Abstract
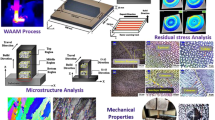
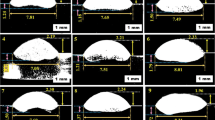
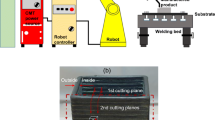
This study investigates the metallurgical and mechanical properties of a nickel-based superalloy produced through wire + arc additive manufacturing (WAAM). It is a novel and fast fabrication technique based on layer-by-layer construction for rapid product development. A thin-wall component of Inconel 625 was successfully manufactured using a cold metal transfer (CMT)-based WAAM technique with an ErNiCrMo-3 wire after identifying suitable process parameters based on trial runs. The microstructure varies based on the travel and build directions, resulting in columnar, cellular, and equiaxed dendrites found in bottom, middle, and top regions. These dendritic structures evolve throughout the deposition process, predominantly influenced by temperature circumstances. The results of SEM/EDS analysis indicated that Nb and Mo segregation was lower in the interdendritic areas compared to the dendritic core areas of the thin-wall part. The XRD results discovered that the main crystal structure found in the WAAMed samples was a γ-FCC (face-centered cubic). Additionally, through EBSD analysis, the average grain size was identified as 86.45 µm in the travel direction and 89.15 µm in the build direction. The grain properties of the material were influenced by the reheating phenomenon and the circumstances of solidification that occurred throughout the layer-by-layer additive manufacturing process. The larger proportion of higher angle grain boundaries improves the mechanical properties. The average hardness in the travel direction was higher in the top (312 HV), middle (297 HV), and bottom (303 HV) sections than in the build direction (305 HV), (290 HV) and (294 HV), respectively. The mechanical properties, specifically tensile strength, exhibit anisotropy that varies depending on the direction of travel and build. The residual stress analysis shows that the as-built specimen is mainly affected by tensile stress in the travel and build directions.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Liu, X. Wang, J.P. Oliveira, J. He, and X. Guan, Spatial and Directional Characterization of Wire and Arc Additive Manufactured Aluminum Alloy Using Phased Array Ultrasonic Backscattering Method, Ultrasonics, 2023, 132(04), p 107024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultras.2023.107024
I.O. Felice, J. Shen, A.F.C. Barragan, I.A.B. Moura, B. Li, B. Wang, H. Khodaverdi, M. Mohri, N. Schell, E. Ghafoori, T.G. Santos, and J.P. Oliveira, Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing of Fe-Based Shape Memory Alloys: Microstructure, Mechanical and Functional Behavior, Mater. Des., 2023, 231(05), p 112004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2023.112004
M.D. Barath Kumar, and M. Manikandan, Assessment of Process, Parameters, Residual Stress Mitigation, Post Treatments and Finite Element Analysis Simulations of Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing Technique, Metals Mater. Int., 2022 https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-021-01015-5
T. DebRoy, H.L. Wei, J.S. Zuback, T. Mukherjee, J.W. Elmer, J.O. Milewski, A.M. Beese, A. Wilson-Heid, A. De, and W. Zhang, Additive Manufacturing of Metallic Components—Process, Structure and Properties, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2018, 92, p 112–224.
M.D.B. Kumar and M. Manikandan, Evaluation of Microstructure, Residual Stress, and Mechanical Properties in Different Planes of Wire + Arc Additive Manufactured Nickel-Based Superalloy, Met. Mater. Int., 2022, 28(12), p 3033–3056. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-022-01185-w
P.P. Nikam, D. Arun, K.D. Ramkumar, and N. Sivashanmugam, Microstructure Characterization and Tensile Properties of CMT-Based Wire plus Arc Additive Manufactured ER2594, Mater Charact, 2020, 169(09), p 110671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2020.110671
D.G. Ahn, Direct Metal Additive Manufacturing Processes and Their Sustainable Applications for Green Technology: A Review, Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., 2016, 3(4), p 381–395.
F.M. Scotti, F.R. Teixeira, L.J. da Silva, D.B. de Araújo, R.P. Reis, and A. Scotti, Thermal Management in WAAM Through the CMT Advanced Process and an Active Cooling Technique, J. Manuf. Process., 2020, 57(06), p 23–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.06.007
J. Feng, H. Zhang, and P. He, The CMT Short-Circuiting Metal Transfer Process and Its Use in Thin Aluminium Sheets Welding, Mater. Des., 2009, 30(5), p 1850–1852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2008.07.015
M. Karmuhilan and S. Kumanan, Location-Dependent Microstructure Analysis and Mechanical Behavior of Inconel 625 Using Cold Metal Transfer(CMT) Based Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing, Vacuum, 2023, 207(08), p 111682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2022.111682
A. Gamon, E. Arrieta, P.R. Gradl, C. Katsarelis, L.E. Murr, R.B. Wicker, and F. Medina, Microstructure and Hardness Comparison of As-Built Inconel 625 Alloy Following Various Additive Manufacturing Processes, Res. Mater., 2021, 12, 100239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinma.2021.100239
A.N. Tanvir, M.R. Ahsan, C. Ji, W. Hawkins, B. Bates, and D.B. Kim, Heat Treatment Effects on Inconel 625 Components Fabricated by Wire+ Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM)—Part 1: Microstructural Characterization, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2019, 103, p 3785–3798.
