Abstract
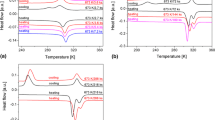
Grain size refinement is a highly desirable characteristic in TiNi-based shape memory alloys (SMA) because they prevent the loss of recoverable strain. The current study elucidates the role of rolling temperature on grain refinement in TiNiCu shape memory alloy. The control of deformation temperature, ranging from room temperature to cryogenic temperatures, allowed for control over the stored energy in the rolled samples. Observations revealed that the as-rolled samples stabilized the deformation-induced austenite phase below the martensite finish temperatures, effectively inhibiting the phase transformation. Consequently, this resulted in constant electrical resistivity values. However, subjecting the samples to heat treatment under similar conditions led to varying grain sizes, ranging from a few hundred nm to tens of microns. This subsequently restored the B2 → B19′ transformation. These findings signify the importance of rolling temperature on grain refinement in TiNiCu SMAs. Lower rolling temperature correlated with coarser grain size due to higher stored energy driving the early recrystallization and grain growth.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used in the current study are part of an ongoing project and therefore could not be shared at the moment.
References
A. Nespoli and S. Besseghini, A Complete Thermo-Mechanical Study of a NiTiCu Shape Memory Alloy Wire, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim., 2011, 103(3), p 821–826.
K.N. Lin, S.K. Wu, and L.M. Wu, Martensitic Transformation of Cold-Rolled and Annealed Ti50Ni40Cu10 Shape Memory Alloy, Mater. Trans., 2009, 50(11), p 2637–2642.
K. Otsuka and X. Ren, Physical Metallurgy of Ti-Ni-Based Shape Memory Alloys, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2005, 50(5), p 511–678.
T. Waitz, V. Kazykhanov, and H.P. Karnthaler, Martensitic Phase Transformations in Nanocrystalline NiTi Studied by TEM, Acta Mater., 2004, 52(1), p 137–147.
M. Peterlechner, T. Waitz, and H.P. Karnthaler, Nanocrystallization of NiTi Shape Memory Alloys Made Amorphous by High-Pressure Torsion, Scr. Mater., 2008, 59(5), p 566–569.
Y. Ren, A. Shuitcev, D.V. Gunderov, L. Li, R.Z. Valiev, and Y.X. Tong, The Role of Temperature in the Microstructural Evolution of HPT-Processed NiTiHf High-Temperature Shape Memory Alloy, Mater. Lett., 2022, 322(May), p 18–21.
Y.X. Tong, B. Guo, F. Chen, B. Tian, L. Li, Y.F. Zheng, E.A. Prokofiev, D.V. Gunderov, and R.Z. Valiev, Thermal Cycling Stability of Ultrafine-Grained TiNi Shape Memory Alloys Processed by Equal Channel Angular Pressing, Scr. Mater., 2012, 67(1), p 1–4.
B. Kockar, I. Karaman, J.I. Kim, and Y. Chumlyakov, A Method to Enhance Cyclic Reversibility of NiTiHf High Temperature Shape Memory Alloys, Scr. Mater., 2006, 54(12), p 2203–2208.
A.O. Moghaddam, M. Ketabchi, and Y. Afrasiabi, Accumulative Roll Bonding and Post-Deformation Annealing of Cu-Al-Mn Shape Memory Alloy, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2014, 23(12), p 4429–4435.
A. Shamsolhodaei, A. Zarei-Hanzaki, and M. Moghaddam, Structural and Functional Properties of a Semi Equiatomic NiTi Shape Memory Alloy Processed by Multi-Axial Forging, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, 700(February), p 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.04.011
X.B. Shi, F.M. Guo, J.S. Zhang, H.L. Ding, and L.S. Cui, Grain Size Effect on Stress Hysteresis of Nanocrystalline NiTi Alloys, J. Alloys Compd., 2016, 688, p 62–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.07.168
S. Miyazaki, T. Imai, Y. Igo, and K. Otsuka, Effect of Cyclic Deformation on the Pseudoelasticity Characteristics of Ti-Ni Alloys, Metall. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci., 1986, 17(1), p 115–120.
