. Hui, Phase Composition and Solid Solution Strengthening Effect in TiZrNbMoV High-Entropy Alloys, Mater. Des., 2015, 83, p 651–660.
H.J. Ellingham, Transactions and Communications, J. Soc. Chem. Ind., 1944, 63(5), p 125–160.
L. Backman and E.J. Opila, Thermodynamic Assessment of the Group IV, V and VI Oxides for the Design of Oxidation Resistant Multi-principal Component Materials, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2019, 39(5), p 1796–1802.
S.V. Astafurov, G.G. Maier, I.A. Tumbusova, E.V. Melnikov, V.A. Moskvina, M.Y. Panchenko, A.I. Smirnov, N.K. Galchenko and E.G. Astafurova, The Effect of Solid-Solution Temperature on Phase Composition, Tensile Characteristics and Fracture Mechanism of V-Containing CrMn-Steels with High Interstitial Content C+N>1 Mass, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2020, 770, p 138534.
H. Xue, Y. Liang, S.-L. Shang, Z.-K. Liu and J. Lin, Atomic-Scale Unveiling of Strengthening in Interstitial Solid Soluted Nb-Rich TiAl Alloys, J. Alloys Compd., 2022, 917, p 165484.
R.L. Fleischer, Rapid Solution Hardening, Dislocation Mobility, and the Flow Stress of Crystals, J. Appl. Phys., 1962, 33(12), p 3504–3508.
R. Labusch, A Statistical Theory of Solid Solution Hardening, Phys. Status Solidi, 1970, 41(2), p 659–669.
D.V. Louzguine, H. Kato, L.V. Louzguina and A. Inoue, High-Strength Binary Ti–Fe Bulk Alloys with Enhanced Ductility, J. Mater. Res., 2004, 19(12), p 3600–3606.
R. Guan, Y. Shen, Z. Zhao and X. Wang, A High-Strength, Ductile Al-0.35Sc-0.2Zr Alloy with Good Electrical Conductivity Strengthened by Coherent Nanosized-Precipitates, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2017, 33(3), p 215–223.
Acknowledgment
Financial supports from Changzhou Science and Technology Bureau (No. CJ20235060, CQ20210086, CJ20210065), the Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (23KJD430005), the Sichuan Science and Technology Program (No. 2022NSFSC1978), the Graduate Practice and Innovation Projects of Jiangsu University of Technology (XSJCX22_01), and Undergraduate Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program of Jiangsu Province (202211463053Y) are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, K., Chao, L., Li, Y. et al. Effect of Oxygen on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti1.5ZrNbMoV Refractory High-Entropy Alloy. J. of Materi Eng and Perform (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-024-09230-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-024-09230-y