V. Votruba, I. Diviš, L. Pilsová, P. Zeman, L. Beránek, J. Horváth, and J. Smolík, Experimental Investigation of CMT Discontinuous Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing of Inconel 625, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2022, 122(2), p 711–727. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-09878-7
T.A. Rodrigues, F.W. Cipriano Farias, J.A. Avila, E. Maawad, N. Schell, T.G. Santos, and J.P. Oliveira, Effect of Heat Treatments on Inconel 625 Fabricated by Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing: An in Situ Synchrotron x-ray Diffraction Analysis, Sci. Technol. Welding Join., 2023, 13, p 1–6.
T.A. Rodrigues, F.W. Farias, K. Zhang, A. Shamsolhodaei, J. Shen, N. Zhou, N. Schell, J. Capek, E. Polatidis, T.G. Santos, and J.P. Oliveira, Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing of 316L Stainless Steel/Inconel 625 Functionally Graded Material: Development and Characterization, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2022, 21, p 237–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.08.169
W. Zhang, Y. Lei, W. Meng, Q. Ma, X. Yin, and L. Guo, Effect of Deposition Sequence on Microstructure and Properties of 316L and Inconel 625 Bimetallic Structure by Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2021, 30(12), p 8972–8983. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06137-w
C. Zhang, Z. Qiu, H. Zhu, Z. Wang, O. Muránsky, M. Ionescu, Z. Pan, J. Xi, and H. Li, On the Effect of Heat Input and Interpass Temperature on the Performance of Inconel 625 Alloy Deposited Using Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing-Cold Metal Transfer Process, Metals., 2021, 12(1), p 46.
B. Tomar, S. Shiva, and T. Nath, A Review on Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing: Processing Parameters, Defects, Quality Improvement and Recent Advances, Mater. Today Commun., 2022, 31(05), p 103739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.103739
M. Raja, Y. Tiwari, M. Mukherjee, B. Maji, and A. Chatterjee, Effect of Bidirectional and Switchback Deposition Strategies on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Wire Arc Additive Manufactured Inconel 625, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2022, 119(7–8), p 4845–4861. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-08687-2
R. Sasikumar, A.R. Kannan, S.M. Kumar, R. Pramod, N.P. Kumar, N.S. Shanmugam, Y. Palguna, and S. Sivankalai, Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing of Functionally Graded Material with SS 316L and IN625: Microstructural and Mechanical Perspectives, CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol., 2022, 38, p 230–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirpj.2022.05.005
M. Xu, Y. Chen, T. Zhang, J. Xie, P. He, and K. Wei, Effect of Grain Refinement on Strain Hardening Behavior of Nickel—Based Superalloy Fabricated by Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing, Mater. Lett., 2022, 324, p 132723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2022.132723
A. Kreitcberg, V. Brailovski, and S. Turenne, Effect of Heat Treatment and Hot Isostatic Pressing on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Inconel 625 Alloy Processed by Laser Powder Bed Fusion, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, 689(02), p 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.02.038
M. Xu, Y. Chen, T. Zhang, J. Xie, P. He, and K. Wei, Effect of Grain Refinement on Strain Hardening Behavior of Nickel—Based Superalloy Fabricated by Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing Mingfang, Mater. Lett., 2022, 324(06), p 132723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2022.132723
W. Yangfan, C. Xizhang, and S. Chuanchu, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Inconel 625 Fabricated by Wire-Arc Additive Manufacturing, Surf. Coatings Technol., 2019, 374(05), p 116–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2019.05.079
J.F. Wang, Q.J. Sun, H. Wang, J.P. Liu, and J.C. Feng, Effect of Location on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Additive Layer Manufactured Inconel 625 Using Gas Tungsten Arc Welding, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016, 676(10), p 395–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.09.015
Z. Qiu, Z. Wang, A.A. Gazder, S. van Duin, A. Studer, U. Garbe, Q. Gu, B. Wu, H. Zhu, D. Wexler, and H. Li, Stabilised Mechanical Properties in Ni-Based Hastelloy C276 Alloy by Additive Manufacturing under Different Heat Inputs Incorporated with Active Interlayer Temperature Control, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2023, 862, p 144434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2022.144434
R. Madesh and K.G. Kumar, Development of Metallurgical and Mechanical Properties of Nickel-Based Superalloy Employed by Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing Technique, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2023 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08399-y
A. Chintala, M. Tejaswi Kumar, M. Sathishkumar, N. Arivazhagan, and M. Manikandan, Technology Development for Producing Inconel 625 in Aerospace Application Using Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing Process, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2021, 30, p 5333–5341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05781-6
J. Hönnige, C.E. Seow, S. Ganguly, X. Xu, S. Cabeza, H. Coules, and S. Williams, Study of Residual Stress and Microstructural Evolution in As-Deposited and Inter-Pass Rolled Wire plus Arc Additively Manufactured Inconel 718 Alloy after Ageing Treatment, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2021, 13(801), p 140368.