J. Koike, D.M. Parkin, and M. Nastasi, Crystal-To-Amorphous Transformation of NiTi Induced by Cold Rolling, J. Mater. Res., 1990, 5(7), p 1414–1418.
P. Liu, Q. Sun, and M. Xia, Grain Size Effects on Young’s Modulus and Hardness of Nanocrystalline NiTi Shape Memory Alloy, Adv. Struct. Mater., 2017, 73, p 191–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-53306-3
Y. Li, J.Y. Li, M. Liu, Y.Y. Ren, F. Chen, G.C. Yao, and Q.S. Mei, Evolution of Microstructure and Property of NiTi Alloy Induced by Cold Rolling, J. Alloys Compd., 2015, 653, p 156–161.
M. Karimzadeh, M.R. Aboutalebi, M.T. Salehi, S.M. Abbasi, and M. Morakabati, Effects of Thermomechanical Treatments on the Martensitic Transformation and Critical Stress of Ti-50.2 at.% Ni Alloy, J. Alloys Compd., 2015, 637, p 171–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.02.195
T. Leitner, I. Sabirov, R. Pippan, and A. Hohenwarter, The Effect of Severe Grain Refinement on the Damage Tolerance of a Superelastic NiTi Shape Memory Alloy, J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater., 2017, 71(November 2016), p 337–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2017.03.020
E.M. Sharifi, F. Karimzadeh, and A. Kermanpur, The Effect of Cold Rolling and Annealing on Microstructure and Tensile Properties of the Nanostructured Ni50Ti50 Shape Memory Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 607, p 33–37.
H. Zhang, X. Li, and X. Zhang, Grain-Size-Dependent Martensitic Transformation in Bulk Nanocrystalline TiNi under Tensile Deformation, J. Alloys Compd., 2012, 544, p 19–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.08.014
T. Waitz and H.P. Karnthaler, Martensitic Transformation of NiTi Nanocrystals Embedded in an Amorphous Matrix, Acta Mater., 2004, 52(19), p 5461–5469.
H. Nakayama, K. Tsuchiya, and M. Umemoto, Crystal Refinement and Amorphisation by Cold Rolling in TiNi Shape Memory Alloys, Scr. Mater., 2001, 44(8–9), p 1781–1785.
J. Frenzel, J.A. Burow, E.J. Payton, S. Rezanka, and G. Eggeler, Improvement of NiTi Shape Memory Actuator Performance through Ultra-Fine Grained and Nanocrystalline Microstructures, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2011, 13(4), p 256–268.
H.F. López, Transformation Induced Toughening in a Ni-Ti52 Shape Memory Alloy, Mater. Lett., 2001, 51(2), p 144–150.
H.F. Lopez, A. Salinas, and H. Calderón, Plastic Straining Effects on the Microstructure of a Ti-Rich NiTi Shape Memory Alloy, Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci., 2001, 311(32), p 717–729.
H.C. Lin and S.K. Wu, Determination of Heat of Transformation in a Cold-Rolled Martensitic Tini Alloy, Metall. Trans. A, 1993, 24(2), p 293–299.
H. Sehitoglu, Y. Wu, and E. Ertekin, Elastocaloric Effects in the Extreme, Scr. Mater., 2018, 148, p 122–126.
M. Nishida, T. Nishiura, H. Kawano, and T. Inamura, Self-Accommodation of B19 ′ Martensite in Ti-Ni Shape Memory Alloys-Part I. Morphological and Crystallographic Studies of the Variant Selection Rule, Philos. Mag., 2012, 92(17), p 2215–2233.