N. Peterson, Y. Kobayashi, and P. Sanders, Assessment and Validation of Cosα Method for Residual Stress Measurement, 13th Inernational Conf. Shot Peen., p 80–86. (2017)
M. Andurkar, T. Suzuki, M. Omori, B. Prorok, and J. Gahl, Residual Stress Measurements via x-ray Diffraction Cos α Method on Various Heat-Treated Inconel 625 Specimens Fabricated via Laser-Powder Bed Fusion, p 1048–1060 (2021)
J. Lin, N. Ma, Y. Lei, and H. Murakawa, Measurement of Residual Stress in Arc Welded Lap Joints by Cosα x-ray Diffraction Method, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2017, 243, p 387–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2016.12.021
M. Andurkar, T. Suzuki, B.C. Prorok, J. Gahl, and S.M. Thompson, Residual Stress Measurements via x-ray Diffraction Cos-α Method on Various Heat-Treated Inconel 625 Specimens Fabricated via Laser-Powder Bed Fusion, 32nd Int. Solid Free. Fabr. Symp., p 1048–1060 (2021).
R. Madesh and G.K. K, Multi-Layer Additive Manufacturing on Nickel-Based Superalloy by Optimization of Pulsed Mode Process Parameters of Single-Layer Bead Geometry, Mater. Today Commun., 2023, 37(11), p 107463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2023.107463
R. Madesh, M. Makeshkumar, S.R. Surender, K.P. Shankar, and M. Sasi Kumar, Performance Characteristics of GMAW Process Parameters of Multi-Bead Overlap Weld Claddings, IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng., 988(1). (2020)
Y. Hua and Z. Liu, Experimental Investigation of Principal Residual Stress and Fatigue Performance for Turned Nickel-Based Superalloy Inconel 718, Materials., 2018, 11(6), p 879.
K. Barath, K.M. Aravindan, J.A. Vinoth, and K.T. Sampath, Effect of Post-Fabrication Treatments on Surface Residual Stresses of Additive Manufactured Stainless Steel 316L, FME Trans., 2021, 49(1), p 87–94. https://doi.org/10.5937/FME2101087B
F. Ceritbinmez, A. Günen, U. Gürol, and G. Çam, A Comparative Study on Drillability of Inconel 625 Alloy Fabricated by Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing, J. Manuf. Process., 2023, 89, p 150–169.
S. Mohan Kumar, A. Rajesh Kannan, N. Pravin Kumar, R. Pramod, N. Siva Shanmugam, A.S. Vishnu, and S.G. Channabasavanna, Microstructural Features and Mechanical Integrity of Wire Arc Additive Manufactured SS321/Inconel 625 Functionally Gradient Material, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2021, 30(8), p 5692–5703. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05617-3
U. Gürol, M. Tümer, and S. Dilibal, Experimental Investigation of Wire Arc Additively Manufactured Inconel 625 Superalloy, Trans. Indian Inst. Met., 2023, 76(5), p 1371–1379. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-022-02797-x
N. Hasani, M.H. Ghoncheh, R.M. Kindermann, H. Pirgazi, M. Sanjari, S. Tamimi, S. Shakerin, L.A.I. Kestens, M.J. Roy, and M. Mohammadi, Dislocations Mobility in Superalloy-Steel Hybrid Components Produced Using Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing, Mater. Des., 2022, 220, p 110899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2022.110899
A. Kumar, K. Maji, and A. Shrivastava, Investigations on Deposition Geometry and Mechanical Properties of Wire Arc Additive Manufactured Inconel 625, Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., 2023 https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-023-00827-2
M. Alizadeh-Sh, S.P.H. Marashi, E. Ranjbarnodeh, R. Shoja-Razavi, and J.P. Oliveira, Prediction of Solidification Cracking by an Empirical-Statistical Analysis for Laser Cladding of Inconel 718 Powder on a Non-Weldable Substrate, Opt. Laser Technol., 2019, 128, p 106244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106244
F.W.C. Farias, V.R. Duarte, I.O. Felice, J. da, C.P. Filho, N. Schell, E. Maawad, J.A. Avila, J.Y. Li, Y. Zhang, T.G. Santos, and J.P. Oliveira, In Situ Interlayer Hot Forging Arc-Based Directed Energy Deposition of Inconel® 625: Process Development and Microstructure Effects, Addit. Manuf., 2023, 66, p 103476.
R. Medeiros, M.J. Roy, R. Morana, and P.B. Prangnell, Process Response of Inconel 718 to Wire + Arc Additive Manufacturing with Cold Metal Transfer, Mater. Des., 2020, 195, p 109031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2020.109031
G.H.S.F.L. Carvalho, G. Venturini, G. Campatelli, and E. Galvanetto, Development of Optimal Deposition Strategies for Cladding of Inconel 625 on Carbon Steel Using Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing, Surf. Coatings Technol., 2023, 453, p 129128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2022.129128
Z. Wang, Z. Gui, J. Wu, Q. Zhang, X. Wu, S. Lin, J. Tian, and C. Guo, Microstructure and High-Temperature Mechanical Properties of Inconel 718 Superalloy Weldment Affected by Fast-Frequency Pulsed TIG Welding, J. Manuf. Process., 2023, 89, p 338–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2023.01.076
M. Xu, S. Chen, T. Yuan, X. Jiang, and H. Zhang, Effect of Thermal Cycles on the Microstructure and Properties of the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy during Wire-Arc Additive Manufacturing, J. Alloys Compd., 2022, 928, p 167172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.167172
R.M. Kindermann, M.J. Roy, R. Morana, and P.B. Prangnell, Process Response of Inconel 718 to Wire + Arc Additive Manufacturing with Cold Metal Transfer, Mater. Des., 2020, 195, p 109031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2020.109031
H. Raushan, A. Bansal, V. Singh, A.K. Singla, J. Singla, A. Omer, J. Singh, D.K. Goyal, N. Khanna, and R.S. Rooprai, Dry Sliding and Slurry Abrasion Behaviour of Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing—Cold Metal Transfer (WAAM-CMT) Cladded Inconel 625 on EN8 Steel, Tribol. Int., 2023, 179, p 108176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2022.108176
J. Han, B. Liu, X. Chen, G. Zhang, L. Lu, Y. Xin, Z. Luo, X. Zhang, Y. Cai, and Y. Tian, Wire and Arc Additive Manufactured an Innovative Material Ti-Al-V-Ni-Cr-Mo-Nb-Cu Alloy: Study of Its Microstructure and Mechanical Properties, Mater. Lett., 2023, 330, p 133304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2022.133304
G.G. Goviazin, D. Rittel, and A. Shirizly, Achieving High Strength with Low Residual Stress in WAAM SS316L Using Flow-Forming and Heat Treatment, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2023, 873(04), p 145043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2023.145043
A. Pandey and V. Gaur, Effect of Dwell Time on Fatigue Properties of Wire-Arc Additively Manufactured IN718 Alloy, Int. J. Fatigue, 2023, 176, p 107863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2023.107863
V. Gornyakov, J. Ding, Y. Sun, and S. Williams, Understanding and Designing Post-Build Rolling for Mitigation of Residual Stress and Distortion in Wire Arc Additively Manufactured Components, Mater. Des., 2022, 213, p 110335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2021.110335
Y. Jing, X. Fang, N. Xi, T. Chang, Y. Duan, and K. Huang, Improved Tensile Strength and Fatigue Properties of Wire-Arc Additively Manufactured 2319 Aluminum Alloy by Surface Laser Shock Peening, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2023, 864(01), p 144599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2023.144599
Y. Koli, S. Arora, S. Ahmad, N.Y. Priya, and Z.A. Khan, Investigations and Multi-Response Optimization of Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing Cold Metal Transfer Process Parameters for Fabrication of SS308L Samples, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2023, 32(5), p 2463–2475. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07282-6
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge School of Mechanical Engineering, Vellore Institute of Technology, Vellore, for providing research facilities to the successful completion of work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest stated by the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mahendiran, S., Ramanujam, R. Investigation of Surface Residual Stress, Mechanical Properties, and Metallurgical Characterization of Inconel 625 Multilayer Thin-Wall Component Using Cold Metal Transfer Technique. J. of Materi Eng and Perform (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-09119-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-09119-2