H.C. Lin, S.K. Wu, T.S. Chou, and H.P. Kao, The Effects of Cold Rolling on the Martensitic Transformation of an Equiatomic TiNi Alloy, Acta Metall. Mater., 1991, 39(9), p 2069–2080.
K.S. Suresh, D.I. Kim, S.K. Bhaumik, and S. Suwas, Evolution and Stability of Phases in a High Temperature Shape Memory Alloy Ni49.4Ti38.6Hf12, Intermetallics, 2014, 44, p 18–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2013.08.005
M. Pattabi and M.S. Murari, Effect of Cold Rolling on Phase Transformation Temperatures of NiTi Shape Memory Alloy, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2015, 24(2), p 556–564.
K. Tsuchiya, M. Inuzuka, D. Tomus, A. Hosokawa, H. Nakayama, K. Morii, Y. Todaka, and M. Umemoto, Martensitic Transformation in Nanostructured TiNi Shape Memory Alloy Formed via Severe Plastic Deformation, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 438–440, p 643–648.
A. Sinha, B. Mondal, B.C. Maji, and P.P. Chattopadhyay, Enhanced Shape Recovery in Cryogenically Treated Martensitic Ti-Ni Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 580, p 273–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2013.05.036
H. Shahmir, M. Nili-Ahmadabadi, M. Mohammadi, Y. Huang, M. Andrzejczuk, M. Lewandowska, and T.G. Langdon, Effect of Cu on Amorphization of a TiNi Alloy during HPT and Shape Memory Effect after Post-Deformation Annealing, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2020, 22(1), p 1–9.
H. Shahmir, M. Nili-Ahmadabadi, Y. Huang, J.M. Jung, H.S. Kim, and T.G. Langdon, Shape Memory Characteristics of a Nanocrystalline TiNi Alloy Processed by HPT Followed by Post-Deformation Annealing, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2018, 734(June), p 445–452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.08.019
A.I. Tagiltsev, E.Y. Panchenko, Y.I. Chumlyakov, E.E. Timofeeva, and E.S. Marchenko, Two-Way Shape Memory Effect and Viscoelastic Properties in NiTiHf Polycrystals Containing Nanosized Particles, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2023 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-07812-w
J. Dadda, H.J. Maier, I. Karaman, and Y.I. Chumlyakov, Cyclic Deformation and Austenite Stabilization in Co35Ni35Al30 Single Crystalline High-Temperature Shape Memory Alloys, Acta Mater., 2009, 57(20), p 6123–6134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2009.08.038
J. Uchil, K.P. Mohanchandra, K.G. Kumara, and K.K. Mahesh, Study of Critical Dependence of Stable Phases in Nitinol on Heat Treatment Using Electrical Resistivity Probe, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1998, 251(1–2), p 58–63.
Z. Deng, Q. Li, Y. Onuki, and Q. Sun, Multifunctional Nanostructured NiTi Alloy with Invar, Elinvar and Rinvar Properties, J. Alloys Compd., 2022, 909, p 164682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.164682
J. Uchil, K.K. Mahesh, and K.G. Kumara, Electrical Resistivity and Strain Recovery Studies on the Effect of Thermal Cycling under Constant Stress on R-phase in NiTi Shape Memory Alloy, Phys. B Condens. Matter, 2002, 324(1–4), p 419–428.
T. Hoshiya, F. Takada, Y. Ichihashi, and H.R. Pak, Restoration Phenomena of Neutron-Irradiated TiNi Shape Memory Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1990, 130(2), p 185–191.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support of the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), India (Grant no. ECR/2016/000883). Characterization facilities available at the Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering (MMED) and the Institute Instrumentation Centre (IIC), IIT Roorkee, are also acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Varukuti, S.M.R., Chaithanya Kumar, K.N. & Suresh, K.S. Effect of Rolling Temperature and Annealing on Grain Refinement in TiNiCu Shape Memory Alloys. J. of Materi Eng and Perform (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08825-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08825-1